Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction to Hashing Algorithms
Hashing algorithm is an algorithm that is used to map data using a hash function. A hash function is a mathematical comparison that gives the summary of data from the original data. In their words, the hash function converts the size of one value to a certain size. In the world of cyber-attacks, various hashing algorithms at being used to secure our data.
Because of their security features, hashing algorithms are used in the field of digital signature, authentication, message authentication codes, fingerprinting, face lock, detecting corrupt files, checksum, etc. Here in this article, we are going to discuss the two most important hashing algorithms – message digest and secure hash function.
Message Digest
A message digest is a summary of an original message. A message digest is used to verify data integrity. Integrity means it ensures that the data sent from the user and the data received at the receiver are the same. Any third party does not alter them. There are different versions available for message digest. The first one is MD that is a message digest that Ron Rivest develops. After that, he came up with another version with new features, which was known for MD2. But MD2 was looking quite weak, so Rivest started working on MD3. MD3 was also a failed version. That’s why it was not released.
After that, Rivest developed MD4. And soon, he develops MD5. MD5 is quite fast and meets the requirements. Hence it was very popular for data integrity. Here in this section, we are going to see the Message digest 5, i.e. MD5 algorithm. MD5 generates a 128-bit message digest. It takes input yes as 512 but blocks which are divided into 16(each of 32 bit ) sub-blocks. It generates output as a set of four 32 bit blocks, i.e. it generates a 128-bit message digest.
Working of MD5
Step 1: Padding – in the first step, adds padding bits with the original message so that the length of the original message will equal to values that are 64 bit less than multiple of 512.
Step 2: Append length – once the padding bit is added, the original message’s length is calculated and added to the end of the message.
Step 3: Divide input into 512-bit blocks – the input message is divided into blocks, each consisting of 512 bits in length.
Step 4: Initialize chaining variables – Four variables A, B, C, D are initialized in this step. Each variable is of a 32-bit number.
Step 5: Process blocks – once the variables are initialized, the algorithm’s main work will start.
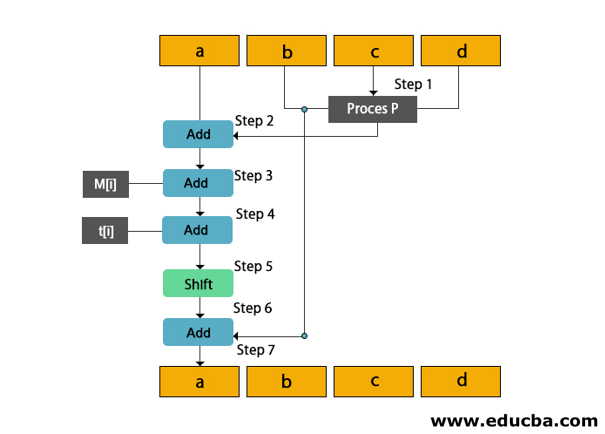
Copy all variables A, B, C, D into a, b, c, d
Divide 512-bit current block into 16 sub-blocks(each of 32 bit).
7 rounds are performed in this step. Iteration of these rounds are as follows
- The process is performed on the b, c, and d. This process p will be different in all four rounds.
- Variable a to the output of process p.
- Message subblock M[i] to step 2.
- Constant t[k] to the output of step 3.
- The output of step 4 is left-shifted by s bits.
- Add variable b to the output of step 5.
- Next, abcd will be the output of step 6.
You can understand the working of MD5 more easily with the help of the following diagram.
SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm)
SHA stands for the secure hash algorithm. It is developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). SHA was developed after the MD5. SHA is designed to obtain the original message and generate the message digest of the original message. The main goal behind this algorithm is to identify the message that generates the same message digest.
Working of SHA Algorithm
Step 1: Padding – in this step, passing is added at the end of the original message in such a way that. The length of the message is 64 bits less than multiple of 512.
Step 2: Append length – length of the message except the padding length is calculated and added at the end of padding as a 64-bit block.
Step 3: Divide input into 512-bit blocks. The input is divided into sub-blocks, each of 512 bits in length.
Step 4: Initialize chaining variables – five variables, i.e. A, B, C, and E, are initialized.
Step 5: After the variables are initialized, the main working of the algorithm will be started.
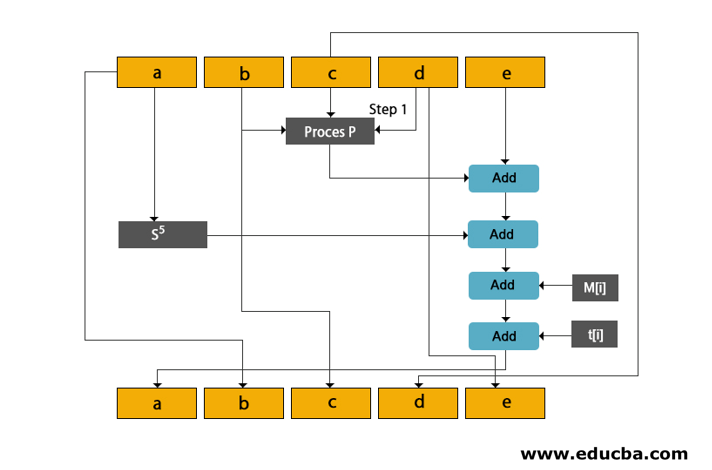
Cope all variables A to E into a to e.
Divide the 512-bit current block into 16 sub-block, each of 32 bits.
SHA performs four rounds where each is of 20 steps. Each round takes a 521-bit current block, register a, b, c, d and E and constant k[t] as three inputs.
You will understand How SHA works with the help of the given diagram.
Among the SHA family, SHA-512 is the most widely used. Here we are going to discuss the SHA-512 algorithm.
SHA- 512
SHA -512 algorithm takes input as 2 raised to 128 bits of message length and generates message digest which is of 512 bits in length.
Working of SHA-512
Step 1: Padding – add placing at the end of the message in such a way that the message length will be 128 bits less of multiple of 1024.
Step 2: Append length – The Length of the message except padding is calculated and added at the end of the padding as a 128-bit block
Step 3: Divide input into 1024 bit block – Divide input blocks into sub-blocks each pf 1024 bits.
Step 4: Initialize chaining variables – Initialize variables from A to H.
Step 5: Process blocks – the process for the blocks is as follows:
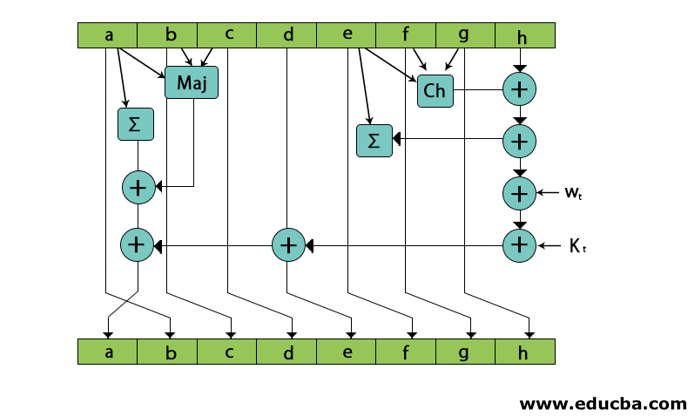
Copy all chaining variables A to H into a to h.
Divide 1024 bit current block into 16 sub-block each of 64 bits.
In SHa-512, 80 rounds are performed.
Conclusion – Hashing Algorithms
So, we have seen some popular hashing algorithms such as MD5, SHA, SHA- 512, and their working.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Hashing Algorithms. Here we discuss the introduction, message digest, and working for better understanding. You may also look at the following article to learn more –