Updated April 11, 2023

Introduction to #else in C
The following article provides an outline for #else in C. Else is a directive in C programming language that helps to provide the statements those needs to be executed when the conditions given using #if, #ifdef or #ifndef directives evaluates to false. Once the condition given in these directives evaluates to false, #else directives provides an alternate statements to be executed. It is a part of preprocessor directive since it is called by the compiler automatically before actual compilation starts. Before a C program is compiled by the compiler source code is processed thus this process is called preprocessing. All the commands used for the preprocessor are known as preprocessor directives and all preprocessor directives are defined using #.
Syntax of #else in C
Preprocessors is a feature provided in C to process the source code written by the programmer before its actual compilation is done. Before the program is passed through a preprocessor compiler passes the code through the preprocessor where specific instructions such as directives are looked for in the C program known as preprocessor directives that can be easily understood by the preprocessor. These preprocessor directives are must begin with (#) sign.
Preprocessor is that part of the compiler which executes essential operations in the given code before the compiler actually compiles it. The transformations performed by the preprocessors are lexical which tells that the output of the preprocessor is in text form.
#if _condition_
// Statements to be executed when condition returns TRUE
#else
// statements to be executed when condition in #if results to false.
#endifExample:
Code:
#if 4>5
printf("Statements inside if block")
#else
printf("Statements inside else block")Here # specifies that it is a preprocessor directive and is compiled using the preprocessor before actual code is sent for the compilation to the compiler. One can use macro defined in the program for the conditions in the if directive and those macros needs to be defined using #define directive in C.
How #else Directive work in C?
Preprocessors refers to the programs that are processed in our source code even before code enters the compiler for compilation. # undef is such a command for the preprocessor.
There are various preprocessor directives that can be defined which can be categorized into below 4 main categories.
There are 4 main types of preprocessor directives:
- Macros
- File Inclusion
- Conditional Compilation
- Other Directives
The source code written by the user is first sent for preprocessing to the preprocessors which generates an expanded source file with same name as that of the program. This expanded file is further sent for the compilation to the compiler to generate an object code of the library functions and once this object code is linked to the various library functions being used, an executable ( .exe) file is generated.
#else directive is used to provide an alternate statements need to be executed when the condition given using #if, #ifdef or #ifndef. Whenever the condition returns false compiler sends the control directly to the #else block statement.
There are certain rules need to be followed for declaring conditional expression:
- Expressions must be of integral. It can also include integer constants, character constants, and the defined operator.
- sizeOf or typecast operator cannot be used in the expression.
- All the types such as int, long or unsigned long are translated in the same manner.
- The expression should not include any query related to the environment on which the program is running.
After the #if or #elif directives #else blocks come into action. All the #if.. #elif.. #else block must be ended using #endif directive that tells the compiler that if- else block is over.
Examples of #else in C
Given below are the examples mentioned :
Example #1
In this example we will use #If directive to declare a condition for the execution for the statements. And if the condition results to false the statements given in else block will be executed. Here we will use LIMIT macro name defined using #define directive.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#define LIMIT 5
int main()
{
int number;
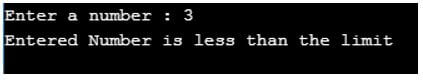
printf("Enter a number : ");
scanf("%d",&number);
#if number < LIMIT
printf("Entered Number is less than the limit \n");
#else
printf("Entered Number is greater than the limit \n");
#endif
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2
In this example we will see if the student has passed or not using PASS variable defined using #define directive. We will compare the marks of the student being entered to the PASS macro name and print the result for that particular student.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#define MARKS 50
int main()
{
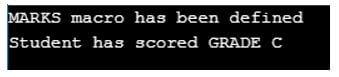
#ifdef MARKS
printf("MARKS macro has been defined \n");
#endif
#if MARKS >90
printf("Student has scored GRADE A");
#elif MARKS >60
printf("Student has scored GRADE B");
#else
printf("Student has scored GRADE C");
#endif
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
While working with preprocessor directives in a large C program one can declare conditional statements for executing some statements using #ifdef or #if or #ifndef directives. Thus #else directive here provides the block to be executed when the condition given in above block results to false.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to #else in C. Here we discuss the introduction to #else in C, how #else directive work along with programming examples respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


