Updated July 21, 2023
Introduction to Gordon Growth Model
The Gordon Growth Model also called the dividend discount model is a kind of valuation of stock methodology that one uses to calculate the intrinsic value of the stock and this model is very useful because it eliminates any external factors like prevailing market conditions.
Gordon growth model is a valuation model where the dividend related to a stock gets distributed and the calculation involves discounting of the dividend based on the present value.
So we see the time value of money plays a major role here. It is a very effective method to determine the valuation of the stock or find the intrinsic value of the stock pertaining to a company. It majorly excludes all the external market conditions and only considers the fair value of the stock. In this method, the time value of money plays a major role.
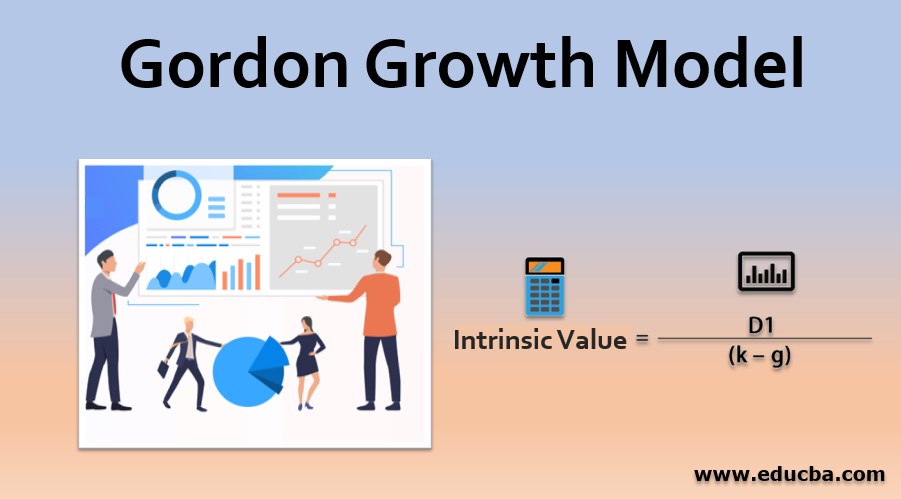
Formula for Gordon Growth Model
The formula for the Gordon Growth Model is as follows:
The metrics included in the Gordon Growth model are D1 which is described as the expected annual dividend per share for the upcoming year; k which is defined as the rate of return required and finally g which is the expected dividend growth rate
Example of the Gordon Growth Model
A classic example of Gordon ‘s growth model can be a scenario where we assume a manufacturing-based in the US paying a dividend of $10 and the expected growth rate is 6% every year. The rate of return which is required by the investor investing in this company is 9%. Our aim is to calculate the intrinsic value of this stock.
Solution:
Gordon Growth Model is calculated using the formula given below
Intrinsic Value = D1 / (k – g)
- Intrinsic Value= $10/ (0.09 – 0.06)
- Intrinsic Value = $333
Using the stable growth model we found out the intrinsic value as$333. Thus if the stock is now trading at $ 250 it is an undervalued stock whereas if the stock is trading at $400 it is an overvalued stock.
Assumptions of the Gordon Growth Model
The assumptions takes into consideration are as follows:
- The most common assumption in this model is that we assume a growth rate associated with the company is constant throughout.
- The business either has stable leverage of finance or has no leverage at all.
- According to going on the concept of accounting here too, we assume that the life of the business is indefinite and it will never be abolished.
- There are absolutely no deviations to the rate of return required and the number remains unchanged.
- The free cash flow generated by the business is not retained back for expansion or growth and is systematically paid back in the form of dividends on a constant basis.
- The rate of dividend growth is also constant for the company.
- The rate of growth of the company is always less when compared to the rate of return required.
- The business model of the company is stable and no significant changes in the operations are brought about.
Importance of the Gordon Growth Model
Following are the importance:
- The Model aims at estimating the intrinsic or the fair value of a stock excluding external factors like market condition.
- The model indicates whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued and based on that investor may take a call.
- If the value estimated by this model is higher than the stock price prevailing currently it means the stock is undervalued and this indicates a buy signal and vice versa.
- It sets up a relation between growth rates, discount rates, and valuation.
- It finds its use more extensively in corporate finance.
- The model is not disturbed by external conditions like changing market scenarios, political conditions, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Gordon Growth Model
Below are the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
The advantages are as follows:
- This model is greatly beneficial for companies that are stable and matured i.e. they have a steady and good flow of cash and minimal expenses related to business.
- The methodology of using the model is really simple and easy and all the assumptions are meaningful.
- The inputs to the model can be easily obtained from the financial reports of the company.
- The model does not get disturbed by external market conditions and thus seems to be realistic.
- This model can be used to compare companies of different sizes and market capitalization and even companies from different industries can also be compared using this model.
- This model is quite famous in the real estate industry where the cash flow is in the form of rent and their growth is easily known.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages are as follows:
- The assumption of dividend growth on a constant basis is the major drawback of the model. It is impossible for any company to grow like that due to changes in market conditions and business cycles.
- The model does not take into account the external market conditions or other factors like the size of the business, the market perception, consumer behavior or the brand.
- The growth rate has always to be more than the required rate of return and if the other way happens the model will result in a negative value.
- The model does not find its way for growing or developing companies with irregular cash flow, dividend patterns or leverage.
- The model is not suited for companies that have no dividend history.
Conclusion
As discussed above Gordon Growth Model have both advantages and disadvantages to it. It is best suited for companies that are matured and developed already and have a steady pattern of dividend or growth. The model is also very easy to use and is less affected by market conditions which makes it more realistic.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Gordon Growth Model. Here we discuss how to calculate the Gordon growth model along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


