Introduction to Googlebot
When you search for something on Google, millions of web pages appear in seconds. But have you ever wondered how Google finds, reads, and ranks these pages? The answer lies in Googlebot, Google’s powerful web crawler. This automated software plays a critical role in indexing the internet, ensuring that the right content appears when users search for it. In this blog, we will explore what Googlebot is, how it works, types of Googlebots, how it affects SEO, common challenges, best practices for optimization, real-world examples, and FAQs.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Meaning
- Working
- Types
- Features
- Importance
- Common Challenges
- Best Practices
- Real World Examples
What is Googlebot?
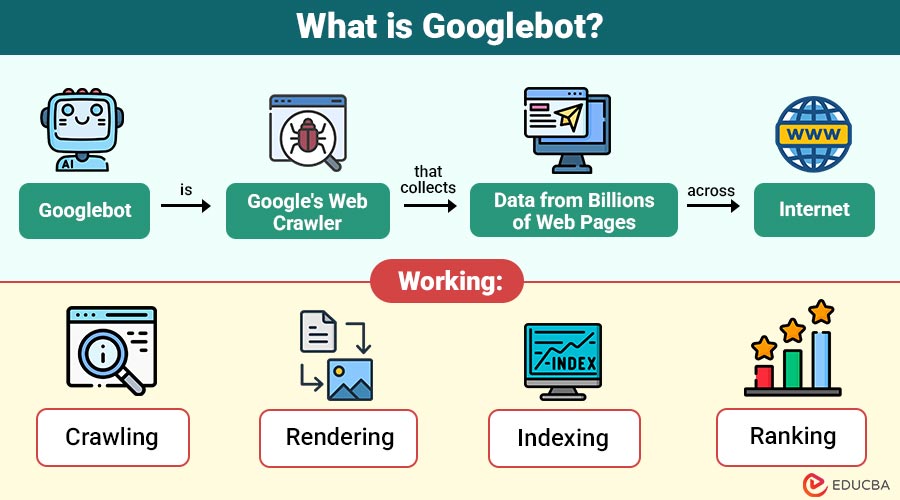
Googlebot is Google’s web crawler (also called a spider or robot) that collects data from billions of web pages across the internet. It systematically visits websites, follows links, reads content, and stores the information in Google’s index.
Key Takeaways:
- Googlebot is the foundation of Google Search, enabling the discovery, organization, and accessibility of online information.
- Optimizing for Googlebot improves visibility, strengthens ranking potential, and drives consistent organic search traffic growth.
- Misconfigurations, blocked resources, or duplicate content reduce crawl efficiency and negatively impact site performance.
- Regular monitoring through Google Search Console ensures websites remain index-friendly, accessible, and optimized for evolving search algorithms.
How Does Googlebot Work?
Googlebot follows a crawl → index → rank process. Let’s break it down:
1. Crawling
Googlebot discovers and visits web pages by following internal and external links, analyzing sitemaps, and processing manually submitted URLs to collect fresh content.
2. Rendering
Googlebot interprets page code, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and media, simulating how a browser loads the page to ensure full visibility of content and layout.
3. Indexing
After processing, Google stores page content in its massive index, analyzing text, metadata, structured data, and context to determine topics, relevance, and search query matching.
4. Ranking
When users search, Google’s algorithms evaluate indexed pages using hundreds of ranking factors, determining relevance, authority, and usability to display the most useful results first.
Types of Googlebot
Google uses different crawlers for different purposes:
1. Googlebot Desktop
Simulates crawling as a desktop browser, ensuring websites display correctly on larger screens, analyzing content, structure, and links for users searching through desktop devices.
2. Googlebot Smartphone
Crawls websites as viewed from mobile devices, crucial for mobile-first indexing, evaluating responsiveness, performance, and usability to prioritize mobile-friendly content in Google’s search results.
3. Specialized Crawlers
Here are the different specialized Google crawlers designed for handling specific types of online content:
- Googlebot Image – Specifically crawls and indexes image files, analyzing attributes like file names, alt text, captions, and surrounding content to display relevant images in Google Image Search.
- Googlebot Video – Crawls video content embedded on pages, analyzing metadata, titles, transcripts, and structured data to index videos for appearing in Google’s video and universal search results.
- Googlebot News – Focuses on crawling timely news articles from approved publishers, indexing headlines, metadata, and article content to ensure visibility in Google News and Top Stories sections.
- AdsBot – Evaluates landing pages used in Google Ads campaigns, checking speed, content quality, and compliance with ad policies to determine quality score and advertising performance.
Key Features of Googlebot
Here are the main features that make Googlebot effective in crawling, indexing, and ranking web content:
1. Automated
Googlebot operates continuously without human intervention, automatically discovering, crawling, and updating billions of web pages daily to keep Google’s search index fresh and reliable.
2. Dynamic
It intelligently adjusts crawl rate depending on a website’s server response, preventing overload while ensuring efficient crawling and indexing of new, updated, and relevant content.
3. Smart
Googlebot avoids wasting resources on duplicate or low-value pages, prioritizing high-quality, authoritative, and relevant content that improves search experience and user satisfaction across queries.
4. Mobile-first
With mobile-first indexing, Google mainly looks at your site as a mobile user would, giving priority to mobile-friendly websites so users get the best experience on their phones.
Importance of Googlebot for SEO
For businesses, blogs, and e-commerce websites, Googlebot is the gateway to visibility. Without being crawled and indexed, your website cannot appear in Google Search Results.
1. Discoverability
Googlebot helps search engines find your content by crawling web pages, following links, and analyzing sitemaps, making your website discoverable to users searching online.
2. Indexing
Once crawled, your website’s content is stored in Google’s search index, enabling it to appear for relevant queries and improving overall online visibility.
3. Ranking
Google uses algorithms to check how relevant, trustworthy, and easy-to-use your pages are. This decides how high your website appears in search results.
4. Traffic
Effective crawling and indexing lead to higher rankings, which attract more visitors, increasing organic traffic, engagement, and potential conversions for businesses, blogs, and e-commerce websites.
Common Challenges with Googlebot
Even though Googlebot is highly advanced, websites often face challenges:
1. Crawl Budget Issues
Large websites with thousands of pages may exceed their crawl budget, causing Googlebot to miss important pages, affecting indexing, visibility, and overall search performance.
2. Blocked Resources
3. Duplicate Content
Multiple sites with equal or similar content confuse Googlebot, making it difficult to determine which version is favored. This can hurt SEO by weakening ranking signals.
4. Slow Loading Pages
Pages with poor performance or heavy resources may load too slowly, causing Googlebot to skip them, resulting in missed indexing opportunities and reduced search visibility.
5. JavaScript Rendering Problems
JS-heavy websites may not render correctly for Googlebot, preventing important content from being processed, indexed, or ranked effectively in Google’s search results.
Best Practices to Optimize for Googlebot
To ensure your website is efficiently crawled, indexed, and ranked, follow these proven best practices when optimizing for Googlebot:
1. Ensure Crawlability
Maintain a clear robots.txt file, avoid blocking essential resources, and submit an XML sitemap in Google Search Console to guide Googlebot effectively.
2. Improve Page Speed
3. Mobile-first Optimization
Implement responsive design, eliminate intrusive pop-ups, and test with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to ensure seamless accessibility for mobile users prioritized by Googlebot.
4. Structured Data Markup
5. Regular Monitoring
To keep crawl efficiency high, use Google Search Console to examine crawl statistics, look for bot activity in server logs, and repair broken links or redirects.
Real World Examples
Here are some practical examples of how different types of websites benefit from Googlebot’s crawling and indexing process:
1. E-commerce Websites
Large e-commerce sites like Amazon and Flipkart rely heavily on Googlebot. They optimize sitemaps and internal linking so Googlebot efficiently crawls millions of products.
2. News Websites
Googlebot News crawls news portals like BBC and Times of India frequently to provide up-to-date news in search results.
3. Bloggers and Content Creators
For blogs, quick crawling and indexing mean trending topics can rank faster and attract readers before competitors.
Final Thoughts
Googlebot powers Google Search by crawling and indexing billions of pages, making the web accessible. For SEO success, website owners must optimize crawlability, site speed, structured data, and monitoring. Treat Googlebot as a partner, not a challenge—better optimization helps ensure effective indexing, improved visibility, and greater chances of reaching the right audience with your content.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How often does Googlebot crawl a website?
Answer: It depends on the site’s authority, content freshness, and server performance. Googlebot may crawl high-authority sites multiple times daily, while it crawls smaller sites only once weekly.
Q2. Can I control Googlebot?
Answer: Yes, you can guide Googlebot using robots.txt, meta robots tags, and canonical tags. However, you cannot force it to crawl instantly.
Q3. Does blocking Googlebot affect SEO?
Answer: Yes. Blocking it prevents pages from being crawled and indexed, which means they won’t appear in search results.
Q4. What is a crawl budget?
Answer: It is the number of pages Googlebot crawls from your site within a given time. Large or poorly optimized sites may face crawl budget issues.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Googlebot” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
