What is Global Marketing?
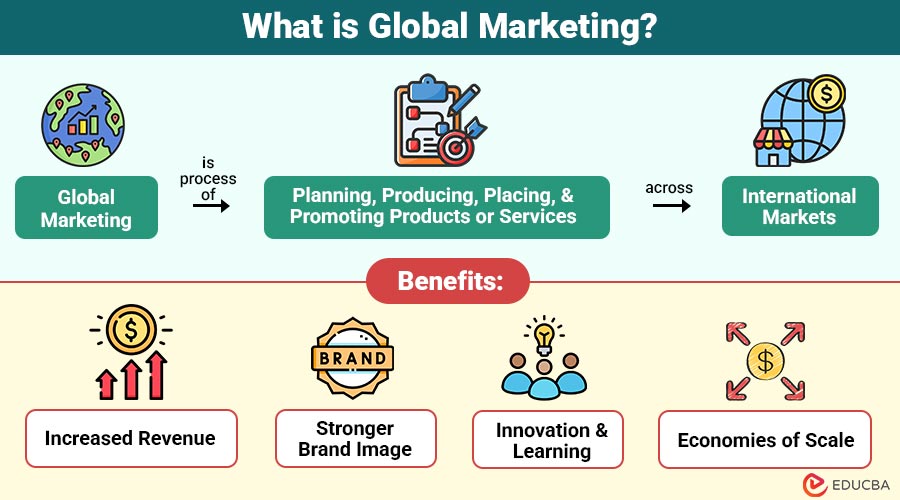
Global marketing is process of planning, producing, placing, and promoting products or services across international markets. Instead of focusing only on local customers, businesses create strategies to reach global audiences while adapting to cultural, economic, and legal differences.
For example, McDonald’s is a classic example of global marketing. It sells burgers worldwide with the same brand identity but adapts its menus to local cultures—such as offering the McAloo Tikki in India and the Teriyaki Burger in Japan.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Strategies
- Steps to Create a Global Marketing Plan
- Benefits
- Challenges
- Real-World Examples
- Use Cases
- Tips
Key Takeaways:
- Global marketing expands business reach, strengthens brands, and ensures growth through international audience engagement.
- Success requires balancing global consistency with localized adaptations to respect cultural, legal, and economic differences.
- Leveraging digital tools and influencers enables faster brand visibility, customer engagement, and cost-effective global expansion.
- Despite challenges like cultural barriers and regulations, global marketing creates innovation, risk diversification, and sustainable growth.
Importance of Global Marketing
Global marketing is more than just selling internationally. It is about building a global brand while adapting to local preferences and needs. Here is why it is important:
1. Larger Customer Base
Expanding globally allows businesses to reach millions of potential customers, increasing demand, engagement, and opportunities beyond their home market.
2. Revenue Growth
By entering multiple international markets, companies boost sales, expand revenue streams, and strengthen financial stability while minimizing over-reliance on a single market.
3. Brand Recognition
Global marketing fosters strong worldwide visibility, enabling companies to establish themselves as trusted household names while creating lasting impressions across diverse cultures and customer groups.
4. Risk Diversification
Operating in several countries reduces dependence on one region, balancing potential economic downturns and ensuring business continuity during unpredictable market fluctuations.
5. Competitive Advantage
Expanding globally helps companies differentiate from local-only competitors, secure stronger positioning, attract international partners, and adapt effectively to diverse customer demands.
Key Strategies in Global Marketing
Different approaches can be used depending on company goals, product type, and target audience. Below are the main strategies:
1. Standardization
Standardization refers to the application of a uniform marketing approach worldwide, ensuring consistency in product design, messaging, and branding to maintain a cohesive global image and recognition.
2. Adaptation
Adaptation involves tailoring products, promotions, and strategies to local cultural values, consumer preferences, and market conditions, ensuring relevance, acceptance, and stronger engagement in each target country.
3. Glocalization
Glocalization blends global brand identity with local adaptations, balancing consistency and customization by maintaining core values while adjusting marketing efforts to align with regional traditions and consumer behaviors.
4. Digital-First Global Marketing
Digital-first global marketing prioritizes online platforms, leveraging social media, SEO, e-commerce, and digital campaigns to connect brands with international audiences efficiently and cost-effectively.
5. Cross-Cultural Marketing
Cross-cultural marketing integrates respect for cultural diversity, traditions, and languages into strategies, creating campaigns that resonate authentically, avoid missteps, and foster deeper emotional connections worldwide.
Steps to Create a Global Marketing Plan
Here are the steps businesses should follow to build an effective global marketing plan:
1. Market Research
Conduct in-depth research on target countries’ culture, consumer preferences, demand patterns, and competitors to identify opportunities and avoid failures.
2. Segmentation
Segment global markets into distinct groups by utilizing demographics, psychographics, purchasing power, and cultural behaviors to tailor strategies for effective targeting.
3. Entry Strategy
Select entry methods—exporting, franchising, licensing, joint ventures, or direct investment—based on resources, risk tolerance, and long-term market objectives.
4. Product Positioning
Decide whether to adapt or standardize product features, design, and branding across markets while ensuring alignment with consumer expectations.
5. Marketing Mix (4Ps)
Customize the marketing mix—product, price, place, promotion—to fit local consumer demands, purchasing habits, distribution systems, and cultural norms.
6. Compliance
Ensure compliance with international trade rules, tariffs, taxation policies, advertising standards, and local legal requirements to avoid operational disruptions globally.
7. Execution & Monitoring
Implement global campaigns, track performance through analytics, assess customer feedback, and continuously optimize strategies to improve ROI and market growth.
Benefits of Global Marketing
Here are the major benefits businesses can achieve by adopting global marketing strategies:
1. Increased Revenue
Expanding into international markets exposes businesses to millions of new customers, significantly increasing sales opportunities, overall revenue, and sustainable growth worldwide.
2. Stronger Brand Image
A global presence enhances brand credibility, builds customer trust, establishes authority, and improves recognition across diverse markets, boosting long-term competitiveness.
3. Innovation & Learning
Operating internationally exposes companies to varied consumer preferences, cultural insights, and trends, inspiring innovative products, strategies, and creative business solutions globally.
4. Economies of Scale
Producing and distributing on a large scale reduces costs per unit, improves operational efficiency, and significantly enhances profitability across international markets.
Challenges in Global Marketing
Global expansion is not without obstacles. Common challenges include:
1. Cultural Differences
Failing to respect cultural values, traditions, and norms may harm brand reputation, mislead audiences, and result in marketing failures internationally.
2. Legal and Regulatory Issues
Different nations enforce unique advertising regulations, trade restrictions, taxation policies, and labeling laws, creating compliance challenges for global businesses.
3. Language Barriers
Inaccurate translations or poor communication can confuse customers, offend cultures, damage trust, and negatively affect brand perception in international markets.
4. Logistics and Supply Chain
Cross-border distribution requires reliable systems, customs coordination, inventory management, and efficient transportation to ensure timely product availability globally.
5. Economic & Political Instability
Currency fluctuations, changing tariffs, unstable governments, or political unrest can disrupt operations, reduce profitability, and threaten international market presence.
Real-World Examples
Here are some leading companies that successfully implement global marketing strategies:
1. Netflix
Netflix markets its service globally by offering both international hits and localized content. For example, “Money Heist” from Spain became a global sensation, while Netflix also produces shows like “Sacred Games” in India for local audiences.
2. Starbucks
Starbucks adapts to local cultures while keeping its premium coffeehouse experience consistent. In Japan, it introduces seasonal flavors like Sakura Cherry Blossom Latte, appealing to cultural traditions.
3. Apple
Apple uses a standardized global strategy with little adaptation. Its sleek design, minimalist ads, and premium positioning remain consistent worldwide, creating a unified luxury appeal.
Use Cases of Global Marketing
Here are some major industries where global marketing plays a crucial role:
1. Fashion Industry
Global fashion brands like Zara and H&M adapt worldwide trends while customizing designs for local cultural preferences.
2. Technology
Tech giants like Microsoft and Google standardize products globally but provide localized support, features, and language options.
3. Food & Beverage
Brands like KFC and Domino’s adapt menus globally while maintaining consistent branding and marketing strategies across regions.
4. E-commerce
Platforms like Amazon and Alibaba connect international buyers and sellers, expanding their reach and driving global commerce.
Tips for Successful Global Marketing
Here are some essential tips businesses should follow to succeed in global marketing:
1. Respect Local Cultures
Research thoroughly before launching campaigns to avoid cultural missteps and build stronger connections with international audiences.
2. Invest in Localization
Translate websites, packaging, and advertisements properly to ensure messaging resonates with local audiences and avoids miscommunication globally.
3. Leverage Digital Marketing
Make efficient use of digital tools and social media platforms to quickly contact individuals across boundaries in order to increase awareness and engagement on a global scale.
4. Use Influencers & Local Partnerships
Collaborate with local influencers, celebrities, or trusted brands to build credibility, enhance trust, and boost regional brand loyalty.
5. Test Before Scaling
Pilot campaigns in selected regions first to analyze performance, gain insights, and optimize strategies before global expansion.
Final Thoughts
Global marketing is no longer a choice but a necessity for companies aiming to grow beyond borders. While challenges such as cultural differences and regulations exist, the rewards—brand recognition, increased revenue, and long-term growth—make it worthwhile. The key is to balance think global, act local. Companies that combine global strategies with local customization are the ones that truly succeed on the world stage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Do small businesses benefit from global marketing?
Answer: Yes, e-commerce and digital marketing platforms allow even small businesses to sell worldwide at low cost.
Q2. What skills are needed for global marketing?
Answer: Cultural awareness, communication skills, adaptability, digital marketing expertise, and knowledge of international trade laws.
Q3. What part does technology play in successful global marketing?
Answer: Technology enables real-time communication, advanced data analytics, e-commerce expansion, and digital marketing campaigns, helping brands connect seamlessly with global audiences.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Global Marketing” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
