What is Funnel Analysis?
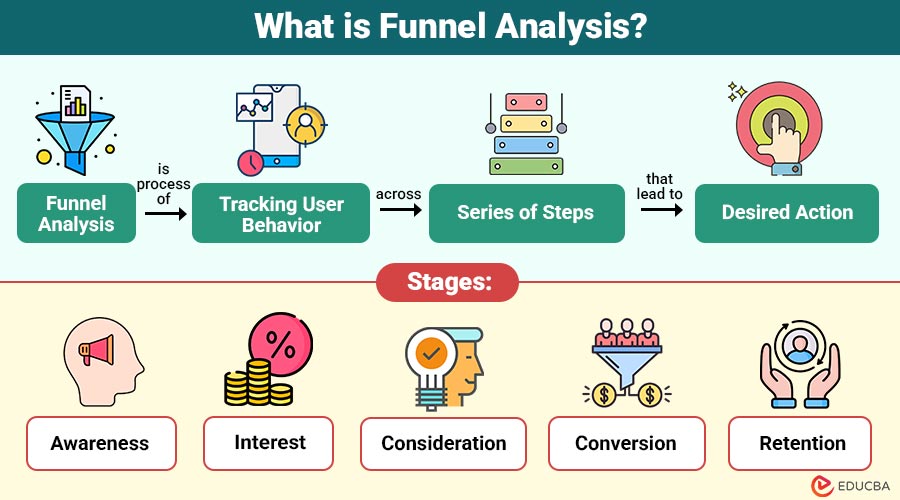
Funnel analysis is a process of tracking user behavior across a series of steps that lead to a desired action.
These actions could include:
- Signing up for a service
- Adding products to a cart
- Completing a purchase
- Filling out a form
- Upgrading to a paid plan
Each step acts like a stage in a funnel—wide at the top and narrow at the bottom—because the number of users decreases as they progress.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Working
- Stages
- Key Metrics
- Types
- Benefits
- Common Drop-Off Points
- Tools
- Real-World Examples
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
Key Takeaways:
- Funnel analysis identifies user drop-off points, helping businesses optimize each stage for higher conversions.
- Tracking micro-conversions and segmenting users provides deeper insights into behavior and engagement patterns.
- Continuous optimization, testing, and reliable data ensure better decision-making and improved funnel performance.
- Implementing funnel analysis boosts revenue, enhances UX, and informs data-driven marketing and product strategies.
Why is Funnel Analysis Important?
Funnel analysis is important because it provides clarity into customer behavior, reveals obstacles, and helps boost performance.
1. Identifies Drop-Off Points
Helps pinpoint the exact stages where users abandon the process before completing actions.
2. Improves Conversion Rates
Reveals problem areas affecting customer decisions, enabling targeted fixes that increase successful conversions.
3. Enhances User Experience
Removes friction across user journeys, creating smoother interactions that encourage task completion and satisfaction.
4. Supports Data-Driven Decisions
Offers actionable behavioral insights that replace assumptions with evidence-based improvements to improve business performance.
5. Increases Revenue
Higher conversion rates boost overall business profitability by turning more visitors into paying customers efficiently.
How does Funnel Analysis Work?
Funnel analysis breaks the user journey into specific, trackable steps. Each step is monitored to measure the percentage of users who continue or drop off.
1. Define the Goal
Define the funnel goal clearly to measure user progression toward actions like purchases or signups.
2. Break the Journey into Steps
Break the user journey into sequential steps, such as product viewing, adding items to the cart, and final checkout.
3. Collect User Data
Collect relevant user interaction data using analytics tools to understand behavior across every stage of the flow.
4. Analyze Conversion and Drop-off
Analyze conversion and drop-off percentages at each funnel step to identify significant behavioral patterns.
5. Identify Issues
Identify issues that cause user abandonment, such as slow load times, navigation issues, confusing layouts, or technical glitches.
6. Optimize
Optimize funnel performance by improving the UI, simplifying forms, offering discounts, and continually testing updates.
Stages of Funnel Analysis
Although funnels vary by industry, most have the following stages:
1. Awareness
Users first discover your product through marketing channels, initiating their journey and initial engagement awareness.
Examples:
- Social media ads
- Google search
- Word-of-mouth
2. Interest
Visitors explore offerings, engaging with content to learn more about features, benefits, and potential value.
Examples:
- Browsing products
- Reading blogs
- Watching demos
3. Consideration
Users compare alternatives, evaluate benefits, and decide whether your product meets needs before taking action.
Examples:
- Checking pricing
- Adding items to the cart
- Reading reviews
4. Conversion
Users complete intended goal actions like purchasing, signing up, or downloading after evaluating value propositions.
Examples:
- Purchase
- Signup
- Download
5. Retention
Users return repeatedly, sustaining engagement through subscription renewals, product reorders, and ongoing service interactions.
Examples:
- Renewing subscription
- Reordering products
Key Metrics in Funnel Analysis
Here are the essential metrics for evaluating performance and identifying bottlenecks across any funnel.
1. Conversion Rate
Determines percentage of users who complete a specific step compared to those who begin it.
2. Drop-Off Rate
Shows the percentage of users abandoning a step, calculated by subtracting the conversion rate from one hundred.
3. Completion Rate
Indicates the number of total visitors who successfully reach the final goal relative to the initial audience size.
4. Time to Convert
Measures the total duration users take to complete the entire intended conversion journey step-by-step.
5. Funnel Velocity
Tracks how quickly users move through funnel stages, indicating journey efficiency and potential friction points.
6. Cohort Conversion
Analyzes conversion performance over time across user groups, revealing trends such as monthly acquisition patterns.
Types of Funnels
Here are the different types of funnels used to analyze user behavior and business performance.
1. Acquisition Funnel
Tracks how new users discover your platform and engage through early stages, measuring initial interaction quality.
2. Conversion Funnel
Focuses on user actions that drive desired outcomes, such as purchases, signups, or downloads, within digital experiences.
3. Sales Funnel
Used in B2B processes to track lead progression from initial prospect awareness toward becoming paying customers.
4. Marketing Funnel
Covers awareness, interest, and engagement stages that guide potential customers toward deeper interaction and future conversions.
5. Retention Funnel
Monitors returning user behavior after conversion, measuring loyalty patterns and long-term engagement with your product continually.
Benefits of Funnel Analysis
Here are the key benefits that funnel analysis provides to businesses:
1. Better Customer Understanding
Helps businesses understand user motivations, behavioral patterns, and preferences, enabling more personalized experiences and targeted improvements overall.
2. Higher Conversions
Enhances conversion outcomes by resolving weak funnel stages, encouraging smoother user progression, and increasing completed actions.
3. Cost Efficiency
Improves marketing budget effectiveness by identifying waste, optimizing spending, and maximizing overall return on investment.
4. UX and UI Optimization
Identifies friction points such as slow pages, long forms, and confusing steps, improving overall user experience significantly.
5. Improved Product Strategy
Reveals which features increase engagement, require enhancement, or hinder usability, enabling better, data-driven product decisions.
Common Drop-Off Points in Funnels Analysis
Here are some common areas where users often drop off during a funnel analysis.
1. Overly Complicated Signup Forms
Overly complex signup forms cause frustration, leading users to abandon registration before completing the required fields.
2. Hidden Fees during Checkout
Hidden fees during checkout create distrust, prompting users to leave before completing their intended purchase.
3. Slow-loading Product Pages
Slow-loading product pages frustrate visitors, causing them to abandon browsing before viewing crucial product details.
4. Poor Mobile Experience
Poor mobile experience causes navigation issues, prompting users to exit early without completing intended actions.
5. Long payment processes
Long payment processes overwhelm users, increasing abandonment before they complete transactions within the checkout flow.
Funnel Analysis Tools
Here are some widely used tools that help businesses analyze funnels and understand user behavior effectively.
| Tool | Key Features | Best For |
| Google Analytics 4 (GA4) | Free, powerful funnel exploration, strong web and e-commerce tracking | Websites, e-commerce platforms |
| Mixpanel | Advanced behavioral analytics, in-depth event insights | SaaS products, mobile apps |
| Amplitude | Deep user journey analysis, cohort analysis, retention funnels | Product analytics, growth teams |
| Hotjar | Visual heatmaps, behavior insights, and screen recordings combined with funnel data | UX research, behavior understanding |
| Adobe Analytics | Enterprise-level analytics, real-time funnel tracking | Large enterprises, complex digital ecosystems |
| Heap Analytics | Auto-captures all events, extremely fast funnel setup | Startups, rapid product teams |
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world examples of funnel analysis:
1. E-commerce Store
Funnel Steps: Product view → Add to cart → Checkout → Payment → Order success
If the drop-off is highest at payment:
- Add more payment options
- Enable guest checkout
- Reduce additional charges
2. SaaS Application
Funnel Steps: Landing page → Signup → Onboarding → Activation
If onboarding drop-offs are high:
- Provide tutorials
- Use guided tours
- Improve UI clarity
3. Mobile App
Funnel Steps: App install → Open app → Register → Use feature
If users open the app but don’t register:
- Simplify login
- Enable social sign-in
- Provide first-use incentives
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Funnel Analysis
Here are some key mistakes commonly seen in funnel analysis:
1. Tracking Too Many Steps
Adding excessive funnel steps complicates analysis and obscures truly important insights that require focused attention.
2. Ignoring Micro-Conversions
Overlooking micro-conversions such as clicks, scroll depth, and video plays misses valuable opportunities to understand user behavior.
3. Using Outdated or Incomplete Data
Inaccurate judgments and poor company optimization choices result from relying on out-of-date or insufficient data.
4. Not Segmenting Users
Failing to segment users ignores behavioral differences across devices, location, or traffic source, undermining insights.
5. Making Changes Without Testing
Implementing changes without proper A/B testing risks reducing performance instead of improving conversion outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Funnel analysis is powerful technique for understanding user behavior, identifying drop-off points, and improving conversions. It offers comprehensive insights on how users engage with your product, app, or website. By analyzing each stage and continuously optimizing the journey, businesses can boost sales, enhance engagement, and build better user experiences. Funnel analysis should be an essential component of any growth strategy, regardless of your role as a marketer, product manager, or company owner.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is funnel analysis used for?
Answer: It is used to analyze how users move through stages toward conversion and to identify drop-offs.
Q2. How does funnel analysis improve conversions?
Answer: By highlighting friction points that can be optimized—like poor UI, long forms, or hidden fees.
Q3. Can funnels be used for mobile apps?
Answer: Yes. Funnels help track installs, registrations, feature usage, and retention.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Funnel Analysis” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
