Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction to fscanf Matlab
There is a need to access the text file in some application to do operations like data reading from a text file, data writing on a text file. For reading data from a text file, we use a fscanf statement. fscanf is an inbuilt function available on MatLab for reading data from a text file ( .txt extension). For reading data, firstly, we must need to open that file using a fopen statement, and we specify the type of access mode to reading ‘r’.
Syntax:
The syntax for fscanf Matlab is as shown below:
A = fscanf (fileID,formatSpec)
A = fscanf (fileID,formatSpec,sizeA)
[A,count] = fscanf (_)
How to do Matlab fscanf?
For reading data from a text file, we use a fscanf statement. For to open that file using a fopen statement. In the fopen statement, we write a text file name which we want to open and specify a type of access mode.
The steps for reading a text file using a fscanf statement:
- Step 1: First, open a file using fopen statement and specify the type of access mode.
- Step 2: Specify the formats specifies and, if needed, then sizeA.
- Step 3: Then, we use a fscanf statement and display the read data.
- Step 4: Close the file using fclose statement.
Examples of fscanf Matlab
Given below are the examples of fscanf Matlab:
Example #1
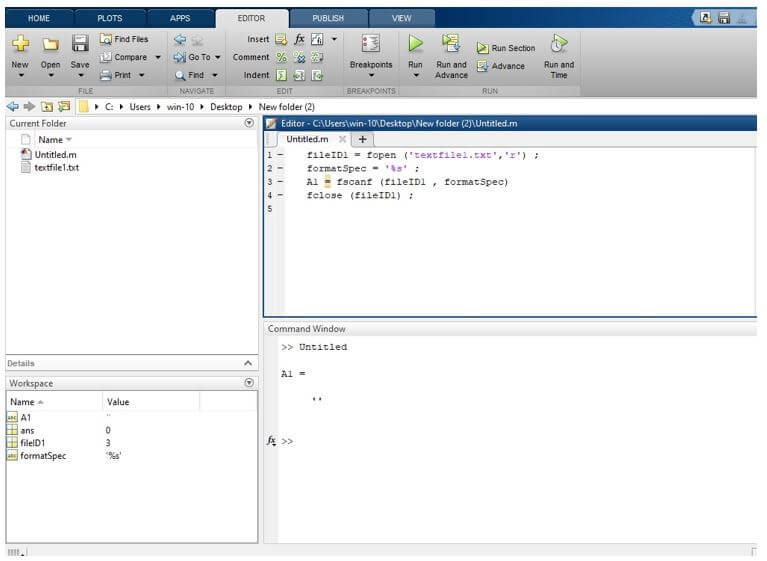
Let us see the example for reading operation; for reading operation, we take a text file textfile1.txt, for a reading operation firstly, we specify the type of access for that we use a fopen statement, we take fopen in parenthesis, we take the text file name which we want to read (filetext1.txt) and the type of access that is reading the file which is specified by ‘r’, and a comma separates these two arguments. Then specify the format using ‘formatspec’ we defined as a float. Then we use the fscanf statement; basically, it is used for reading a text file. We take fscanf in parenthesis we write a fileID1 (text file is indicated by file identifier fileID1) and format specifier, which we defined earlier that is formatSpec and these two arguments are separated by a comma. This read data stored in variable A1. And we close the file using fclose statement.
Code:
fileID1 = fopen ('textfile1.txt','r') ;
formatSpec = '%s' ;
A1 = fscanf (fileID1 , formatSpec)
fclose (fileID1) ;
Output:
Example #2
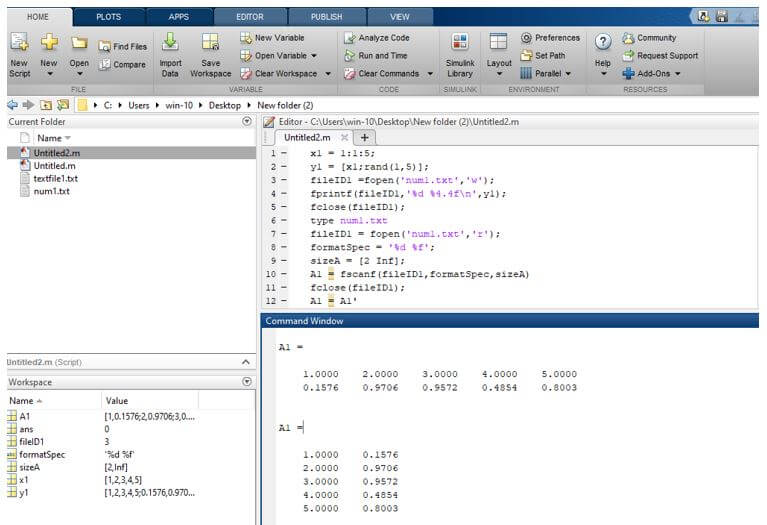
Let us consider another example; in this example, we take an integer number as we as float numbers, integer numbers are stored in x1 variable, and floating numbers are created by using a rand function (rand function returns a random float number) and these float numbers are stored in y1 variable. Then we open a file using a fopen statement, and then we write these numbers using a fprintf statement, and then we close the file using a fclose statement. Then we see that data using a type function; the type function is used to display the data of contents. Then we open a file again using a fopen statement, and we specify the type of access mode in reading ‘r’, and then we assign that fopen return data to fileID1; fileID1 is a file identifier of an open file. Then we specify the format on a format specifier ( formatSpec), then a sizeA, sizeA must be a positive integer. Then we take a fscanf statement, in fscanf in a parenthesis, take a file identifier (fileID1), format specifier (formatSpec) and a sizeA and the return read data are stored in the A1 variable. Then we need to close that opened file using a fclose statement. Then we just transpose the A1 using a transpose symbol. Then we see a result on the command window.
Code:
x1 = 1:1:5;
y1 = [x1;rand(1,5)];
fileID1 =fopen('num1.txt','w');
fprintf(fileID1,'%d %4.4f\n',y1);
fclose(fileID1);
type num1.txt
fileID1 = fopen('num1.txt','r');
formatSpec = '%d %f';
sizeA = [2 Inf];
A1 = fscanf(fileID1,formatSpec,sizeA)
fclose(fileID1);
A1 = A1'
Output:
Example #3
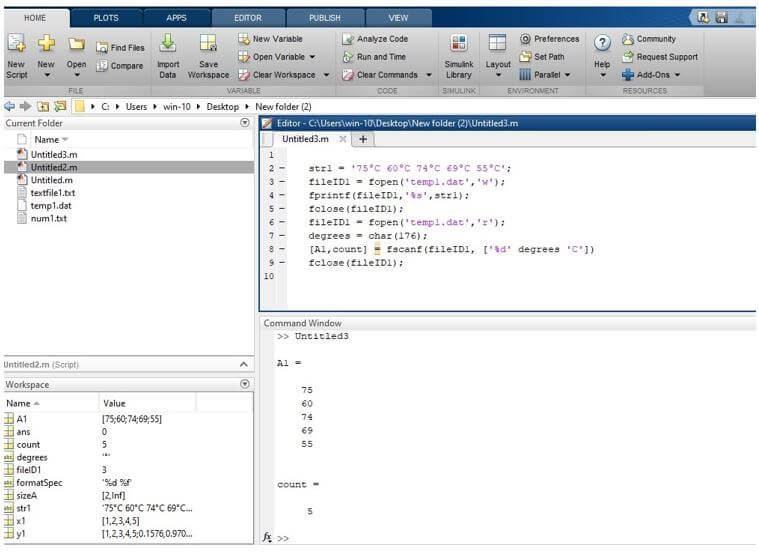
Let us see an example related to the fscanf statement; in this example, we skip the text that is °C text in a string. We take one temperature string on a variable str1. We open a temp1.txt file using a fopen statement and specify the type of access mode to write, and these fopen statements assign to file identifier fileID1. Then we write that temperature string on a temp1.txt file using a fprintf statement. Then we close that opened file using a fclose statement. Then we again open that file for reading using the fopen statement; in fopen, we specify the type of access mode to read ‘r’, then it assigns to file identifier fileID1. The ASCII code of °C is 176; these are passed to degrees variable. Then we take a fscanf statement; in fscanf, we take the file identifier of an open file, and in square brackets, we take an integer number of degrees that is nothing but °C, these data are assigned to A1 and count. A1 is a temperature and in count stores a number of °C. Then we simply close that opened file using a fclose statement.
Code:
str1 = '75°C 60°C 74°C 69°C 55°C';
fileID1 = fopen('temp1.dat','w');
fprintf(fileID1,'%s',str1);
fclose(fileID1);
fileID1 = fopen('temp1.dat','r');
degrees = char(176);
[A1,count] = fscanf(fileID1, ['%d' degrees 'C'])
fclose(fileID1);
Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we saw the concept of fscanf; basically, fscanf is used for reading data from a text file. Then saw syntax related to fscanf statements and how it’s used in MatLab code. Also, we saw some examples related to fscanf statement.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to fscanf Matlab. Here we discuss the introduction, how to do Matlab fscanf? Along with examples, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –