Updated March 28, 2023

Introduction to File Handling in C
File handling in C is a process where some bytes of data can be written and stored permanently in the disk so that in a later point of time, the relatable data can be fetched and referred. File Handling in C makes use of structure pointer of the file type to declare a file. For Example, An application is developed, and it is very much needed to store some important file settings then it is mandatory to support file handling to store that data of the settings permanently for later reference and manipulation.
File Handling Functions in C
Most often programs are executed on terminals but in industries, the application runs should have some proof or records to be referred at some point in time. Therefore, it is very much needed to store these applications executed data somewhere and then file handling is used. It is used to write those data somewhere and save it permanently. Some pointer related structures are used to point towards that sort of file for reference. Different File handling Functions in C are as follows:
- fopen [with an extra attribute such as ‘a’ or ‘b’]: For creating a new file.
- fopen: Opening of an existing file.
- fscanf or fgetc: Reading from a file.
- fprintf or fputs: Writing to file.
- rewind, fseek: Moving to a certain or specific location within a file.
- fclose: Closing of a file.
Attributes to File Handling
For creating a new file using different attributes of file handling:
There are certain privileges which are needed to be provided to the file while opening or we can say kind of access control. As mentioned earlier certain specific types of pointer structures are needed for file to point these attributes are part of that only. These attributes are as follows:
- “r”: It is used to search a file and then once the search gets complete and the file is opened, fopen will load it into memory and will set up a pointer that will point to the first character of the file. In case the file is not able to open then it will return a NULL value.
- “w”: It will first search for a file and once a file gets searched successfully and it exists then all the contents get overwritten. In case the file is not existing, it will create a new file and returns null if the file is not able to open.
- “a”: It also works in similar fashion as that of r, but the only difference Is that the pointer will point to the last character of the file. In case the file is not able to get opened it will again return a NULL value.
- “r+”: It is also an attribute that works the same as r just naming Is different, attribute points to the first character only.
- “w+”: It also works the same as ‘w’ just the difference lies in the naming convention.
- “a+”: It also works the same as ‘a’ just the difference lies in the naming convention.
Syntax:
FILE *filePointer;So, the file can be opened as
filePointer = fopen ("file.txt", "a")Some main functions with its syntaxes to perform some common operations are as follows:
- Reading from a file.
- Writing a file.
- Closing a file.
1. Reading from a file
Reading from a file involves the usage of both fscanf and fgets. Both functions are almost similar to the fact that both have the same functionality with a difference of using an additional parameter, the file pointer which can be used either to read a file line by line or character by character.
Syntax:
FILE * filePointer;
filePointer = fopen ("file.txt", "r");
fscanf (filePointer, "%s %s %s %d", str1, str2, str3, &date);2. Writing a file
Writing in a file can be done using both the functions fprintf and fputs in the same way as read operations.
Syntax:
FILE *filePointer;
filePointer = fopen ("file.txt", "w");
fprintf (filePointer, "%s %s %s %d", "we", "live", "in",2020);3. Closing a file
Once all operations are performed successfully and it is always asked to close the file and for closing any file it is very much needed to use fclose function.
Syntax:
FILE *filePointer;
filePointer= fopen ("file.txt", "w");
# Perform some file operations and then close it
fclose(filePointer)Examples to Implement File Handling in C
Below are the examples to implement in File Handling in C:
Example #1
Program for opening a file, writing and closing a file.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main ()
{
FILE *filePointer;
char dataToWrite [50] = "Educba - portal for learning";
filePointer = fopen ("file_handling_test.c", "w");
if (filePointer == NULL)
{
printf ("file_handling_test.c file fails to get open.");
}
else
{
printf ("The file gets opened.\n");
if (strlen (dataToWrite) > 0)
{
fputs (dataToWrite, filePointer);
fputs ("\n", filePointer);
}
fclose(filePointer);
printf ("Data gets successfully written in file file_handling_test.c\n");
printf ("File now gets closed.");
}
return 0;
}Output: For the main file, the output is as.
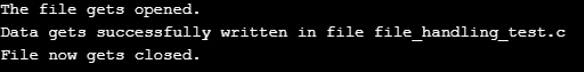
Output: For file_handling_test is as.
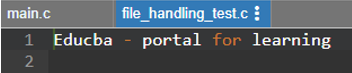
Example #2
Program to Open a file, Read from it and close that file.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main ()
{
FILE *filePointer;
char dataToRead [50];
filePointer = fopen ("File_Read_Test.c", "r");
if (filePointer == NULL)
{
printf ("File_Read_Test.c file gets failed to open.");
}
else
{
printf ("The file then gets opened.\n");
while(fgets (dataToRead, 50, filePointer) != NULL)
{
printf ("%s", dataToRead);
}
fclose(filePointer);
printf ("Data successfully gets read from the file File_Read_Test.c\n");
printf ("The file then gets closed.");
}
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
Conclusion
File Handling in any programming language not only in C plays a very important role especially in the industry as it will store the data in memory permanently which can be referred later at any point in time. This is a special characteristic of the file handling feature.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to File Handling in C. Here we discuss function in fil handling, different attributes with examples to implement with appropriate syntax as well. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


