What is Few-Shot Prompting?
Few-shot prompting is a technique where you provide a language model with a small number of examples to guide its response to a new query. Unlike traditional programming, where rules are hardcoded, few-shot prompting allows the model to learn patterns from examples on the fly.
Key points:
- You provide 2–5 examples (sometimes more) within your prompt.
- The model generalizes from these examples to handle similar tasks.
- It works well for tasks like text summarization, translation, classification, and code generation.
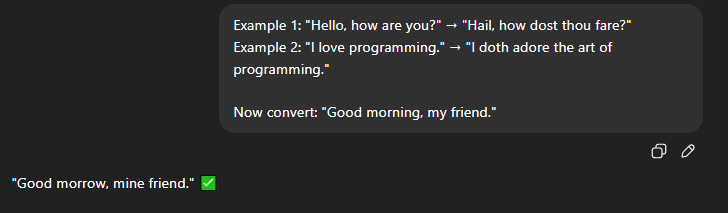
Example: Suppose you want the AI to convert English sentences into Shakespearean style. A few-shot prompt might look like this:
Here, the AI learned the pattern from just two examples.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Why is it Important?
- How Few-Shot Prompting Works?
- Tools and Platforms
- Practical Examples
- Common Mistakes
- Real-World Applications
- Future
Why is it Important?
Few-shot prompting is particularly valuable for several reasons:
- Reduces training requirements: Instead of retraining the model on a specific dataset, you can guide it with a few examples.
- Improves accuracy: Providing examples reduces ambiguity and helps the model generate outputs closer to your expectations.
- Flexible across tasks: Few-shot prompting can be applied to many tasks, including text classification, summarization, and creative writing.
- Faster deployment: For businesses, this means you can implement AI solutions quickly without massive datasets.
How Few-Shot Prompting Works?
Few-shot prompting works because large language models learn patterns from vast amounts of training data. They can recognize patterns and relationships between examples and new tasks.
The process generally involves three steps:
- Define the task: Describe what you want the model to do.
- Provide examples: Give the model 2–5 examples that represent the desired output.
- Ask the model to continue: End the prompt with a new input that the model must process.
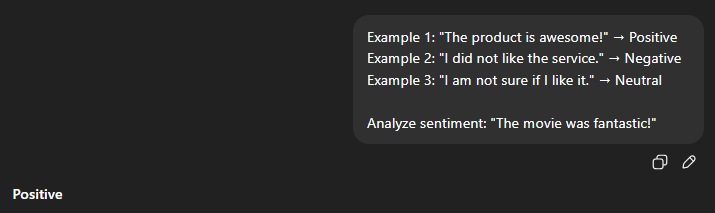
Example Prompt:
Example 1: “The product is awesome!” → Positive
Example 2: “I did not like the service.” → Negative
Example 3: “I am not sure if I like it.” → Neutral
Analyze sentiment: “The movie was fantastic!”
Output:
This is a simple yet powerful illustration of how few-shot learning guides the AI.
Tools and Platforms
Several platforms allow easy experimentation with few-shot prompting:
- OpenAI GPT-4/GPT-3.5: Supports few-shot learning directly in the prompt.
- Cohere: Offers large language models with prompt-based learning.
- Anthropic Claude: Optimized for conversational AI tasks with few-shot examples.
- LangChain: A framework to automate prompt design and dynamic example selection.
These tools can help you implement few-shot prompting in real-world applications such as chatbots, automated customer support, content generation, and more.
Practical Examples
Here are some of the practical examples that you can try:
1. Chain-of-Thought Prompts
Encouraging the model to reason step-by-step improves performance on complex tasks like math or logic.
Example: Solving a math problem
Example 1: “If a car travels 60 km in 2 hours, what is its speed?”
Step 1: Distance = 60 km, Time = 2 hours
Step 2: Speed = Distance / Time = 60 / 2 = 30 km/h
Answer: 30 km/h
Now solve: “A train covers 150 km in 3 hours. What is its speed?”
Output:
Here, the AI can produce detailed reasoning instead of a simple answer, enhancing reliability.
2. Role Assignment
Assigning roles within the prompt helps guide the AI’s behavior.
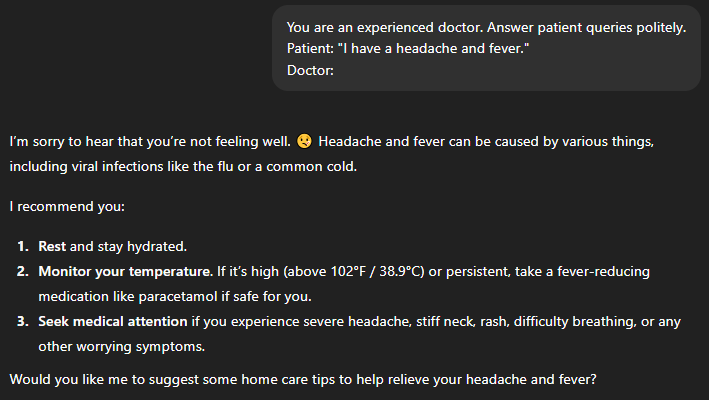
Example: Acting as a doctor
Patient: “I have a headache and fever.”
Doctor:
The AI will respond in a professional, empathetic tone suitable for healthcare contexts.
3. Dynamic Prompting
Dynamic prompting involves modifying prompts in real-time based on AI responses to improve output quality.
Example: Iterative Story Generation
Output 1: “The fox discovered the stone could grant wishes.”
Example 2: “A dragon guarded the enchanted forest.”
Output 2: “The villagers feared the dragon, but it turned out to be friendly.”
Prompt for AI: “A young girl stumbled upon a secret portal.”
Output:
The model continues the story while maintaining consistency with previous examples.
4. Multi-Task Prompting
Advanced users can teach models to handle multiple tasks simultaneously using few-shot examples.
Example: Translation and Sentiment Analysis
Input: “Good morning”
Output: “Bonjour”
Task 2: Sentiment Analysis
Input: “I hate waking up early”
Output: Negative
New Input: “The food was amazing!”
Output:
The model can understand which task to perform based on example patterns.
Common Mistakes
Even experienced users make mistakes when using few-shot prompting. Avoid these pitfalls:
- Too Few Examples: One or two examples might not capture enough patterns.
- Inconsistent Formatting: Mixing styles or structures confuses the AI.
- Overloading Prompts: Too many examples can exceed token limits and reduce model efficiency.
- Ambiguous Instructions: Vague language leads to unpredictable results.
Real-World Applications
Few-shot prompting finds applications across various industries:
- Customer Support: Automate answers for common questions with minimal examples.
- Content Creation: Generate blog ideas, social media captions, or ad copies with a few guiding examples.
- Data Labeling: Quickly categorize datasets or create training labels.
- Education: Personalized tutoring by generating examples and explanations based on student queries.
- Healthcare: Summarize patient notes, extract important information, or provide medical advice patterns (with supervision).
Future of Few-Shot Prompting
As AI models grow larger and more capable, few-shot prompting remains crucial because:
- It reduces the need for costly, full-scale fine-tuning.
- It allows rapid adaptation to new tasks.
- It is the foundation for in-context learning, where models learn patterns from examples dynamically.
Researchers are also exploring one-shot and zero-shot learning enhancements that complement few-shot approaches, making AI even more versatile.
Final Thoughts
Few-shot prompting is a powerful technique that empowers AI to perform complex tasks efficiently with minimal data. By understanding the fundamentals, applying intermediate strategies, and experimenting with advanced techniques like chain-of-thought reasoning and dynamic example selection, you can harness the full potential of modern language models. Whether you are a beginner aiming to explore AI capabilities or an advanced user building sophisticated applications, mastering few-shot prompting is essential for unlocking accurate, efficient, and context-aware AI outputs.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on few-shot prompting helps you master AI tasks effectively. Explore these recommended articles for more tips and insights on advanced prompting techniques.