Updated April 6, 2023

Introduction Error Handling in C
Error handling is the concept where it is conducted to respond to the occurrences of the error during computations of programs, applications, etc which also includes detection and process of how to resolve these errors. There are different ways of handling errors in different programming languages. In C programming language there is no support for error handling but instead, it provides methods and variables that are provided by the C standard library file called error.h which helps to find the errors and return to the function call. In general, the C language usually returns the function values in either -1 or NULL for error cases.
Working of Error Handling in C
As we know that error handling is not supported by the C programming language instead it has an error.h header file which provides few methods and variables that return values that are considered to detect the error occurrences while executing the programs. Therefore in any C program, it checks for the return value of the function to detect what kind of error has been occurred. It is usually better to follow the practice of assigning errno to 0 at the initializing a program which helps to indicate that there are no errors in the program.
Methods of Error Handling in C
In the C program, there are different functions or methods of error handling in C. They are specified as:
1. Global variable Errno
In C programming language, this is a variable where it is known as errno and is assigned a specific number or code that is used within the program to detect the type of error. Such type of error is declared in the header file known as error.h, so there are different error numbers for different types of errors and some of them are listed below:
| Error number | Error description |
| 1 | Operation not permitted |
| 2 | No such file or directory |
| 3 | No such process |
| 4 | Interrupted system calls |
| 5 | I/O error |
| 6 | No such device or address |
Now let us see an example, to see what error value will be displayed if the file does not exists.
Below is the example are as follows:
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
FILE * f;
f = fopen("article.txt", "r");
printf(" Value of error number as errno: %d\n ", errno);
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
In the above program, we are trying to open a file that does not exist, and hence it will give an error that has been assigned a value and it is errno 2.
2. Perror() and strerror()
There are two different methods or functions in C, which are used to display the error message instead of just displaying the errno as we did it in the above program. They are as follows:
- perror(): This function takes the message to be displayed which also displays the textual representation of errno.
Syntax:
void perror (const char *s)s: – can be a string or message to be printed before the error message.
- strerror(): This function points to the string or message or textual representation of the errno value and this function is defined in the header file string.h library.
Syntax:
char *strerror( int errornum)errornum: this contains the error number i.e. errno.
The above two functions can be demonstrated by the below program. Below is the example are as follows:
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
extern int errno ;
int main () {
FILE * f;
int errornum;
f = fopen ("article.txt", "rb");
if (f == NULL) {
errornum = errno;
fprintf(stderr, "The Value of errno: %d\n", errno);
perror("Error message that is printed by perror");
fprintf(stderr, "Error message for opening file that does not exist: %s\n", strerror( errornum ));
} else {
fclose (f);
}
return 0;
}Output:
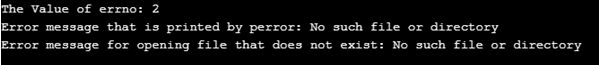
In the above program, we are trying to open a file that does not exist so to print the customized message for such error we using perror() and strerror() function which will print the error message along with errno with a customized error message.
3. Exit Status
In this, it provides an exit() function which takes two values for printing successful or unsuccessful termination by using EXIT_SUCCESS and EXIT_FAILURE. This exit() function is defined in the standard library stdlib.h header file. This also can be demonstrated by the below program.
Below is the example are as follows:
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main ()
{
FILE * f;
f = fopen ("article.txt", "rb");
if (f == NULL)
{
printf("The Value of errno printed is : %d\n", errno);
printf("Error message printed while opening the file with errno: %s\n",
strerror(errno));
perror("Error message printed by perror");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
printf("The message will not be printed\n");
}
else
{
fclose (f);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
printf("The message will be printed\n");
}
return 0;
}Output:

4. Divide by Zero Error
The statement itself defines the error as this is displayed or occurred when the divisor is zero before a division command so this leads to dividing by zero error.
Example:
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void function(int);
int main()
{
int x = 0;
function(x);
return 0;
}
void function(int x)
{
float f;
if (x==0)
{
printf("Division by Zero is not allowed as it leads to the error");
fprintf(stderr, "Division by zero error\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else
{
f = 10 / x;
printf("f(x) is: %.5f", f);
}
}Output:
![]()
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the error handling in C programming language is not supported as to instead it provides few functions and error number values that are printed as error messages. In this article, we have seen the few error values list such that the number indicates a different type of error. In this article we have also seen few functions like perror(), strerror(), and exit() which prints the customized error message to the particular error type with errno.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Error Handling in C. Here we discuss the Introduction and Working of Error Handling in C along with Various Methods and its Examples along with its Code Implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


