What is Economic Research?
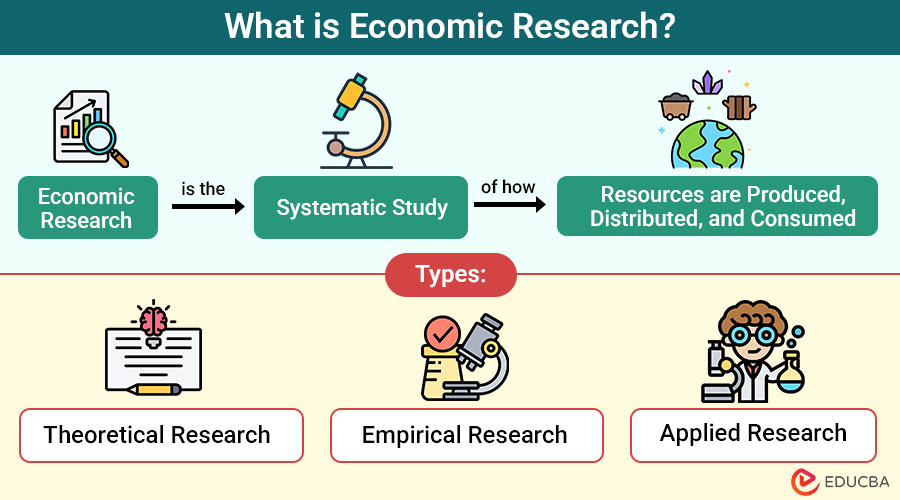
Economic research is the systematic study of how resources are produced, distributed, and consumed. It involves gathering data, applying statistical methods, and interpreting results to understand economic behavior, trends, and policy outcomes.
For example, a government agency wants to understand why unemployment is rising in a specific region. Economic researchers collect data on job openings, education levels, wages, and industry activity. They use statistical models to analyze this information and determine that automation in manufacturing has displaced many workers. Based on this research, policymakers may consider introducing job retraining programs to assist affected workers in transitioning to new careers.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Economic research enables policymakers and businesses to make informed, evidence-based strategic decisions in the face of uncertainty.
- It bridges theory and practice to improve real-world economic outcomes across diverse sectors and regions.
- The way economists study and forecast trends is being redefined by new technologies like behavioral insights and artificial intelligence (AI).
- Robust data and adaptable models are crucial for maintaining economic relevance in a rapidly evolving world.
Why Economic Research Matters?
Here are the key reasons why economic research plays a vital role in shaping decisions across sectors:
1. Policy Formulation and Evaluation
Governments rely on economic research to design and evaluate policies. For instance, before implementing a tax reform, researchers study its potential impact on consumer spending, business investment, and government revenue.
2. Business Strategy and Forecasting
Companies use economic insights to forecast market demand, set pricing strategies, and allocate investments. A firm anticipating a recession might delay expansion plans based on macroeconomic indicators.
3. Academic and Educational Advancement
Academic institutions conduct economic research to test theories, contribute to public debates, and train students. Research outputs often influence the direction of future economic studies and methodologies.
4. Global Development and Aid Programs
Economic research is used by international institutions like World Bank & International Monetary Fund to assist developing nations. It helps identify bottlenecks to growth and develop tailored economic assistance programs.
Types of Economic Research
Economic research can be broadly classified into theoretical, empirical, and applied research.
1. Theoretical Research
This research develops abstract models to explain economic behaviors and interactions. For instance, game theory analyzes how firms or individuals make strategic decisions in competitive or cooperative environments.
2. Empirical Research
Empirical research collects and analyzes real-world data to test economic theories. For example, it employs econometrics to examine how changes in interest rates affect household consumption patterns.
3. Applied Research
Applied research tackles specific economic problems using data and analysis. Governments may commission studies on how raising the minimum wage impacts employment levels in certain industries or regions.
Key Methods Used in Economic Research
Economic researchers use a combination of qualitative and quantitative techniques, including:
1. Econometric Modeling
Econometric modeling utilizes statistical techniques to analyze economic data, allowing researchers to test hypotheses and measure relationships between variables, such as inflation, income, employment, and interest rates, in real-world contexts.
2. Surveys and Field Experiments
Researchers collect firsthand data from individuals or businesses through surveys and field experiments, providing insights into preferences, behavior, or decision-making that existing secondary data may not capture.
3. Time-Series Analysis
Time-series analysis examines how economic indicators, such as GDP, inflation, or unemployment, change over time, enabling researchers to identify trends, cycles, and long-term relationships between variables.
4. Cross-Sectional Studies
Cross-sectional studies analyze data from multiple subjects or units at a specific point in time, allowing comparisons across demographics, industries, or geographic regions to identify structural differences or trends.
5. Case Studies and Historical Analysis
Case studies and historical analysis offer detailed examinations of specific economic events or policies, enabling researchers to understand the causes, consequences, and lessons learned across different periods and contexts.
Applications of Economic Research
Given below is a list of key areas where economic research is actively applied to support decision-making and policy development:
1. Monetary Policy
By using economic research to inform their decisions on interest rates, inflation management, and currency stability, central banks such as the Federal Reserve and the Reserve Bank of India can foster sustainable economic growth.
2. Labor Markets
Research explores employment patterns, wage behavior, skill gaps, and the effects of automation or education, providing insights to shape labor policies and workforce development strategies effectively.
3. International Trade
Economic studies assess the impact of tariffs, trade deals, and currency fluctuations, guiding countries in forming trade policies that boost competitiveness and protect domestic industries.
4. Healthcare Economics
Researchers evaluate healthcare delivery, insurance models, and treatment costs to determine resource allocation, assess the effectiveness of policies, and identify ways to improve affordability and access to quality healthcare services.
5. Environmental and Climate Policy
Economic research helps design and assess green policies by analyzing the long-term costs, benefits, and efficiency of carbon pricing, renewable energy investments, and climate adaptation initiatives.
Emerging Trends in Economic Research
The landscape of economic research is evolving rapidly. Some of the key trends include:
1. Big Data and AI Integration
Economists leverage big data and machine learning to analyze vast datasets, enhancing the accuracy of economic forecasts, detecting hidden patterns, and evaluating policy outcomes with greater precision and speed.
2. Behavioral Economics
A more nuanced understanding of how people and organizations make economic decisions is now possible, thanks to researchers’ incorporation of psychological and emotional factors, which extends beyond conventional theories of rational behavior.
3. Inclusive and Sustainable Development
To supplement GDP with more thorough indicators of development and social justice, economic research is increasingly concentrating on broader metrics, including well-being, inequality, and environmental impact.
4. Real-Time Economic Indicators
Economists can now monitor economic activity in real-time using sources such as credit card usage and job advertisements, which enables quicker reactions to shifting conditions and more prompt policy decisions.
Challenges in Economic Research
Despite its importance, economic research faces several challenges:
1. Data Limitations
Many countries lack timely, accurate, and detailed economic data—especially at the micro level—making it difficult to conduct reliable analysis or create informed policy recommendations.
2. Model Uncertainty
Economic models often simplify complex realities and may omit critical variables, resulting in predictions that do not accurately reflect actual economic outcomes or behaviors.
3. Bias and Assumptions
Political, institutional, or personal biases can influence research, and relying too heavily on assumptions may distort conclusions or misguide policy formulation.
4. Rapid Change
Technological advances and global shifts can render traditional models obsolete, requiring constant adaptation and reevaluation of existing economic frameworks and theories.
Final Thoughts
In today’s interconnected and dynamic world, economic research is more important than ever. In addition to explaining how the economy works, it provides the knowledge necessary to handle issues such as inequality, climate change, and technological disturbance. By investing in robust economic research, societies empower themselves with the knowledge to build a better, more inclusive future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Who conducts economic research?
Answer: Economic research is carried out by governments, universities, think tanks, central banks, and international institutions such as the World Bank and IMF.
Q2. How is economic research different from financial research?
Answer: While economic research looks at broader macroeconomic issues (like inflation or employment), financial research focuses on individual markets, companies, or investments.
Q3. Can economic research predict recessions?
Answer: While it can identify warning signs, predicting recessions precisely is challenging due to the complexity of economic systems.
Q4. What skills are needed for a career in economic research?
Answer: Strong analytical skills, knowledge of economics and statistics, proficiency in software like R or STATA, and the ability to interpret data critically are essential.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Economic Research” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

