Updated April 1, 2023
Introduction to Double Pointer in C
In the C programming language, we have seen what pointers are and what they are used for. In C, a pointer means pointing directly to another variable. In general, Pointers are the variables that store the address of another variable. Whereas pointer to pointer which means a pointer stores the address of another pointer, and this second pointer will be storing the address of the previous or first pointer which is also known as double-pointer in C. Therefore, double pointers are used when we want to store the address of the pointers. Usually, pointers are used to access the address of the variables that we want to get the value or access it.
How does Double Pointer work in C?
In this article, we will see how to declare double-pointer with syntax and example, and also we will see how to use them in the C programming language. So let us start from the syntax.
Syntax:
int **pointer_var;In the above syntax, we can see the variable pointer_var is prefixed with two stars (**), also known as the indirection operator (*) for declaring the double-pointer.
So in general if the pointer is pointing to or referring to an object in memory then double-pointer is a pointer that would be pointing to or referring to another point where it is pointing to an object in memory. Let us see how this exactly works by below example and pictorial form:
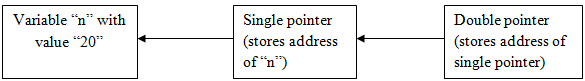
Examples to Implement Double Pointer in C
Below are the examples are mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
void main ()
{
int n = 20;
int *pr;
int **pr1;
printf("\nThe address of the variable n is: %x\n", &n);
pr = &n;
printf("\nThe address of variable n stored in single pointer is: %x\n",pr);
pr1 = ≺
printf("\nThe address of pointer pr stored in double pointer is: %x\n",pr1);
printf("\nThe address of double pointer pr1 is: %x\n", &pr1);
printf("\nThe value stored at pointer pr: %d\n",*pr);
printf("\nThe value stored at another pointer pr1: %d\n",**pr1);
}Output:

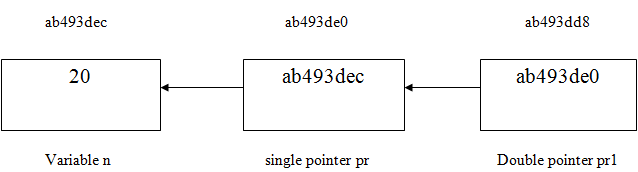
Explanation: In the above code, we have declared a variable “n” and initialized it to value “20” now we have declared a single pointer “*pr” and double pointer “**pr1” where the address of variable n will be stored in pointer”*pr” and the address of this single pointer “*pr” is stored in the pointer “**pr1” which is now a double-pointer. So when we print the value of a single pointer or double pointer the value will be 20 as double-pointer is indirectly pointing to the variable “n” and it will access its value. This can be shown as
Example #2
In this article, let us see why and where double pointers can be used. There are several uses of a pointer to pointer where it is the address of a data. This can be explained by writing this code.
Code:
int n = 50;
int* p1 =&n;
int** p2= &p1;If we see the above code if “n” is at the address 100 and pointer “p1” is pointing or assigned to the address of n (100) and p1 also has address 200 and pointer “p2” is now assigned to the address of p1 (200). Another use of a double pointer is when we want to allocate space in the matrix. This can be explained in the below code.
Code:
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int **matrix;
int row=5,col=5;
int i;
matrix = (int**)malloc(row*sizeof(int*));
for (i=0;i<row;i++)
matrix[i]= (int*)malloc(col*sizeof(int));
}Explanation: In the above code, as “matrix” is a double pointer it uses malloc function which dynamically allocates memory for the matrix of 5 rows and 5 columns. As we know that in the code “matrix” is integer data type so integer pointer can be used in the starting of the array as the address of the “matrix” pointer is an integer. Therefore, in the same way, a pointer to an integer pointer can have the starting address in the array of an integer as that is also an integer.
Example #3
Double pointers can also be used when we want to alter or change the value of the pointer. In general double pointers are used if we want to store or reserve the memory allocation or assignment even outside of a function call we can do it using double pointer by just passing these functions with ** arg. As we did it in the previous code. Let us consider an example where we want to change or update a character from a function.
Code:
void func(char ch)
{
ch = 'B';
}
int main()
{
char ptr;
ptr = 'A';
printf("%c", ptr);
func(ptr);
printf("%c\n", ptr);
}The above code will not execute as we have passed the value to the function so this can be done by using pointers while passing by reference.
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
void func( char *p)
{
*p = 'Y';
}
int main()
{
char *p;
p = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 1);
*p = 'X';
printf("%c\n", *p);
func(p);
printf("%c\n", *p);
}Output:
![]()
Explanation: So in the above code, it will allow you to update the character at the pointer “p” with value “X” to the value “Y”.
Conclusion
In this article, we can conclude that pointers are also variables that can store values. But a pointer usually stores the value as the address of another variable. So commonly we can define double-pointer as pointer to pointer, which means a pointer stores the address of another pointer. In this way, double pointers are used in allocating the memory or assigning the value as the address of another pointer to access the value even outside the function call bypassing the reference to the argument using ** arg.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to Double Pointer in C. Here we discuss how Double Pointer works in C and examples for better understanding. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


