What is a Distributed Operating System?
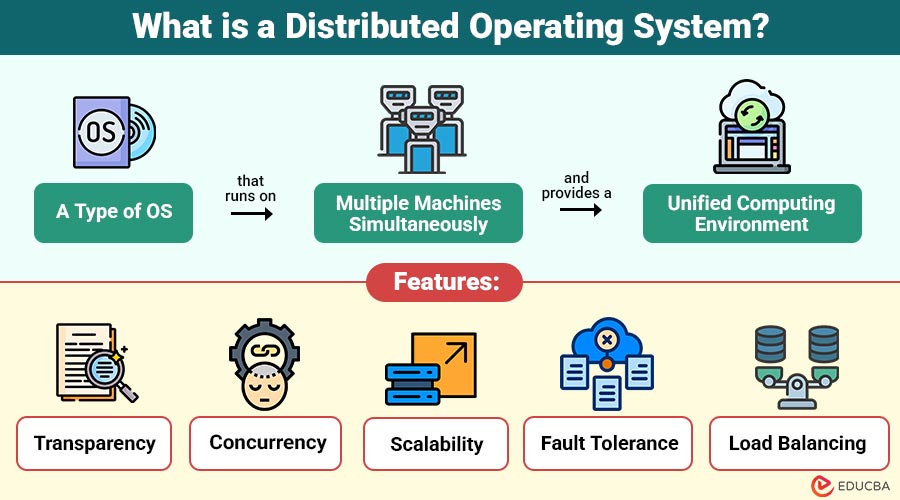
A Distributed Operating System (DOS) is type of OS that runs on multiple machines simultaneously and provides a unified computing environment. Each machine in the system has its own local memory and processor, but all nodes cooperate to execute tasks.
In a distributed Operating System:
- Processes can run on any machine
- Files and resources are shared
- Workloads are distributed automatically
- Failures of one node do not collapse the entire system
The system behaves as a single virtual computer rather than multiple independent machines.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Key Objectives
- Architecture
- Components
- Key Features
- Differences
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Examples
Key Takeaways:
- Distributed operating systems unify multiple computers, providing seamless collaboration, enhanced performance, and transparent resource management across nodes.
- Fault tolerance in a distributed OS ensures system reliability, enabling uninterrupted operations despite individual node failures or network issues.
- Scalability enables distributed systems to scale efficiently by integrating additional machines without compromising existing performance or stability.
- Distributed OS architecture, whether client-server, peer-to-peer, or hybrid, determines resource allocation, communication, and process coordination strategies.
Key Objectives of Distributed Operating System
The design of a distributed operating system focuses on the following goals:
1. Transparency
Conceals system complexity by presenting multiple computers as a single, unified operating environment to users.
2. Resource Sharing
Allows efficient utilization of hardware, software, and data resources across interconnected machines within the system.
3. Scalability
Enables seamless system expansion by adding nodes without negatively impacting overall performance or functionality.
4. Reliability & Fault Tolerance
Maintains continuous system operation by detecting failures and redistributing tasks across remaining active nodes.
5. Performance Improvement
Enhances system speed and efficiency through parallel processing, intelligent load balancing, and distributed task execution.
Architecture of Distributed Operating System
The architecture defines how nodes interact and share responsibilities.
1. Client-Server Architecture
- Centralized servers provide services
- Clients request resources or computations
- Simple but may cause server bottlenecks
2. Peer-to-Peer Architecture
- All nodes act as both clients and servers
- No central authority
- High scalability and fault tolerance
3. Hybrid Architecture
Components of Distributed Operating System
A distributed OS consists of several core components:
1. Process Management
Manages process creation, scheduling, execution, and migration efficiently across multiple interconnected nodes within the system.
2. Memory Management
Handles distributed shared memory and ensures data consistency, synchronization, and coherence across all nodes.
3. File Management
Provides a global file system enabling transparent, location-independent access to files across machines.
4. Communication System
Enables reliable message passing and data transfer using synchronized protocols across distributed nodes.
5. Security Management
Ensures authentication, authorization, data protection, and secure communication throughout the environment.
Types of Distributed Operating Systems
It can be categorized based on their structure and functionality:
| Type | Description |
| Network Operating System | Manages networked computers but lacks transparency |
| True Distributed OS | Offers a unified system image |
| Cluster OS | Designed for tightly coupled clusters |
| Middleware-based OS | Uses middleware to provide distributed services |
Key Features of Distributed Operating System
Here are the key features mentioned below:
1. Transparency
Users experience a single unified system that completely hides node locations, resource distribution, and underlying system complexity.
2. Concurrency
Multiple processes execute simultaneously across different machines, significantly improving efficiency, throughput, and overall system responsiveness.
3. Scalability
New nodes can be added seamlessly without disrupting existing operations or degrading overall system performance.
4. Fault Tolerance
Failure of a single node does not disrupt system operation, thereby ensuring continuous availability and reliability across distributed environments.
5. Load Balancing
Workloads are evenly distributed across nodes to prevent overload and optimize resource utilization.
Differences Between Distributed Operating System and Network Operating System
Below is a comparison highlighting how distributed operating systems and network operating systems differ across key aspects.
| Aspect | Distributed Operating System | Network Operating System |
| System View | Single system image | Multiple independent systems |
| Transparency | High | Low |
| Resource Sharing | Automatic | Manual |
| Scalability | High | Moderate |
| Examples | Amoeba, Plan 9 | Windows Server, UNIX |
Advantages of Distributed Operating System
Below are the key advantages of a distributed operating system:
1. Improved Performance
Parallel processing enables faster execution of large tasks by distributing workloads across multiple machines.
2. Resource Utilization
Idle computing resources across machines are efficiently utilized, maximizing overall system productivity and performance.
3. High Reliability
The system continues to operate even when individual nodes fail, ensuring uninterrupted service.
4. Cost Efficiency
Uses multiple low-cost machines rather than expensive supercomputers, thereby reducing overall infrastructure and maintenance costs.
Disadvantages of Distributed Operating System
Below are the key disadvantages of a distributed operating system:
1. Complexity
Designing, implementing, and managing requires advanced expertise and careful coordination.
2. Security Risks
Multiple interconnected nodes increase attack surfaces, making distributed systems more vulnerable to security breaches.
3. Network Dependency
Overall system performance depends heavily on network reliability, latency, bandwidth, and connection stability.
4. Synchronization Issues
Maintaining data consistency across nodes becomes difficult due to concurrency, delays, and communication failures.
5. Debugging Difficulty
Identifying, tracing, and resolving errors across distributed components is complex and time-consuming.
Real-World Examples
Here are some notable real-world examples:
1. Sprite OS
Designed for academic research, Sprite OS emphasizes efficient process migration and high-performance distributed file systems.
2. Google File System
Although not a traditional operating system, GFS implements core principles effectively.
3. Apache Hadoop
Uses distributed processing and storage concepts to handle large-scale data computation across clustered computing environments.
Final Thoughts
A distributed operating system plays a vital role in modern computing by enabling multiple machines to work together seamlessly. By providing transparency, scalability, and fault tolerance, it addresses the growing demand for high-performance and reliable computing systems. Despite challenges related to complexity and security, distributed operating systems remain a cornerstone of cloud computing, big data, and large-scale enterprise applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main purpose of a distributed operating system?
Answer: The main purpose is to manage multiple computers as a single unified system.
Q2. Is Linux a distributed operating system?
Answer: Linux itself is not a distributed OS, but can be used to build distributed systems.
Q3. How is fault tolerance achieved?
Answer: Through redundancy, replication, and failure detection mechanisms.
Q4. Where are distributed operating systems used?
Answer: They are used in cloud platforms, data centers, and high-performance computing systems.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Distributed Operating System” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
