What is Digital Identity?
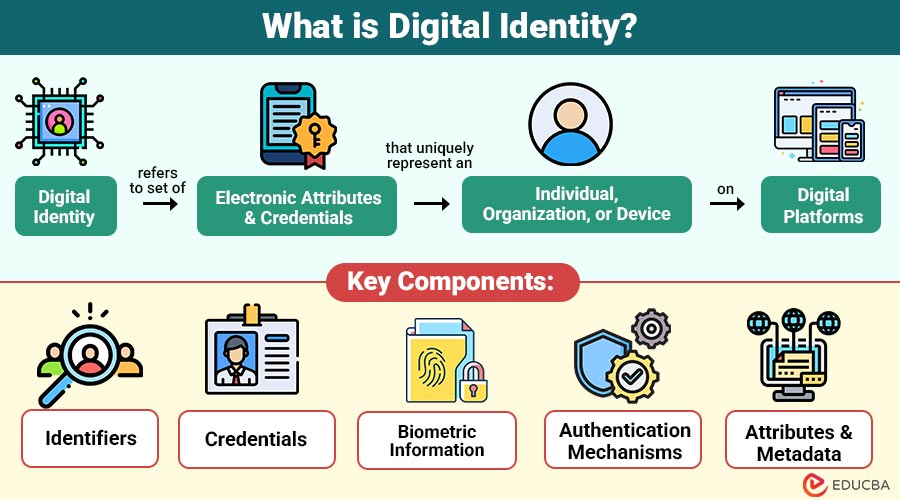
Digital identity refers to the set of electronic attributes and credentials that uniquely represent an individual, organization, or device on digital platforms.
It may include:
- Identifiers: such as usernames, email addresses, or digital IDs.
- Biometric data: like fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns.
- Behavioral attributes: such as browsing habits, device usage, or transaction patterns.
- Credentials: including passwords, digital certificates, or cryptographic keys.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Digital identity empowers secure, verified interactions, establishing digital trust across personal, enterprise, and governmental ecosystems.
- Effective identity frameworks enhance inclusion, granting equitable access to finance, healthcare, education, and essential services.
- Advanced technologies like blockchain and AI power modern digital identity systems that are decentralized, smart, and prepared for the future.
- Balancing security, privacy, and convenience is crucial for the sustainable adoption of global solutions.
Importance of Digital Identity
The adoption of robust solutions is no longer optional. Its importance extends across multiple dimensions:
1. Security
It confirms who you are, blocks unauthorized access, protects sensitive data, and builds trust in areas like finance, healthcare, and online services.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Robust frameworks support adherence to GDPR, eIDAS, Aadhaar, and other regulations, ensuring that organizations maintain transparency, accountability, and effective legal compliance.
3. Operational Efficiency
Automated identity checks speed up new user registration, reduce mistakes, make processes faster, and cut costs, helping organizations work more efficiently and go digital smoothly.
4. Financial and Social Inclusion
Digital identities give underserved communities fair access to banking, healthcare, education, and government services, supporting inclusion and growth.
5. Customer Experience
Key Components of Digital Identity
Here are the key components that collectively define and secure a user’s digital identity.
1. Identifiers
Identifiers are distinct digital markers, such as usernames, email addresses, or phone numbers, that uniquely identify one user, device, or entity online securely.
2. Credentials
Credentials consist of confidential information, such as passwords, PINs, or cryptographic certificates, serving as proof of identity during secure authentication across various digital platforms globally.
3. Biometric Information
Biometric information includes unique physiological or behavioral traits—such as fingerprints, facial scans, or iris patterns—ensuring highly secure, user-specific authentication in systems.
4. Authentication Mechanisms
Authentication mechanisms involve advanced processes, such as multi-factor authentication, single sign-on, and passwordless login, ensuring that validated user access to protected digital resources is effectively and securely maintained.
5. Attributes and Metadata
Types of Digital Identity
Digital identities come in different forms depending on their use cases and verification methods:
1. Centralized Identity
Centralized identity is managed by a single authority, such as governments, banks, or corporations, offering control but increasing dependency risks.
2. Federated Identity
Federated identity enables users to access multiple platforms with one credential set, streamlining authentication while improving convenience and reducing friction.
3. Decentralized Identity
Decentralized identity uses blockchain to give people full control over their data, reduce middlemen, protect privacy, and increase user freedom worldwide.
4. Device Identity
Device identity gives each smartphone, IoT device, or smart card a unique ID, allowing secure communication between devices in connected digital systems.
5. Biometric Identity
Biometric identity relies on physical or behavioral traits, including fingerprints, iris scans, and facial recognition, ensuring highly secure, personalized authentication processes.
Benefits of Digital Identity
Here are the key benefits that brings to individuals, businesses, and societies globally.
1. Trust and Transparency
It builds trust by verifying interactions between users, businesses, and governments, increasing transparency and reducing online fraud.
2. Seamless User Experience
A strong digital identity makes logging in easier, avoids repeated password entry, and allows password-free access, making online use more convenient and efficient.
3. Cost Savings
Automated identity verification significantly reduces manual processes, minimizes administrative overhead, and lowers costs for businesses, governments, and institutions managing digital ecosystems.
4. Scalability
5. Inclusion and Accessibility
Challenges of Digital Identity
Despite its benefits, digital identity comes with several challenges:
1. Privacy Concerns
Storing sensitive information raises privacy risks, including unauthorized surveillance, misuse of personal data, and potential loss of individual control.
2. Cybersecurity Threats
Cybercriminals are increasingly attacking identity systems using phishing, stolen credentials, and hacking, putting personal data and global digital trust at risk.
3. Interoperability Issues
Without standard rules across platforms and countries, digital identities can’t work smoothly worldwide, limiting global collaboration.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Complying with stringent laws like GDPR and CCPA requires continuous governance, monitoring, and accountability, making digital identity management increasingly complex.
5. Trust Deficit
Users often hesitate to share personal data due to concerns about transparency, fears of data misuse, and skepticism regarding centralized authority control mechanisms.
Real-World Applications
Here are the real-world applications where digital identity is transforming operations, enhancing security, and enabling seamless digital interactions.
1. Banking and Finance
Enables secure mobile banking logins, KYC compliance, fraud prevention, and seamless financial transactions, enhancing security and trust significantly.
2. E-commerce
In e-commerce, digital identity helps verify customers, secure payments, reduce fraud, and offer personalized shopping, making online shopping safer and easier.
3. Government Services
Governments use digital identity for tax filing, subsidy distribution, e-voting, and public service access, ensuring transparency, efficiency, and equitable citizen participation.
4. Healthcare
Digital identity verifies patients, protects medical records, enables telemedicine, and ensures privacy compliance, improving healthcare delivery worldwide.
5. Education
6. Workplace and Enterprises
Organizations use digital identity for employee authentication, secure remote access, collaboration tools, and compliance, protecting sensitive enterprise systems and critical information.
Future Trends
Here are the emerging innovations and advancements shaping the next generation of secure and user-centric digital identity systems.
1. Blockchain-Based Identities
Blockchain-based digital IDs let people control their own data, cut out middlemen, and make online interactions safe and secure worldwide.
2. Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication means logging in without using a password. Instead, it uses things like your fingerprint, face, a security key, or your usual behavior on a device. This makes logging in safer, easier, and faster for users.
3. AI-Powered Identity Verification
4. Interoperable Global Standards
Global standards that work together will allow digital identities to be used across countries, making transactions easier, ensuring compliance, and verifying users consistently worldwide.
5. Integration with IoT
Final Thoughts
Digital identity has evolved from being a basic login credential to becoming the core of digital trust, security, and personalization. Digital identities let people and organizations use online services safely and easily, whether in banking, healthcare, shopping, or government. In the future, identity systems will use AI, work across different platforms, and give users more control, making them secure, convenient, and private. Using these new systems is important for a safe and trustworthy digital world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is digital identity different from physical identity?
Answer: Physical identity involves tangible documents (passport, ID card), while digital identity consists of electronic credentials and data stored online.
Q2. Is digital identity safe?
Answer: Digital identity remains secure through encryption, multi-factor authentication, and adherence to privacy regulations, though hacking risks persist.
Q3. Can digital identity be used globally?
Answer: Yes, but interoperability and regulatory differences remain challenges. Emerging standards and blockchain-based identities aim to make global use seamless.
Q4. What role does blockchain play in digital identity?
Answer: Blockchain supports decentralized, tamper-proof, and user-controlled identity systems, reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Digital Identity” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
