What is Digital Banking?
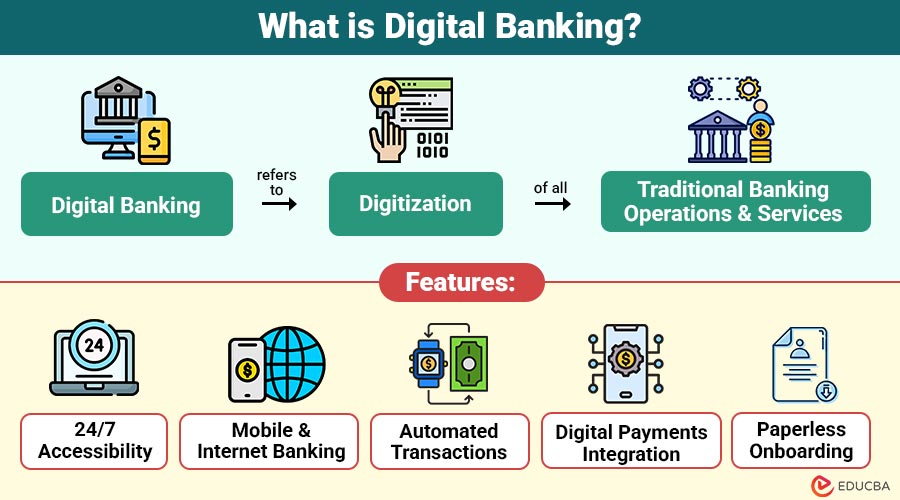
Digital Banking refers to digitization of all traditional banking operations and services. It allows customers to access banking products, perform transactions, and manage accounts through digital platforms — such as websites, mobile apps, and online portals — without visiting a physical branch.
For instance, using HDFC Bank’s mobile app or Chase Bank’s online portal, customers can open savings accounts, transfer funds, pay bills, check balances, and even apply for loans entirely online — all without having to visit a physical branch.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Features
- Components
- Benefits
- Digital Banking vs Traditional Banking
- Challenges
- Use Cases
- Real-World Examples
Key Takeaways:
- Digital banking enables customers to access, manage, and transact financial services at any time through online platforms.
- Automation, AI insights, and digital payments enhance efficiency, personalization, and convenience for both banks and users.
- Regulatory compliance and adapting to evolving digital finance standards remain essential for secure banking operations.
- Emerging technologies, such as biometrics and blockchain, continue to shape a faster, safer, and globally connected banking future.
Features of Digital Banking
Here are the main features that make digital banking convenient, efficient, and user-friendly:
1. 24/7 Accessibility
Enables the customers to access their accounts and perform transactions at any time and from anywhere, eliminating the restrictions imposed by traditional branch operating hours.
2. Mobile and Internet Banking
Banks offer secure, user-friendly mobile apps and web platforms that enable customers to transfer funds, invest, and manage their financial services remotely with ease and convenience.
3. Automated Transactions
Automates recurring activities such as bill payments, fund transfers, and loan repayments, ensuring timely execution and reducing manual intervention for customers significantly.
4. Digital Payments Integration
Through platforms like UPI, QR codes, and digital wallets, users can make instant, secure payments directly from linked bank accounts without additional steps.
5. Paperless Onboarding
Account setup, document submission, and Know Your Customer (KYC) verification are completed digitally using e-signatures, biometric checks, and online verification tools efficiently.
Components of Digital Banking
To understand digital banking comprehensively, it is essential to explore its core components:
1. Digital Platforms
Mobile apps, online portals, and AI-powered chatbots enable customers to conduct banking transactions conveniently without needing to visit a branch location.
2. Core Banking System
CBS connects all bank branches and digital channels, ensuring seamless real-time transaction processing, data synchronization, and efficient customer account management.
3. Customer Relationship Management
CRM tools analyze customer behavior and data to deliver personalized banking solutions, enhance engagement, and improve overall customer satisfaction effectively.
4. Digital Payment Infrastructure
Digital payment systems, such as NEFT, RTGS, UPI, and mobile wallets, facilitate fast, secure, and convenient electronic fund transfers both globally and locally.
5. Cybersecurity Framework
Banks deploy advanced encryption, firewalls, fraud detection, and multi-factor authentication measures to safeguard sensitive financial and personal customer information.
6. Regulatory Compliance Tools
Automated compliance tools ensure adherence to national and international regulations, such as AML, KYC, and data protection standards, efficiently.
Benefits of Digital Banking
It offers numerous benefits to both banks and customers, enhancing efficiency, accessibility, and transparency.
For Customers:
- Convenience: Banking anytime, anywhere via smartphones or computers.
- Speed: Instant fund transfers, digital loan approvals, and real-time payments.
- Transparency: Access to transaction history and account details in real-time.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower transaction costs compared to physical banking.
- Personalization: AI-driven financial planning and investment advice.
For Banks:
- Operational Efficiency: Reduced paperwork and manpower through automation.
- Wider Reach: Ability to serve remote and rural customers through digital platforms.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Insights from analytics improve product offerings.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: Chatbots and self-service options improve satisfaction.
- Lower Overheads: Reduced infrastructure and branch maintenance costs.
Digital Banking vs. Traditional Banking
Here is a comparison of key aspects between digital and traditional banking:
| Aspect | Digital Banking | Traditional Banking |
| Access | Online via web or app | In-person at branches |
| Availability | 24/7 availability | Limited to working hours |
| Transaction Speed | Instant, automated | Manual processing |
| Paperwork | Paperless and electronic | Physical forms required |
| Customer Service | AI chatbots and online support | Face-to-face interaction |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower transaction costs | Higher operational costs |
| Security | Advanced encryption and biometrics | Physical verification |
Challenges of Digital Banking
Despite its benefits, it faces certain challenges that institutions must address:
1. Cybersecurity Risks
With the rise of online transactions, banks are facing increased threats from cyberattacks, phishing scams, malware, and sensitive data breaches worldwide.
2. Digital Literacy Gap
Many customers, particularly in rural or less tech-savvy areas, struggle to understand and use digital banking platforms effectively.
3. Technical Glitches
Frequent app crashes, slow servers, or unexpected downtime can disrupt essential banking operations and negatively impact customer experience.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Banks must continuously adapt to complex, evolving digital finance regulations and ensure full compliance with global and national standards.
5. Privacy Concerns
One of the ongoing challenges for digital financial institutions is safeguarding sensitive customer data from misuse and illegal access.
Use Cases of Digital Banking
Here are some practical use cases that showcase the versatility:
1. Mobile Wallets and UPI Payments
Apps like Google Pay, Paytm, and Apple Pay enable fast, secure, and seamless digital money transfers anytime, anywhere.
2. Robo-Advisors
Platforms such as Betterment and Wealthfront provide automated, algorithm-driven investment advice, optimizing portfolios based on user preferences and risk tolerance.
3. Neobanks
Fully digital banks, such as Revolut, Chime, and Monzo, offer comprehensive banking services without physical branches, ensuring convenience and lower operational costs.
4. Digital Lending
AI-driven platforms offer instant loan approvals through automated algorithms, online verification, and digital document submission, enabling faster disbursement.
5. Blockchain Banking
Blockchain technology ensures secure, transparent, and tamper-proof financial transactions, enhancing trust and efficiency in modern systems.
6. Biometric Security
Fingerprint, facial, and voice recognition technologies enhance authentication accuracy, reducing fraud and strengthening overall digital banking security.
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world examples of digital banking platforms showcasing modern financial services:
1. Revolut (UK)
Revolut offers international money transfers, cryptocurrency trading, budgeting tools, and multi-currency accounts through an easy-to-use mobile banking app.
2. Chime (USA)
Chime is a neobank providing early direct deposits, fee-free banking, automatic savings features, and financial management tools for users conveniently.
3. DBS Bank (Singapore)
DBS leverages Artificial Intelligence and automation to deliver personalized, seamless, and efficient experiences across multiple financial services.
4. Kotak 811 (India)
Kotak 811 offers a fully digital, paperless savings account with online KYC verification, instant account activation, and easy mobile banking access.
Final Thoughts
Digital banking is no longer a futuristic concept—it is the present reality of the financial world. With its ability to combine technology, convenience, and innovation, it has revolutionized how individuals and organizations manage their finances. Even if issues like cybersecurity and digital literacy still exist, developments in open banking, blockchain, and artificial intelligence will continue to improve and broaden the reach. As banks embrace transformation, the future of finance will undoubtedly be digital, inclusive, and globally connected.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is digital banking secure?
Answer: Yes. Digital banks implement robust security measures, including encryption, biometric verification, and multi-factor authentication, to safeguard transactions and data.
Q2. Can I open an account without visiting a branch?
Answer: Absolutely. Most banks now offer paperless digital account opening through online verification and e-signature.
Q3. How does AI improve digital banking?
Answer: AI enables personalized customer support, automated fraud detection, and intelligent financial recommendations.
Q4. What is the future of digital banking?
Answer: The future lies in fully integrated financial ecosystems powered by AI, blockchain, and open banking, delivering a seamless, secure, and personalized banking experience.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Digital Banking” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
