Introduction to Design Modeling in Software Engineering
Design modeling in software engineering represents the features of the software that helps engineer to develop it effectively, the architecture, the user interface, and the component level detail. Design modeling provides a variety of different views of the system like architecture plan for home or building. Different methods like data-driven, pattern-driven, or object-oriented methods are used for constructing the design model. All these methods use set of design principles for designing a model.
Working of Design Modeling in Software Engineering
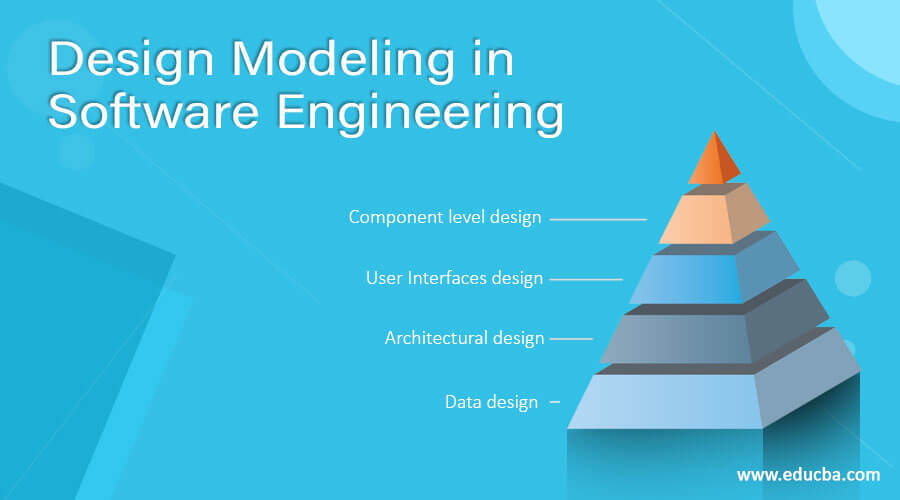
Designing a model is an important phase and is a multi-process that represent the data structure, program structure, interface characteristic, and procedural details. It is mainly classified into four categories – Data design, architectural design, interface design, and component-level design.
- Data design: It represents the data objects and their interrelationship in an entity-relationship diagram. Entity-relationship consists of information required for each entity or data objects as well as it shows the relationship between these objects. It shows the structure of the data in terms of the tables. It shows three type of relationship – One to one, one to many, and many to many. In one to one relation, one entity is connected to another entity. In one many relation, one Entity is connected to more than one entity. un many to many relations one entity is connected to more than one entity as well as other entity also connected with first entity using more than one entity.
- Architectural design: It defines the relationship between major structural elements of the software. It is about decomposing the system into interacting components. It is expressed as a block diagram defining an overview of the system structure – features of the components and how these components communicate with each other to share data. It defines the structure and properties of the component that are involved in the system and also the inter-relationship among these components.
- User Interfaces design: It represents how the Software communicates with the user i.e. the behavior of the system. It refers to the product where user interact with controls or displays of the product. For example, Military, vehicles, aircraft, audio equipment, computer peripherals are the areas where user interface design is implemented. UI design becomes efficient only after performing usability testing. This is done to test what works and what does not work as expected. Only after making the repair, the product is said to have an optimized interface.
- Component level design: It transforms the structural elements of the software architecture into a procedural description of software components. It is a perfect way to share a large amount of data. Components need not be concerned with how data is managed at a centralized level i.e. components need not worry about issues like backup and security of the data.
Principles of Design Model
- Design must be traceable to the analysis model:
Analysis model represents the information, functions, and behavior of the system. Design model translates all these things into architecture – a set of subsystems that implement major functions and a set of component kevel design that are the realization of Analysis classes. This implies that design model must be traceable to the analysis model.
- Always consider architecture of the system to be built:
Software architecture is the skeleton of the system to be built. It affects interfaces, data structures, behavior, program control flow, the manner in which testing is conducted, maintainability of the resultant system, and much more.
- Focus on the design of the data:
Data design encompasses the manner in which the data objects are realized within the design. It helps to simplify the program flow, makes the design and implementation of the software components easier, and makes overall processing more efficient.
- User interfaces should consider the user first:
The user interface is the main thing of any software. No matter how good its internal functions are or how well designed its architecture is but if the user interface is poor and end-users don’t feel ease to handle the software then it leads to the opinion that the software is bad.
- Components should be loosely coupled:
Coupling of different components into one is done in many ways like via a component interface, by messaging, or through global data. As the level of coupling increases, error propagation also increases, and overall maintainability of the software decreases. Therefore, component coupling should be kept as low as possible.
- Interfaces both user and internal must be designed:
The data flow between components decides the processing efficiency, error flow, and design simplicity. A well-designed interface makes integration easier and tester can validate the component functions more easily.
- Component level design should exhibit Functional independence:
It means that functions delivered by component should be cohesive i.e. it should focus on one and only one function or sub-function.
Conclusion
Here in this article, we have discussed the basics of design modeling in software engineering along with its principles. We have also discussed its working and some other areas.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Design Modeling in Software Engineering. Here we discuss the Introduction, Principles of Design Model. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –