Updated July 19, 2023

Definition of Deferred Income Tax
Deferred Income Tax is the taxes applicable on the taxable income of the entity which is payable in the future years as they are not due for payment in the current financial year, which arises because of the difference in the tax amount reported in the accounting framework opted by the company and the tax amount reported in the taxation regime of the local tax authorities.
Explanation
Due to variations in regulations and rules between the tax regime and accounting framework, there may be differences in the taxable proportion reported and the tax liability recorded in a company’s financial statements. Still, tax is due after that reporting period as per the regulations of the tax authorities. The same will be payable in other financial periods or reporting periods.
Example of Deferred Income Tax
Let’s take an example for more clarity.
Suppose a company has a fixed asset costing $ 50000.00. International accounting standards compel the corporation to charge depreciation at a rate of 10% per year using the straight-line technique, resulting in a $5,000 yearly depreciation expense. This figure will appear in the company’s financial statements. This creates a temporary difference between the accounting and taxable profits, leading to the recognition of a deferred tax asset. However, the taxation of $ 2500.00 will need to be paid in the future; as a result, liability for it should be included in the company’s financial accounts.
Deferred Income Tax on the balance sheet
As explained above, the deferred income tax must be presented in the entity’s financial statements. It should be noted that the main reason for the creation of deferred tax assets or liability is due to the difference arising due to a temporary timing difference, as the same would be reversed in the future. In case the scenario occurs where due to a quick time difference, the assessee has to pay low taxes at the current time but may have to pay high taxes later in the future, deferred tax liability should be created in the year by appropriating the profit & loss of that year of the company.
The deferred tax liability will be shown on the balance sheet in the Non-current liabilities schedule. However, if the scenario reveals that the current taxable profit is greater than the book profit, a deferred tax asset should be formed and recorded in the balance sheet’s non-current asset schedule.
Deferred Income Tax Journal Entry
In case of deferred tax cases, the following journal entries are typically booked:
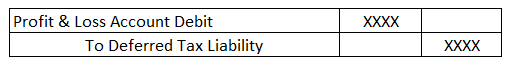
- In Case of Deferred Tax Liability
When the book profit exceeds the taxable profit, a deferred tax liability must be recorded in the company’s books.
- In Case of Deferred Tax Assets
Deferred tax assets must be formed in the company’s financials when book profit is smaller than taxable profit.

Deferred Income Tax vs Deferred Tax Liability
Following are the key differences between the deferred tax assets & deferred tax liabilities:
- When an assessee’s book profit exceeds the taxable profit under income tax regulations, a deferred tax liability is created. This signifies that the assessee’s tax burden for the current year is less than the assessee’s financials, resulting in more taxes to be paid later.
- Deferred tax assets are formed when an assessee’s book profit is less than the taxable profit under income tax laws. This indicates that the current year’s tax liability is higher than the financials of the assessee, allowing for potential tax benefits or reductions in future tax payments.
- In contrast, deferred tax assets indicate that the current year’s tax liability is less than the financials of the assesse, which means the assessee has to pay more in the current year and less in the later years.
Benefits
The following are the benefits of deferred income tax:
- It provides an accurate & fair view of the financials by accommodating certain future liabilities or benefits that will arise for the company.
- The deferred income tax procedures help validate the tax liability of the company’s financials per the company’s acts and accounting frameworks, with the tax liability arising per the income tax rules.
Disadvantages
The following are the disadvantages of deferred income tax:
- The deferred tax rules can be complex and difficult for common people, who are users of financial statements, to understand. They may struggle to comprehend the purpose and rationale behind these rules.
- In the case of deferred tax assets, the company may have to bear a substantial increase in actual tax liabilities, which may have a considerable effect on the financial output of the company for the fiscal year.
Conclusion
It provides the methods for the assesse to deal with the differences arising in the tax liability of the assesse as per the accounting frameworks and the local income tax rules due to the temporary time differences. However, permanent time differences do not result in deferred income tax.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Deferred Income Tax” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


