Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to Decision Tree in Machine Learning
Decision Tree in machine learning is a part of classification algorithm which also provides solutions to the regression problems using the classification rule(starting from the root to the leaf node); its structure is like the flowchart where each of the internal nodes represents the test on a feature (e.g., whether the random number is greater than a number or not), each leaf node is used to represent the class label( results that need to be computed after taking all the decisions) and the branches represents conjunction conjunctions of features that lead to the class labels.
Decision Tree in Machine Learning has got a wide field in the modern world. There are a lot of algorithms in ML which is utilized in our day-to-day life. One of the important algorithms is the Decision Tree used for classification and a solution for regression problems. As it is a predictive model, Decision Tree Analysis is done via an algorithmic approach where a data set is split into subsets as per conditions. The name itself says it is a tree-like model in the form of if-then-else statements. The deeper is the tree and more are the nodes, the better is the model.
Types of Decision Tree in Machine Learning
Decision Tree is a tree-like graph where sorting starts from the root node to the leaf node until the target is achieved. It is the most popular one for decision and classification based on supervised algorithms. It is constructed by recursive partitioning where each node acts as a test case for some attributes and each edge, deriving from the node, is a possible answer in the test case. Both the root and leaf nodes are two entities of the algorithm.
Let’s understand with the help of a small example as follows:
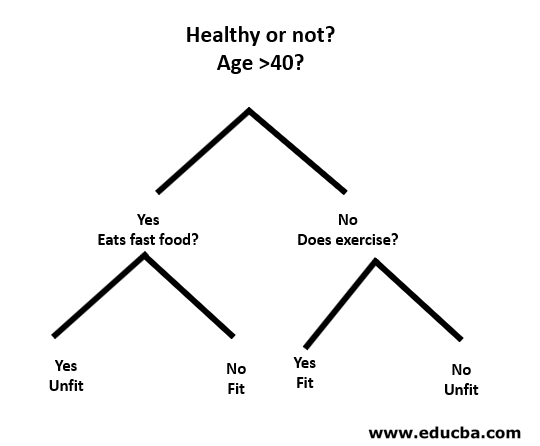
Here, the root node is whether you are less than 40 or not. If so, then do you eat fast food? If yes, then you are unfit, or else, you are fit. And if you are more than 40, then do you do exercise? If so, then you are fit, or else, you are unfit. This was basically a binary classification.
There are two types of Decision Trees:
- Classification Trees: The above example is a categorial based Classification Tree.
- Regression Trees: In this type of algorithm, the decision or result is continuous. It has got a single numerical output with more inputs or predictors.
In the Decision tree, the typical challenge is to identify the attribute at each node. The process is called attribute selection and has some measures to use in order to identify the attribute.
a. Information Gain (IG)
Information Gain measures how much information an individual feature gives about the class. It acts as the main key to construct a Decision Tree. An attribute with the highest Information Gain splits first. So, the Decision Tree always maximizes the Information Gain. When we use a node to partition the instances into smaller subsets, then the entropy changes.
Entropy: It is the measure of uncertainty or impurity in a random variable. Entropy decides how a Decision Tree splits the data into subsets.
The equation for Information Gain and entropy are as follows:
Information Gain= entropy(parent)- [weighted average*entropy(children)]
Entropy: ∑p(X)log p(X)
P(X) here is the fraction of examples in a given class.
b. Gini Index
Gini Index is a metric that decides how often a randomly chosen element would be incorrectly identified. It clearly states that attribute with a low Gini Index is given first preference.
Gini Index: 1-∑ p(X)^2
Split creation
- To create a split, first, we need to calculate the Gini score.
- The data is split using a list of rows having an index of an attribute and a split value of that attribute. After the right and left dataset is found, we can get the split value by the Gini score from the first part. Now, the split value will be the decider where the attribute will reside.
- The next part is evaluating all the splits. The best possible value is calculated by evaluating the cost of the split. The best split is used as a node of the Decision Tree.
Building a Tree – Decision Tree in Machine Learning
There are two steps to building a Decision Tree.
1. Terminal node creation
While creating the terminal node, the most important thing is to note whether we need to stop growing trees or proceed further. The following ways can be used for this:
- Maximum tree depth: When the tree reaches the maximum number of nodes, execution stops there.
- Minimum node records: It can be defined as a minimum of patterns that a node requires. Then we can stop adding terminal nodes immediately we get those minimum node records.
2. Recursive splitting
Once, the node is created, we can create a child node recursively by splitting the data set and calling the same function multiple times.
Prediction
After a tree is built, the prediction is done using a recursive function. The same prediction process is followed again with left or right child nodes and so on.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Decision Tree
Below are given some advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
The decision tree has some advantages in Machine Learning as follows:
- Comprehensive: It takes consideration of each possible outcome of a decision and traces each node to the conclusion accordingly.
- Specific: Decision Trees assign a specific value to each problem, decision, and outcome(s). It reduces uncertainty and ambiguity and also increases clarity.
- Simplicity: Decision Tree is one of the easier and reliable algorithms as it has no complex formulae or data structures. Only simple statistics and maths are required for calculation.
- Versatile: Decision Trees can be manually constructed using maths and as well be used with other computer programs.
Disadvantages
The decision tree has some disadvantages in Machine Learning as follows:
- Decision trees are less appropriate for estimation and financial tasks where we need an appropriate value(s).
- It is an error-prone classification algorithm as compared to other computational algorithms.
- It is computationally expensive. At each node, the candidate split must be sorted before ascertaining the best. There are other alternatives which many business entities follow for financial tasks as Decision Tree is too expensive for evaluation.
- While working with continuous variables, Decision Tree is not fit as the best solution as it tends to lose information while categorizing variables.
- It is sometimes unstable as small variations in the data set might lead to the formation of a new tree.
Conclusion – Decision Tree in Machine Learning
As one of the most important and supervised algorithms, Decision Tree plays a vital role in decision analysis in real life. As a predictive model, it is used in many areas for its split approach which helps in identifying solutions based on different conditions by either classification or regression method.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Decision Tree in Machine Learning. Here we discuss the introduction, Types of Decision Tree in Machine Learning, Split creation and Building a Tree. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–

