Updated May 20, 2023

Introduction to DBMS Keys
The DBMS keys or the Database Management System Keys represent one or more attributes (depending on the types of the DBMS Keys used) from any table in the Database system that brings about distinctively categorized rows and a combination of more than one column to identify the relationship between the tuple (row) in the table, or to determine the relationship between the two tables, which applies to the tables that are identified and queried for analysis or reporting purposes.
Different Types of Keys in DBMS
There are many keys in DBMS. Let us take a look at the important keys and their functionality.
- Super Key
- Candidate Key
- Primary Key
- Alternate Key
- Foreign Key
- Compound Key
- Surrogate Key
1. Super Key
A super key is either a single key or a set of keys that help identify distinct rows in a particular table. A Super key can have extra attributes that are redundant for distinct identification.
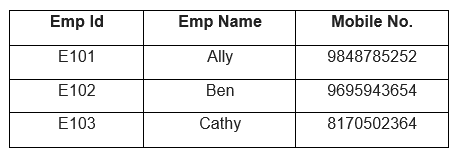
Let us look at an example where the EmpId and the Mobile number can be considered Super Keys.
2. Candidate Key
We refer to a Super Key as a Candidate Key if it has no duplicate attributes. We carefully choose the Primary Key after considering the given Candidate keys. All tables are required to have one candidate key at least. There are a few rules that we need to follow regarding the selection of a Candidate Key.
They are:
- A Candidate Key should comprise distinctive values.
- A Candidate Key can have various attributes.
- A Candidate Key cannot comprise null values.
- A Candidate Key must uniquely identify each row in the table.
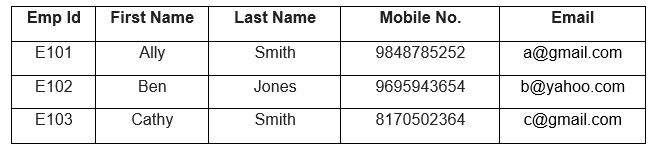
Let us look at an example of a table where the Emp Id, Mobile No, and Email are the Candidate keys. These keys help us distinctly identify any Employee row in the table.
3. Primary Key
A primary Key is a column or a combination of columns in a relationship that helps us uniquely identify a row in that table. There can be no duplicates in a Primary Key, meaning that there can be no two same values in the table. We have a few rules for choosing a key as the Primary Key. They are:
- The Primary Key field cannot be left NULL; the Primary Key column must hold a value.
- Any two rows in the table cannot have identical values for that column.
- If a foreign key refers to the primary key, then no value in this primary key column can be altered or modified.
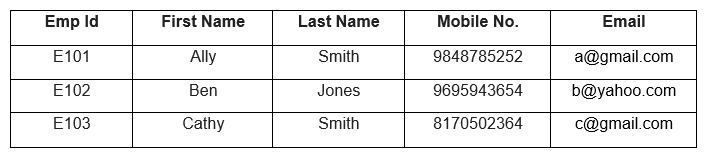
Let us look at an example of a table where the Emp Id is the Primary Key.
4. Alternate Key
You may have multiple options for selecting a key as the Primary Key in a table. Any key capable of being the Primary Key but at the moment is not the Primary Key is known as an Alternate Key. A candidate key that has not been selected as the Primary Key.
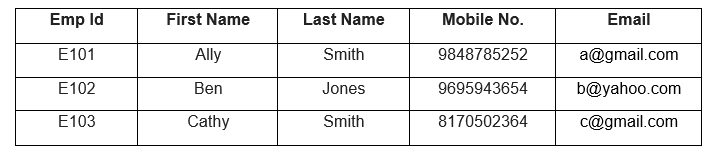
Let us look at an example where the EmpId, Email, and Mobile No. are candidate keys and are capable of being the Primary key. But because Emp Id is the Primary Key, Email and Mobile No. Become the Alternate Key.
5. Foreign Key
Foreign Keys help us establish relationships with other tables. It is also called Referential Integrity. To establish this relationship, you can add a Foreign Key column to a table. They help us maintain data integrity and allow easy navigation between any instances of two entities.
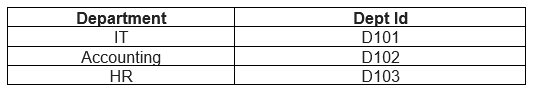
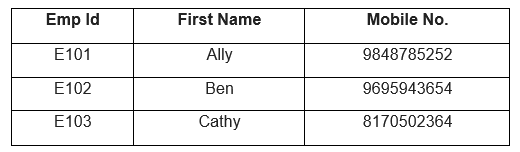
Let us look at an example comprising two tables, Employee and Department tables.
Table: Department
Table: Employee
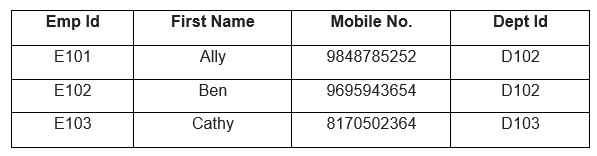
Currently, we do not have any idea about the departments in which the employees are working. By adding the DeptId to the Employee table, we can establish a relationship between the Employee table and the Department table. Here, the DeptId of the Employee table becomes the Foreign Key, and the DeptId of the Department Table becomes the Primary Key for that table.
Table: Employee with DeptId as Foreign Key
6. Compound Key
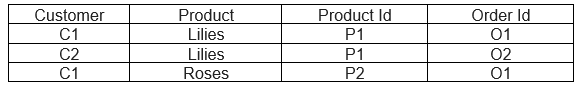
A Compound Key is a primary key that does not consist of a single column but two or more columns that allow us to identify a particular row distinctly. For a compound key, we do not have any unique column; therefore, we need to combine two or more columns to make them unique.
Let us look at an example of a table consisting of product and product details. This table shows that more than one customer can order a product and more than one can be present. Therefore we need to combine the OrderId and the ProductId to create a unique way of identifying the row.
7. Surrogate Key
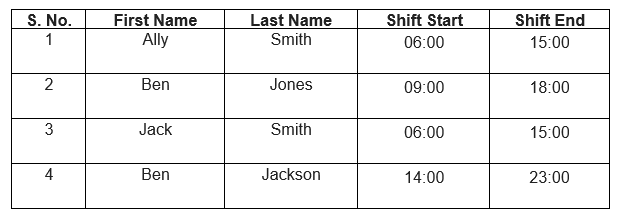
A situation may arise where a particular table does not have a Primary Key. In this case, we use a Surrogate Key, an artificial key that can distinctly identify every row in the table. We use Surrogate Keys specifically when there is no natural primary key. They do not provide any relation to the table data and are usually serially ordered integers.
In this example, we have the data of Employees and their Shift timings. Therefore, we use a Surrogate Key to identify each row uniquely.
In this article, we have explored a few of the most important DBMS Keys, their differences, and when to use them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DBMS Keys. Here we discussed the basic concept and different types of keys in DBMS. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –