Updated March 13, 2023

Introduction to DB2 warehouse
Basically, DB2 provides the warehouse over the cloud; in the DB2 warehouse, we analyze the data and provide the high-level control option on our data and application. DB2 warehouse is very simple to deploy and manage; in DB2 warehouse, we can perform the different operations with different properties of the warehouse such as scalability and performance. In the DB2 warehouse, we can work on large databases as well as complex databases. As per the requirement, we can scale the warehouse and perform the desired operation that users want. The main thing about the DB2 warehouse is that it is suitable for larger data sets, and it also has an integrated development environment for the user.
How DB2 warehouse works?
Now let’s see how the warehouse works in DB2 as follows.
Db2 Warehouse may be reasonable if we choose any of the accompanying models to concern you:
- Our data or information should remain on-premises in view of security prerequisites.
- We need the adaptability of the cloud without surrendering command over your information.
- We have responsibilities to move between a public cloud or machine and a private cloud.
- We are thinking about crossover engineering to modernize your information distribution center.
- We need to utilize a private cloud as an initial step to a public cloud organization.
We can deploy Warehouse in a wide scope of conditions as well as the environment, from a fundamental PC for improvement purposes, right to an enormous creation group. You can pick either a solitary hub (SMP) arrangement or a multi-node (MPP) organization. (It supports different operating systems such as Windows and Mac). An MPP organization has at least three hubs and a limit of one or the other 24 or 60 hubs. The greatest relies upon the number of information segments that were dispensed when you sent. For more data about the most extreme number of hubs, see the “Equipment essentials” part of IBM Warehouse requirements.
Normally DB2 warehouse architecture consists of the different components as follows.
1. LDAP Authentication
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, or LDAP, is one of the center confirmation conventions that were created for registry administrations. LDAP generally has been utilized as a data set of data, fundamentally putting away data such as User, remote user, group of privileges, and many more.
This data was then used to empower verification to IT assets like an application or worker. They would be highlighted the LDAP data set, which would then approve if that client would approach it. That approval would be finished passing a client’s qualifications. Therefore, a typical inquiry is: what is LDAP confirmation? Keep pursuing the response to this inquiry, and figure out how the Jump Cloud Directory Platform can convey LDAP verification as a cloud-based help.
2. Federation
DB2 also supports virtualization; Warehouse upholds db2 information virtualization (we also called league) on Cloud. Information virtualization gives you single-inquiry admittance to the entirety of your information that is on various conveyed data sets anyplace in your association. So, for example, you can get information that is on any of your Db2 or Informix information sources.
3. Apache Spark
This is one of the components of the warehouse; by using Apache Spark, we can process the big data. Apache Spark has built-in different modules, and those modules are helpful to Unified Analytics Engine to handle the big data.
4. Data Server Manager
We can use data server managers for different purposes such as database administration, query optimization, performance optimization, configuration management, autonomic management, storage optimization, etc.
5. DB2 warehouse console
DB2 warehouse provides different functionality such as it includes the integrated RStudio for development purpose, by using RStudio we can directly access the database and load data directly and perform the different operation within minutes.
6. Docker Engine
Docker engine is an open-source technology that acts as the client-server application that means it provides different functions such as a command-line interface, long-running daemon process, and different API.
7. Docker-supported Operating System
Docker supports the different types of operating systems such as Linux, Windows, and macOS, which means we have different platforms for DB2 storage.
8. Server Hardware
In the DB2 warehouse, we required some server hardware prerequisites to handle the client request, to deploy multi-node, single-node deployment, etc.
9. Clustered File system
The clustered file system provides different features such as location, data redundancy, and it improves the reliability of the cluster.
Examples of DB2 warehouse
Now let’s see a different example of DB2 warehouse as follows:
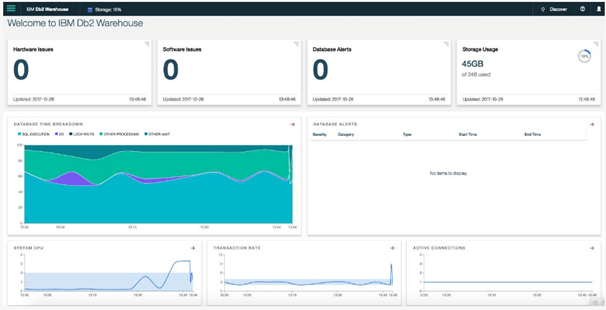
The above screenshot shows the main dashboard of the warehouse; it shows the performance of the database as well as the overall performance of the system, as shown in the above screenshot.
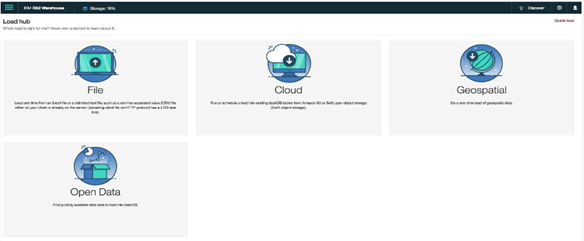
The below screenshot shows the load hub with different options such as a file, cloud, geospatial and open data. We can perform different operations by using this option, such we load a different file by using the file option.
We can also execute the SQL query, which means the warehouse provides the SQL workbench to the user, as shown in the below screenshot.

So in this way, we can perform the different operations by using the warehouse as per the user requirement.
Advantages and disadvantages
Now let’s see the Advantages of the DB2 warehouse as follows:
- First, the performance of the warehouse is very high.
- As per the requirement, we can scale the size of the database.
- We can easily connect to the cloud by using some setup.
- It has Oracle
- It also provides the RStudio Integration.
- We can easily access the data any time, anywhere.
Now let’s see the Disadvantages of the DB2 warehouse as follows:
- First, documentation of DB2 warehouse is somewhat.
- It required skilled people to operate the warehouse.
- It is costly compared to other technology.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn about the warehouse. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of the DB2 warehouse, and we also see different examples of the warehouse. From this article, we learned how and when we use the warehouse.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the DB2 warehouse. Here we discuss the basic syntax of the DB2 warehouse, and we also see different examples of the warehouse. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

