Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to DB2 update
DB2 provides different types of functionality to users like MySQL; the update statement is one of the functionalities that is provided by the DB2. The update statement is used to modify the specified content of columns from the table. Basically, the update command uses the SET keyword to specify the column name for modification and assign a new specified value for that field that we want. When we use the default, so, at that time, we need to use the default keyword; the update command also uses where clause to specify conditions for the update, and we can also use order by clause to make them in order; the order by clause is optional.
Syntax
Update specific table name set colmn 1 field = new specified value, colmn 1 field = new specified value,……….. colmn N field = new specified value
where [Condition.......]
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use an update statement with different parameters as follows.
- First, we need to specify the table name that we need to update.
- After that, we need to specify the column name that we need to update as shown in the above syntax, column 1 field to up to N.
- In the third step, we need to specify the condition using the where clause; if this condition is true, we can successfully update the value; otherwise, it shows the error message.
How DB2 update statement works?
Now let’s see how the update statement works in DB2 as follows.
For the update statement, we need one of the permission for authorizations of ID as follows.
- We need to update privileges on specific tables and views.
- We also need to update privilege on specific columns.
- UPDATE privilege on schema for the specified table.
- As well as we also need control privilege on the specified table.
- We need database access permission for specific tables.
In the event that a row fullselect is remembered for the task, the privileges held by the approval ID of the statement should incorporate at any rate one of the accompanying experts for each referred to table and view.
- We need a SELECT advantage on the specified table.
- We need SELECTIN privilege on a schema that contains the specified table.
- We also need control privilege.
- We need database access privilege on the schema that contains the specified table.
- Finally, we also need the database authority.
For every specified table and view that is referred to by a subquery, the privilege held by the approval ID of the statement should likewise incorporate at any rate one of the accompanying specialists.
- We need a SELECT advantage on the specified table.
- We need SELECTIN privilege on a schema that contains the specified table.
- We also need control privilege.
- We need database access privilege on the schema that contains the specified table.
- Finally, we also need the database authority.
In the event that the package used to handle the statement and they looked through the type of an UPDATE articulation incorporates a reference to a column of the table and view, or moniker in the correct side of the task provision, or anyplace in the pursuit condition, the advantages held by the approval ID of the assertion should likewise incorporate at any rate one of the accompanying specialists:
- We need a SELECT advantage on the specified table.
- We need SELECTIN privilege on a schema that contains the specified table.
- We also need control privilege.
- We need database access privilege on the schema that contains the specified table.
- Finally, we also need the database authority.
Examples of DB2 update
Now let’s see a different example of an update statement in DB2 as follows.
First, create a new table as follows.
create table company (Comp_Id int not null, comp_name varchar(30) not null,
comp_address varchar(30) not null, primary key(Comp_Id));
Explanation
In the above example, we use a create table statement to create a new table name as a company with different attributes such as Comp_id, comp_name, and comp_address with different data types and different sizes as shown in the above statement. Note here comp_name, and comp_address have varchar data type with size 30 as shown.
For confirmation, insert some records by using the following insert into the statement as follows.
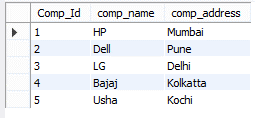
insert into company (Comp_Id, comp_name, comp_address) values(1, "HP", "Mumbai"), (2, "Dell", "Pune"), (3, "LG", "Delhi"), (4, "Bajaj", "Kolkatta"), (5, "Usha", "Kochi");
select * from company;
Explanation
In the above example, we use to insert into a statement to insert new records into the company table. Here we insert string values in the comp_name and comp_address column with minimum length. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now perform the update operation as follows.
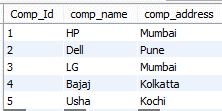
Now suppose we need to update the address of LG company at that time; we can use the following statement as follows.
update company set comp_address = ‘Mumbai’ where Comp_Id = 3 ;
Explanation
In the above statement, we use the update statement; here, we try to update the comp_address from the company table. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
So in this way, we can perform the update statement as per user requirements with different clauses.
Advantages and disadvantages
Now let’s see the advantages as follows:
- We can easily update the specified row as per our requirement.
- If any cluster key is updated to the same value, then the operation of the update statement will be logged.
- It is a high-speed operation; no extra coding is required to update the operation.
- We can update multiple columns by using a single update statement.
Now let’s see the disadvantages as follows:
- We need multiple access permission to perform the update statement.
- The update statement is not supported by, text driver.
- If we omit the where clause, then it will update all records from the specified table.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn the DB2 update statement. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of the DB2 update statement, and we also see different examples of the DB2 update statement. Furthermore, from this article, we learned how and when we use the DB2 update statement.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the DB2 update. Here we discuss the basic syntax of the DB2 update statement, and we also see different examples of the update statement. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –