Updated March 6, 2023

Introduction to DB2 Translate
DB2 translate function is used to replace a certain character string that is present in the original string with some other required character string in DB2 database. It is a scalar function in DB2 which has the capability to convert certain characters to some other characters. In this article, we will study the syntax of the translate scalar function in DB2 and will observe how it returns the string with replaced characters along with the help of certain examples involving string literals in DB2 database.
Syntax:
The syntax of the translate function is as shown below –
TRANSLATE (character/graphic string, expression for to-string, expression for from-string, padding character expression)
Let us see in detail what does each of the argument of TRANSLATE() function stands for.
- Character / graphic string – It can be any expression or literal constant value that evaluates to a value that is in CHAR, GRAPHIC, CHARCHAR or VARGRAPHIC, numeric or datetime in-built datatype of DB2. If the expression doesn’t evaluates to a character string datatype then it is implicitly internally converted into VARCHAR datatype value and is further considered for evaluation by function TRANSLATE. This expression is specified so that its value can be considered as the source string in which some of the characters to be replaced will be searched and further substituted accordingly.
- expression for to-string – This argument is used to specify the character string for the characters with which we want the source characters to replace with. It can be any expression or literal constant value that evaluates to a value that is in CHAR, GRAPHIC, CHARCHAR or VARGRAPHIC, numeric or datetime in-built datatype of DB2. If the expression doesn’t evaluates to a character string datatype then it is implicitly internally converted into VARCHAR datatype value and is further considered for evaluation by function TRANSLATE.
If we don’t specify the second argument of to-string and the source string is not a graphic string then all the characters of the source string gets converted into monocase which in case of small case alphabets gets converted to capital case and in other cases depending on whether the corresponding value for that character is present in code page 850, the characters convert into their uppercase equivalents.
- expression for from-string – This argument is used to specify the character string for the characters which we want the source string presence to replaced. It can be any expression or literal constant value that evaluates to a value that is in CHAR, GRAPHIC, CHARCHAR or VARGRAPHIC, numeric or datetime in-built datatype of DB2. If the expression doesn’t evaluates to a character string datatype then it is implicitly internally converted into VARCHAR datatype value and is further considered for evaluation by function TRANSLATE.
If we don’t specify the to-string expression then we should neither specify this third argument too. Note that is multiple characters specified in the from-string seems to be duplicated then only the first occurrence of that character is considered for corresponding replacement of the value. In case the number of characters mentioned in the to-string second argument are greater than that of a number of characters of from- string then the remaining characters are completely ignored.
- Padding character expression- This argument is used to specify a single character with which the character presence in the source string should be replaced when no matching corresponding value is found in to-string expression. This character comes into the picture and execution only when the expression for to-string is having less number of specified characters compared to expression for from-string. If the function is not of string datatype then it is implicitly converted to VARCHAR before execution of the function.
Note that it is necessary that the argument’s length should be either 0 or 1 having at most one character in it If we specify the zero-length string that means no corresponding character in to-string expression for from-string then all the occurrences of that character in the source string are removed. If we are specifying the source string in graphic format then the specification of padding characters as the last argument is optional in nature. By default, when not specified the padding character considered is a blank character.
Examples
Let us see how the TRANSLATE function can be implemented with the help of certain examples. Firstly, we will consider the case where we don’t specify the to-string and from-string in arguments. We will just pass the source string as the first argument. Let us consider a string “Today is a great day for outing.” If we use the translate function for this string our query statement will be as follows –
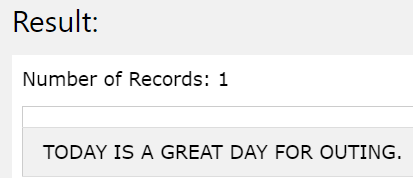
SELECT TRANSLATE(“Today is a great day for outing.” );
The execution of the above query statement gives the following output with all the characters converted to the upper case values as we haven’t specified any to-string or from-string expression.
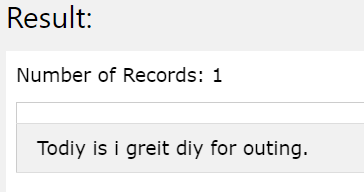
Consider the same source string as first parameter. Now, we will specify the to-string expression of second argument as ‘i’ and the from-string expression of third argument as ‘a’. In that case, we wish to convert all the occurrences of ‘a’ character in the source string to be replaced with ‘i’ character. Hence, our query statement will become as shown below –
SELECT TRANSLATE('Today is a great day for outing.','i','a');
The output of the above query statement is as shown below with all the occurrences of ‘a’ character of the source string get replaced with ‘i’ as shown below and the statement becomes “Today as a great day for outing.”
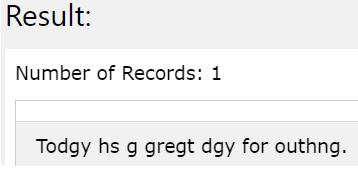
Let us specify two characters simultaneously to be replaced. Let us take to-string expression as ‘gh’ and from-string expression as ‘ai’. Our query statement will become as shown below –
SELECT TRANSLATE('Today is a great day for outing.','gh','ai');
The execution of above query statement gives following output with all occurrences of a replaced with g and all occurrences of i replaced with has shown below –
Conclusion
The TRANSLATE function in DB2 is used for replacing all the occurrences of one or more characters from the source string to some other characters.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 Translate. Here we discuss the Introduction, syntax, examples with an output of the query statement. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

