Updated May 12, 2023

Introduction to DB2 TO_DATE
DB2 TO_DATE function is a scalar function provided by IBM to get the converted value of a character string value into the DATE or DATETIME value in the format that we specify according to requirement and having the datatype of TIMESTAMP. We can use the TO_DATE function to convert the date specified in CHAR or VARCHAR data type into its corresponding DATE or DATETIME in TIMESTAMP datatype that too in the value which we specify. TIMESTAMP_FORMAT function in DB2 also works in the same fashion as that of the TO_DATE function, and one can either choose from any one of them when we need the date datatype value from a string value. In this article, we will study the syntax of the TO_DATE function and also see various forms of formats in which we can specify the date to be converted to. Along with this, we will focus on how we can implement the TO_DATE() function with the help of some examples.
Syntax
The syntax of the TO_DATE() function is as shown below –
TO_DATE(source string, format for date)
In the above syntax, the source string can be any string or expression that returns the value in the CHAR or VARCHAR data type, a built-in datatype. We can even pass a value of source string which is GRAPHIC or VARGRAPHIC datatype provided if we are using the Unicode database because, in Unicode database, the GRAPHIC and VARGRAPHIC datatype values are implicitly converted into the CHAR and VARCHAR datatype respectively, and the evaluation of TO_DATE() function will be done.
It is necessary that the source string should contain the values or components that are required to generate the TIMESTAMP value in the format that we have specified. The second argument is an expression that returns the CHAR or VARCHAR datatyped value. Also, the length of the value that is specified in the format of to date must be greater than 255 bytes. The valid format for the date should not contain more than one specification of the same component of the
TIMESTAMP should contain the specification of at least one of the format elements to be used while converting that string value to TIMESTAMP. One example of the invalid string specified in the format for the date is that we cannot specify YYYY and YY both togetherly as they both are specified for interpreting the year component’s value from the source string. We can separate the multiple element’s formats which we need in the format string of the second parameter by using the following characters for separation –
- ( ) blank
- (:) colon
- (,) comma
- (‘) apostrophe
- (/) slash
- (-) minus sign
- (;) semicolon
- (.) dot or a period
We can use the separator characters in any combination in the string of the format we will specify in the second parameter. Also, note that one or more occurrences of the same separator in the separator characters are also allowed, and separators can also be used at the beginning or ending part of the format that we have specified. The type of formats that can be specified in the TO_DATE function’s second parameter is as shown in the below table –
| YYYY | Year value can be specified in this format. For example, the output value will be 2021. |
| YY | When we used two YY to specify the format, what we mean is the last two digits of the year. For example, 21. |
| RRRR | The year can be either specified as a two-digit value or a four-digit value and for the 20th century, it’s going to be 0 to 49 values; otherwise, it is considered as 20th century. |
| MON | This is used for getting the abbreviated month values. For example, Jan, Feb, Dec, etc. |
| MONTH | This is used for specifying the complete name of the month. For example, January, December, etc. |
| MM | It is used to specify the month value in a numeric format that can range from 1 to 12. |
| DY | It is used for abbreviating the day value, which can range from Sun to Sat. |
| DD | It is used to specify the month value in a numeric format that can range from 1 to 31. |
| HH24 | It is used to specify the hour value in a numeric format that can range from 0 to 23. |
| HH or HH12 | It is used to specify the hour value in a numeric format that can range from 1 to 12. |
| MI | It is used to specify the minute’s value in a numeric format that can range from 0 to 59. |
| SS | It is used to specify the second’s value in a numeric format that can range from 0 to 59. |
Example of DB2 TO_DATE
Let us first use the TO_DATE function to retrieve the value in timestamp data from the string datatype. Consider the date 30 – 03- 2021, which is specified in the yyyy-mm-dd format. Hence, we can make use of the TO_DATE function specifying the value and format in the following query statement.
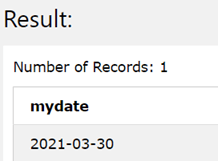
SELECT TO_DATE('2021-03-30', 'YYYY-MM-DD') as mydate;
The execution of the above query statement gives the following output as a result –
Let us consider a new format that involves the date value along with the time and is in the format “%Y-%m-%d %H:%M” stored as a string. We can get the timestamp value of it by using the following query statement.
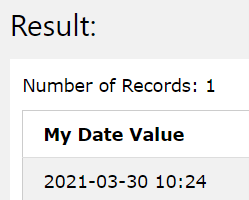
SELECT TO_DATE('2021-03-30 10:24', "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M") as "My Date Value";
The execution of the above query statement gives the following output as a result –
The TO_DATE() function is often used to insert the timestamp value inside the table column with the help of the INSERT statement. Consider the value purchase_time column that is stored in the customer_purchase table, and we have to insert the timestamp value of the string value stored in purchase_time into a table called sales_transactions. This can be done by using the following query statement –
INSERT INTO sales_transactions
VALUES (TO_DATE(SELECT purchase_time FROM customer_purchase WHERE customer_id=1,
'DD/MM/RRRR HH24:MI'));
The execution of the above query statement gives the following output as a result –
Conclusion – DB2 TO_DATE
We can use the TO_DATE function in DB2 to get the converted value in timestamp datatype from the given string value of the date and time, whose format can be further specified by us in the function parameter itself.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 TO_DATE. Here we discuss how we can implement the TO_DATE() function with the help of some examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –