Updated March 6, 2023

Introduction to DB2 Query
DB2 query is actually a table that contains the result or it can also be an intermediate table that holds the result set. When used in statements of SQL, the query can be referred to as the component of the SQL statement. In this article, we will study about three types or forms of the queries used in DB2 relational database, the necessary privileges for executing the queries, and also have a look at the implementation along with the help of certain examples.
Forms of Queries in DB2
There are three types or forms of SQL query which are specified in DB2 as shown below:
- Fullselect
- Subselect
- Select statement
Privileges necessary
When a user or object with a certain authorization id is trying to use the query he must have certain privileges which include at least one of the privileges mentioned in the below-given authorities.
A user should have at least one of the following authorities when working on one of the identified tables or views.
- User should have the privilege of SELECT on the view or table.
- User should have the privilege of SELECTIN on the schema of the view or table
- User should have the privilege of DataAccess on the schema of view or table.
- User should have the privilege of CONTROL over the view on the table which is identified.
Along with one of the above privileges, a user must also possess the DATAACCESS authority.
If we have any of the expression which is global in nature being used in the query then the user or object with authorization id should have one of the specified privileges or authorities from the following:
- If the global variable is not defined inside the module, then it should have the READ privilege over it.
- If the global variable is defined inside the module, then the user should have the EXECUTE privilege over the module in which the variable is defined.
- If the global variable is defined inside the module, then the user should have the EXECUTEIN privilege over the schema which has a module in which the variable is defined.
- If the global variable is defined inside the module, then the user should have the DATAACCESS privilege over the schema which has a module in which the variable is defined.
- If there is any type of modification or update made in the database through query usage then the requirements of authorization are applicable for the query too containing the modifying statement. In the case of group privileges for data definition language statements or the SQL statements which are static in nature, the privileges are not checked for such queries. However, this is the exception if we are using PUBLIC privileges.
Subselect
The subselect is actually a component of full select that helps in specifying the result table containing the result set which is derived from the specified views, tables, or nicknames in the FOR clause of the query statement. The flow is such that the output of a single operation performed by subselect in the input too the other operation which is also called derivation. This is how we can understand the concept of subselect.
However, internally the query execution may not always run in the same manner and can differ a lot. There are many cases where the subselect portion that is mentioned may not even be required for obtaining the final result set. In this case, it might happen that the subselect is not at all executed.
The sequence of execution of sub-select clauses are as shown below:
FROM -> WHERE -> GROUP BY -> HAVING -> SELECT -> ORDER -> OFFSSET -> FETCH
When a subselect statement has to FETCH or OFFSET or ORDER BY clause in it then these clauses cannot be specified in the following places:
- In the materialized query table inside the outer full set.
- If sub-select is not enclosed within the parenthesis.
- In case of view in the outermost full select.
Example of subset
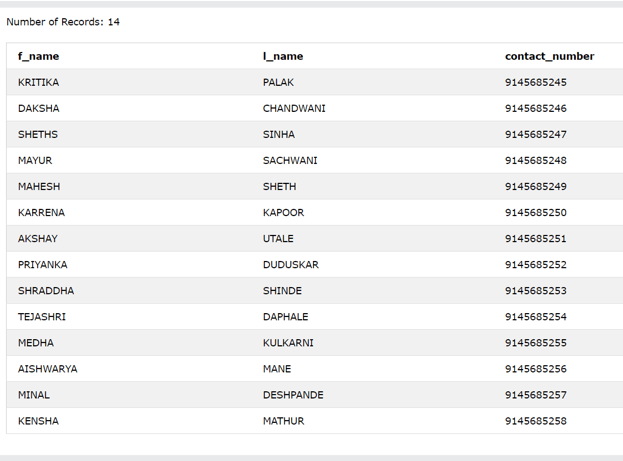
Let’s consider the two tables employee_Details and the customer_Details which contain the following data in them:
Select * from employee_Details;
Output:
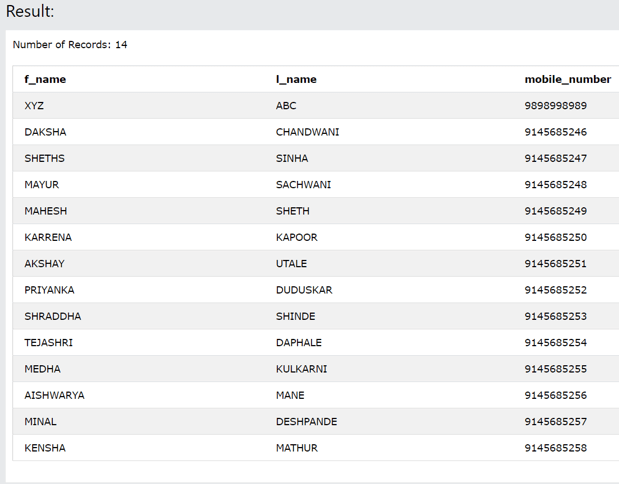
Select * from customer_Details;
Output:
The following statement is not valid because the sub-selects are not mentioned inside the parenthesis-
SELECT * FROM employee_Details
ORDER BY contact_number
UNION
SELECT * FROM customer_Details
ORDER BY mobile_number
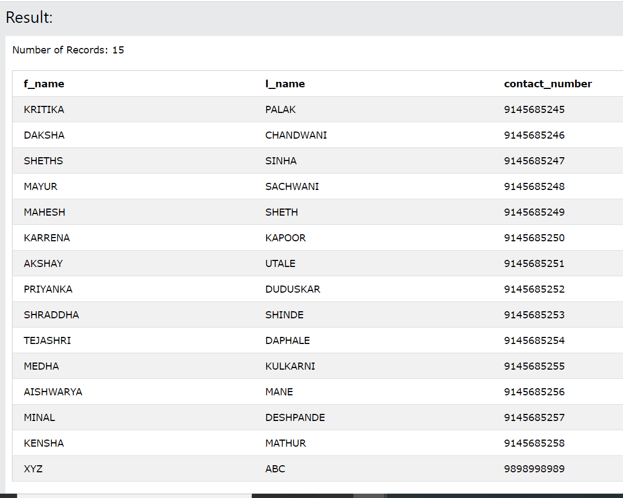
The above statement can be converted to a valid statement by enclosing the sub selects inside the parenthesis as shown below –
(SELECT * FROM employee_Details
ORDER BY contact_number)
UNION
(SELECT * FROM customer_Details
ORDER BY mobile_number)
The output of the above query statement is as given below:
Full select
The full select is the component of the insert or select or create view statement or certain predicates which are the components of the main statement. If it is a component of the predicate then the full select is also referred to as the subquery. In case if it is present inside the parenthesis then it is called a subquery.
The syntax of the full select is as shown below –
Subselect/ fullselect/ value list
(UNION/ UNION ALL/ EXCEPT/ EXCEPT ALL/ INTERSECT/ INTERSECT ALL)
Subselect/ fullselect/ value list
ORDER BY clause
The first occurrence can be a sub-select or full-select statement or a list of columns and expressions to be retrieved from a particular table. Then we have to specify the operator for collecting the two result sets. This operator can be either UNION or UNION ALL or EXCEPT or EXCEPT ALL or INTERSECT or INTERSECT ALL clause then we have to again specify another result set which can be of sub-selector full select or list of column values and expressions. This operator and the second clause can be repeated any number of times. The last thing that we can attach is the order by clause to sort the combined data. The above example as a whole statement represents a full select while its components are sub-selects.
Select
The select is used in DECLARE CURSOR statement and even in dynamic SQL statements which helps the user to see the result set. The result of the full selection after execution leads to the generation of the select table returned as the final result set. For a complete reference of select statements refer to this link.
Conclusion
The DB2 query is a table that contains the intermediate result or table which holds the result set. The different components of DB2 query are sub select, full select, and select.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 Query. Here we discuss the definition, syntax, Forms of Queries in DB2, Different components of DB2 Query, examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

