Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to DB2 NVL
DB2 NVL is used to handle the NULL values that might be present in the data or a list of values that are specified. When the data is stored in DB2 RDBMS, we use the tables and store the data in rows and columns format. If the NOT NULL constraint on the column is not applied, then the default value that gets inserted in those columns when not specified is the NULL value. While retrieving and displaying the data to the user, it is not a good practice to display the NULL values of certain columns. In that case, we can use the NVL function in DB2, which will help us get the first non NULL value from the list of the specified parameters while using it. This article will study the syntax and the implementation of the NVL function in DB2 in different scenarios.
Syntax
The syntax of the NVL function in DB2 is as shown below –
NVL(expr1,expr2)
In the above syntax, the expr1 is the expression that can be any constant value of even the name of the column whose value you wish to retrieve and check if it contains a NULL value in it. Expr2 is the value with which we want to replace the expr1 column if the expr1 contains the NULL value in it. If the expression evaluates to non-null value first, then expr2 value is considered the resultant and returned as an output.
Examples of DB2 NVL
Use of NVL function to retrieve the non- NULL value from the parameters that are specified as the fixed values.
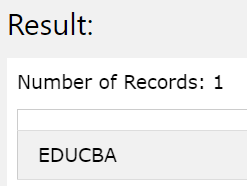
Let us first consider the use of the NVL function with the values (NULL, ‘EDUCBA’)
SELECT NVL (NULL, 'EDUCBA');
The execution of the above query statement gives the following output as the resultant and gives out the first non-null value from the list of specified values in the NVL parameters –
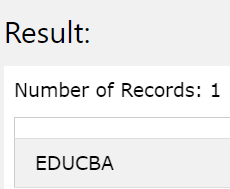
Now, consider that we remove the NULL value from the first place and place the NULL value in the second place. So, the first non-null value from the two parameters will be EDUCBA. Hence, the execution of the following query statement gives out EDUCBA as the output –
SELECT NVL('EDUCBA', NULL);
The output of the execution of the above query statement is as shown in the below image, which is the same as the previous one, but in this case, the NVL function doesn’t go for substituting the expr1 with expr2 for output –
Passing NULL values in both parameters –
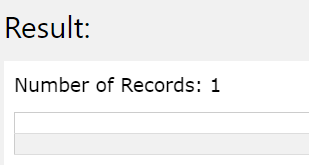
If we supply all the parameters as NULL, then it gives out no error without any output. The NVL function goes for searching the first non- NULL value and fails in finding the same. Hence it returns no output as the first expression is NULL, and the value with which the expr1 is to replace in case of NULL that is expr2 is also NULL. Consider the following query statement –
SELECT NVL(NULL, NULL);
Execution of the above statement gives the following output shown in the image –
Use of NVL function for substituting the NULL values stored in columns of the table –
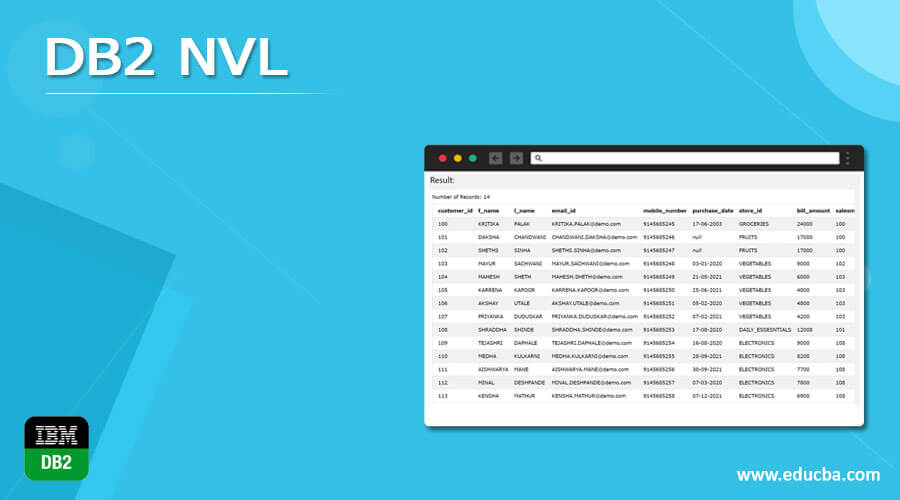
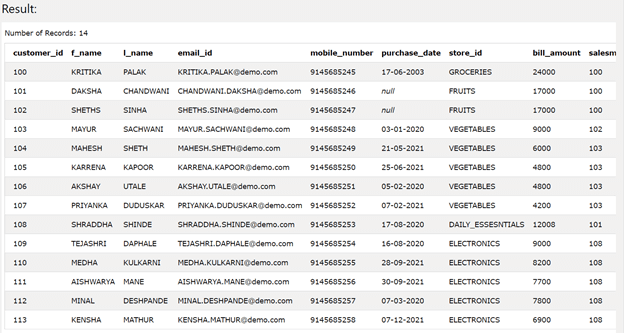
The main purpose of the NVL function is to display any non- NULL value in place of NULL values when a particular column of the table is given the NULL constraint or not provided the NOT NULL constraint. In case if default value is not specified for that column or the column is kept to AUTOINCREMENT value, then by default, the value that gets inserted for that column is the NULL value. Suppose that we have one table named Sales_Customers. If we retrieve the data of the table sales_customers from the database right now by using the following query statement –
SELECT * FROM [Sales_Customers];
Execution of the above statement gives the following result with all the values of the column purchase_date having the value NULL for store_id column having the value of FRUITS in it as shown below –
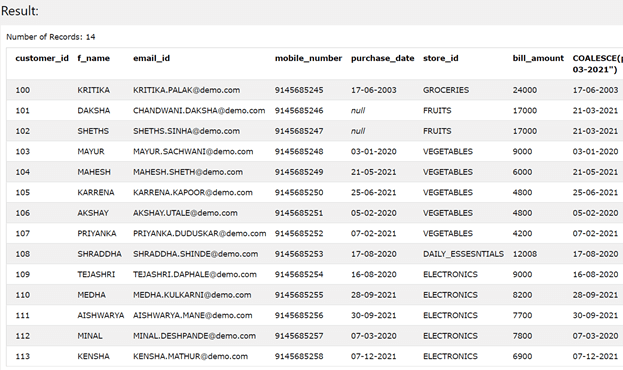
If we have to replace the value of NULL in the purchase_date column, then we can do that by using the NVL function by giving the first argument as the name of the column of purchase_date and then the second argument can be any non-NULL value with which we want to replace the NULL value with. The NVL function will go for searching the first non-NULL value; if the column has any date stored in it, then it displays that date; else, it goes further to replace that null value stored in the column with the value specified in the second parameter. Suppose that we have to show the default date as “21-03-2021”. Then we can make the use of NVL function while retrieving the values of the table by using the following SELECT query statement –
SELECT customer_id, f_name , email_id , mobile_number , purchase_date , store_id , bill_amount , NVL(purchase_date,"21-03-2021") FROM [Sales_Customers];
The output of the above query statement is as shown below with replacing the values of the purchase date column with null values with the date that we have specified in the last value that is retrieved in the select query.
We can also make the use of the NVL function to replace the column value having NULL in it with some other column value by specifying the column containing NULL values as the first argument and the column with which the value needs to be replaced in the second argument. Consider an example where we have the table named workers created by using the following query statement –
CREATE TABLE workers(
employee_id INT NOT NULL ,
f_name VARCHAR(50) NULL,
l_name VARCHAR(50) NULL,
email_id VARCHAR(50) NULL,
mobile_no INT NULL,
joining_date VARCHAR(50) NULL,
food_intake BOOLEAN NULL,
salary FLOAT(10, 2) NULL,
address1 VARCHAR(50) NULL,
address2 VARCHAR(50) NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (employee_id )
)
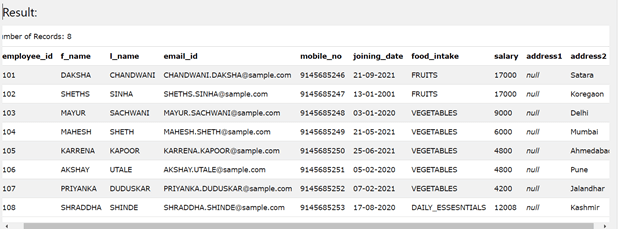
The data of the table is as shown below –
SELECT * FROM [workers]
The output of the above query is as shown below –
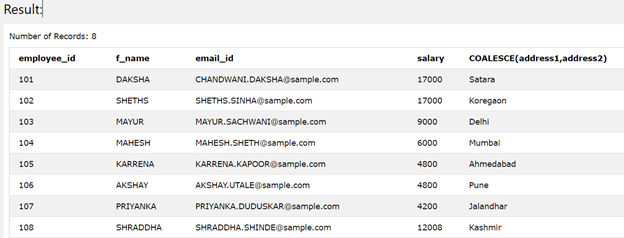
Using the following query statement, we can display the column address2 value in address1 place if it is NULL as shown below –
SELECT employee_id,f_name, email_id, salary, NVL(address1,address2) FROM [workers]
The execution of the above query statement is as shown below –
Conclusion – DB2 NVL
We can make use of the NVL function to handle the NULL values present in the columns of the table or that are present as literal values. The only difference between NVL and COALESCE function is that NVL accepts only two parameters while COALESCE accepts the list of expressions for searching a non-NULL value in it.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 NVL. Here we discuss the syntax and the implementation of the NVL function in DB2 in different scenarios. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –