Updated March 8, 2023

Introduction to DB2 List Tables
The following article provides an outline for DB2 LIST TABLES. When database is designed, we need many tables to store the data related to different objects. After the data is being maintained, stored, updated and retrieved during the usage, there might be a need that we have to sometimes check the structure of the database and the number of the tables present in the database along with some description about all the tables. Also, there might be a need to modify or restructure the database based on certain changed requirement.
In all such cases, we can see the list of all the tables present inside a particular database in DB2 by using one existing internal schema named syscat. Here, we will see about how we can make the use of syscat scheme in order to list out all the tables present inside the database. We will also see how we can use the LIST TABLES command to quickly get the reference of all the system tables present inside the database.
Prerequisite
In order to make the use of the LIST TABLES command, a user should first connect to the database and should have one of the following privileges with him/her.
- Control privileges over the entities of the database
- DBADM
- SYSMAINT
- SELECTIN privilege on the schema named SYSCAT, which helps to know the system catalog information
- SYSMON
- SYSCTRL
First, one should initialize the database connection with the system before listing all the tables inside the database. The establishment of the database connection with the default database automatically exists if we have enabled implicit connection.
Syntax of DB2 LIST TABLES
The syntax of the LIST TABLES command is given below:
LIST TABLES [FOR USER/ALL/SCHEMA name of schema/SYSTEM SHOW DETAIL];
In the above-mentioned syntax, the use of FOR clause is optional, and this clause helps us to retrieve the data for a specific scenario like for all the users or only the current user of can be for a particular schema when we have to retrieve the list of all the tables for a schema other than the default or selected one or FOR clause can also help us to list all the system tables present inside the DB2 RDBMS.
The SHOW DETAIL clause is also optional and can be used to display and retrieve the full names of the database, schemas and the tables. In case if we don’t specify this clause, then the names of the table that are retrieved are in the truncated format, which is upto 30 characters, and the name of the schema that are retrieved are truncated upto characters, and the > symbol specification represents the 31st column in the name of the table while 15th column in the name of the schema.
Alternatively, we can also make the use of the SELECT query statement to list out all the tables from the schema named SYSCAT, which stores the details of all the tables inside the table named tables in it.
Example of DB2 LIST TABLES
Given below is the example of DB2 LIST TABLES:
Let us try to retrieve all the tables inside the schema using the list tables command firstly.
Code:
LIST TABLES;
The execution of the above query statement gives out the following output, which is present in our DB2 database. However, the results may vary depending on the contents and structure of your database.
Output:

As we can observe that the list tables command provides us with the details of all the names of the tables that exist in our database and also provides the details regarding the name of the schema to which the table belongs, type of the table and the time when the table was created. Our database consists of only three tables in it, namely, STORE_LOCATIONS, CUSTOMERS, and SALES. Hence, only three records are retrieved in the result set.
Alternatively, when we make the use of the SYSCAT schema to get the details of the tables by using the SELECT query statement, then our query statement looks like the following.
Code:
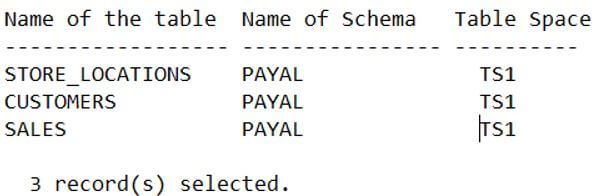
select tabname as "Name of the table", tabschema as "Name of Schema", tbspace as "Table Space" from syscat.tables;
The execution of the above query statement gives out the following output, which is present in our DB2 database. However, the results may vary depending on the contents and structure of your database.
Output:
Before we go for executing any of the above two query statements to list of the tables inside DB2, it is necessary that we first establish the connection with the database using connect to <name of the database to connect>.
For example, suppose that we have a database whose name is store_details, then my connection query statement will become as shown below.
Code:
connect to store_details
Output:
The execution of the above query statement gives out the following output, which is present in our DB2 database.

Conclusion
The LIST TABLES command can be used in DB2 to get the list of all the tables that are present in our database. But before we do that, it is necessary that we have certain privileges with us that are mentioned in the prerequisites section. Any one of these privileges will allow you to use this query statement. We also need to connect to the database whose tables we wish to list out before using the LIST TABLES command. Alternatively, we can also make the use of the SELECT query statement to retrieve the names of the tables inside a particular database from the SYSCAT schema in which table named tables stores the details of all the tables present in the database.
Making the use of the SELECT statement also allows us to filter out the data of the table names using the where clause. We can also retrieve the sorted list that is ordered on the basis of a certain column value, which can be either schema name or the name of the tables. We can also change the details that we are trying to retrieve by specifying the columns that we want and the order in which we want to retrieve the list of the tables.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 LIST TABLES. Here we discuss the introduction and example of DB2 LIST TABLES for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

