Updated March 10, 2023

Introduction to DB2 limit rows
DB2 limit rows are used to retrieve only a particular number of the rows from a particular result set that is retrieved using the SELECT statement in DB2. We can make use of the LIMIT clause in DB2 select statements where we intend to get only the particular number of starting rows from the result. In this article, we will study how we can make use of the DB2 limit clause, study its syntax and see with the help of examples how we can implement the clause with the help of certain examples.
Syntax
The syntax of the DB2 LIMIT clause is as shown below –
SELECT list of the expressions to be retrieved
FROM name of the table
ORDER BY expression which can be used for sorting
LIMIT number of rows [OFFSET rows to be skipped];
Alternatively, we can also make use of the following syntax –
SELECT list of the expressions to be retrieved
FROM name of the table
ORDER BY expression which can be used for sorting
LIMIT rows to be skipped, number of rows;
In the above syntax, the clauses used have the following purpose –
List of expressions – the list of expressions to be retrieved can be any names of the columns of the values that are obtained by manipulation column values or string literal values.
Table name – The name of the table is the table name from which we wish to retrieve the data.
Sort expression – The expression that can be used for sorting is the column’s name on the basis of which the table data is to be sorted. The data that is stored in the table may be unsorted in some cases. It is considered good practice to use the order by clause in the statement as the retrieved data will be in the sorted format.
rows to be skipped – This is the number of the rows that are to be not considered in the final result set while the limit clause is used. The number specified here are the rows that are skipped, after which the records are considered for retrieval by considering the LIMIT clause while retrieving.
The number of rows – This is the number of rows that we want to consider for the final result. This is the limit number.
The use of the ORDER BY clause with a limit is optional. But most of the database engineers go for using this as it retrieves the appropriate data in a sorted format.
Examples of DB2 limit rows
Let us consider the examples to study how we can make use of the LIMIT clause to restrict the number of retrieval columns.
Example #1
Consider that we have one table named employee_details. This table contains detailed information about all the employees of a particular company. To check the contents of this table, we can make the use of the following query statement –
SELECT * FROM [employee_details]
The execution of the above query statement retrieves all the rows that are present in the table of employee details, as shown below. The table contains all 14 different rows of 14 employees –
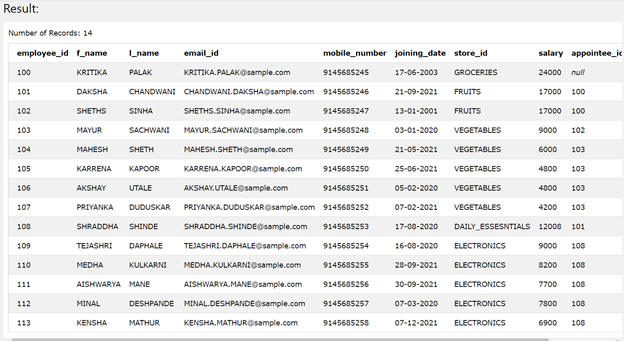
Suppose that we want to retrieve only the first 10 rows. In that case, we can make the use of the LIMIT clause that is applied in the following ways using the below query statement –
SELECT * FROM [employee_details] LIMIT 10;
The execution of the above query statement returns the following result, which consists of the first 10 rows in it as we had applied the limit value for the number of the rows as 10.
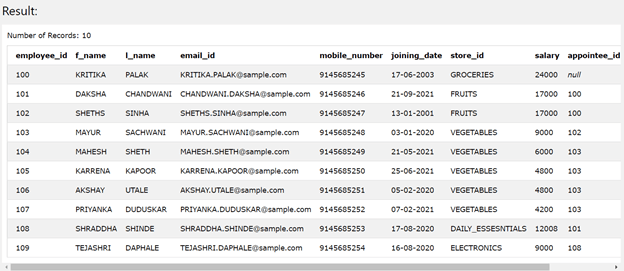
Example #2
What if we want to retrieve a specific number of rows from a table but also make sure that they are not the starting records of the table. We will need to mention the offset value, which will help specify the number of rows from where we have to begin the row count for retrieval of the rows in the final result set. Consider the same table employee details. Suppose we have to retrieve the employees after the first 5 records. In that case, our offset value will be five and take the requirement that only seven rows are to be retrieved. In that case, the row count will be 7, and the offset is 5. Hence, our query statement now will be as shown below –
SELECT * FROM [employee_details] LIMIT 5,7;
The execution of the above query statement returns the following result, which consists of 7 rows in it as we had applied the limit value for the number of the rows like 7, and the records will begin from the 5th row of the table contents as offset is 5.
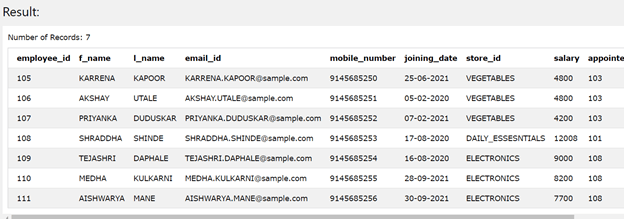
Example #3
There is one more alternative way of specifying the row count and the offset value in the LIMIT clause, which is as shown in the first syntax. Consider the same table employee_details from which we have to get the records beginning from the 10th row, and only 3 rows are to be retrieved. In this case, our row count is 3, and the offset value is 10. This can be specified in the LIMIT clause using the alternative syntax and the following query statement –
SELECT employee_id, f_name, l_name, email_id, mobile_number, salary
FROM employee_details
LIMIT 3 OFFSET 10;
The execution of the above query statement returns the following result, which consists of 3 rows in it as we had applied the limit value for the number of the rows like 3, and the records will begin from the 10th row of the table contents as offset is 10.
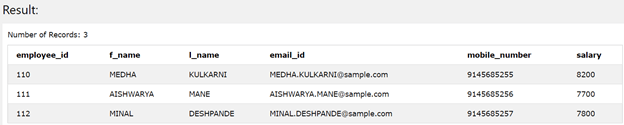
Conclusion
We can make use of the LIMIT clause to restrict the number of rows that we have to retrieve in the final result set. LIMIT clause is mostly used for the purpose of pagination. We can also begin the record retrieval of the limited records from a point other than the first position. This can be done by using the offset. The usage of the ORDER BY clause is mostly suggested along with the LIMIT clause n order to retrieve the data, which is sorted based on a particular column. This sorting can be done either in descending or ascending order and on one or more columns.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 limit rows. Here we discuss how we can make use of the DB2 limit clause, study its syntax and see with the help of examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

