Updated March 10, 2023

Introduction to DB2 length
Database management systems provide different types of function to the user. DB2 length function () is also the one type of function in which we can return the length expression from the specified table. In the DB2 length function, if the expression has a null value, then it returns the null value, and the expression uses a built-in data type. DB2 has different data types, and it uses physical storage for column value. By using the DB2 length function, we can determine the length of expression for any type of data type; we can use the DB2 length function as per the user requirement.
Syntax
select colm name 1, colm name 2……columN, new column name (specified colm name ) from specified table name;
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use a select statement with the different parameters as follows.
colm name 1: Column name from the specified table name.
new column name: It used to create the new column for the result.
specified colm name: Specified column name means actual column name.
specified table name: Actual table name.
How does the length function work in DB2?
Now let’s see how the length function works in DB2 as follows.
Basically, the length function required the expression to return the value.
What is an expression?
An expression uses the bit in data type to return the specified value. In the event that expression can be invalid, the outcome can be invalid; if the expression is invalid, the outcome is the invalid worth.
CODEUNITS16, CODEUNITS32, or OCTETS
It uses a string unit for the result. CODEUNITS16 indicates that the outcome is to be communicated in 16-bit UTF-16 code units. CODEUNITS32 determines that the outcome is to be communicated in 32-bit UTF-32 code units. An OCTET determines that the outcome is to be communicated in bytes.
On the off chance that a string unit is unequivocally indicated, and if the expression is not string information, a blunder is returned (SQLSTATE 428F5). On the off chance that a string unit is indicated as CODEUNITS16 or CODEUNITS32, and articulation is a twofold string or touch information, a blunder is returned (SQLSTATE 428GC). In the event that a string unit is determined as OCTETS and the expression is a parallel string, a mistake is returned (SQLSTATE 42815). For more data about CODEUNITS16, CODEUNITS32, and OCTETS, see String units worked in capacities in Character strings.
On the off chance that a string unit contention isn’t unequivocally indicated and if the expression is a character or realistic string, the string units of expression decide the string unit that is utilized for the outcome. Something else, the worth returned indicates the length in bytes.
The aftereffect of the function is an enormous number. On the off chance that the contention can be invalid, the outcome can be invalid; if the contention is invalid, the outcome is the invalid worth.
The length of character and realistic strings incorporate the following spaces. The length of parallel strings incorporates paired zeros. The length of changing length strings is the real length and not the greatest length. The length of any remaining qualities is the number of bytes used to address the worth as follows.
- 2 are used for the small integer.
- 4 are used for the large integer.
- 8 are used for the big integer.
Examples
Now let’s see the different examples of length function as follows.
First, we need to create by using a create table statement as follows.
create table company (Comp_Id int(20), comp_name varchar(30),
comp_address varchar(30));
Explanation
In the above example, we use a create table statement to create a new table name as a company with different attributes such as Comp_id, comp_name, and comp_address with different data types and different sizes as shown in the above statement.
Now insert some records by using the following insert into the statement as follows.
insert into company (Comp_Id, comp_name,comp_address) values(1, "HP", "mumbai"), (2, "Dell", "Pune");
select * from company;
Explanation
In the above example, we use to insert into statement. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.

Now use the length function as follows.
Suppose users need to know how many characters are present in a particular column, then we can use the following statement as follows.
select comp_address, character_length(comp_address) length from company;
Explanation
In the above example, we use a select statement with a specified column name that is comp_address; here, we use the character_length function to count the total number of characters in that column. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.

Suppose the user needs to find out the maximum character in the specified column at that time; we can use the following statement as follows.
Syntax
select max(length(specified column name)) from specified table name;
Explanation
By using the above syntax, we can find out the max length from the specific column.
Example
select max(length(comp_address)) from company;
Explanation
In the above example, we use max and length functions with select statements. By using the above example, we can determine the highest value of characters. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.

Now let’s see another example to better understand how the DB2 length function works as follows.
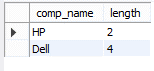
select comp_address, character_length(comp_name) length from company;
Explanation
In the above example, we use a select statement with a specified column name that is comp_name; here, we use the character_length function to count the total number of characters in that column. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
So in this way, we can use the length function as per the user requirement. But keep in mind if the expression has a null value, then it also returns the null value.
Conclusion – DB2 length
We hope from this article you have understood about the DB 2 length functions. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of length functions, and we also see different examples of length functions. We also learned the rules of length functions. From this article, we learned how and when we use the DB 2 length functions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 length. Here we discuss the basic syntax of length functions, and we also see different examples of length functions. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

