Updated March 6, 2023
Introduction to DB2 Join
DB2 join statement is used to get the combined result set that includes the rows from both the tables that are involved in join. The rows to be retrieved are decided on the basis of certain join condition. There are many join functions that are supported by DB2 Relational Database Management System. Some of the supported joins include inner join, left outer join. Right outer join and full outer join. In this article, we will study different types of joins, their syntax, and usage along with implementation with the help of certain examples.
Usage
Joins are mostly used to retrieve and view the data that is a combination of the two tables. The join condition helps in determining which rows should be selected for the final resultant from both of the tables. Generally, the join condition involves matching of different column values that are corresponding in both of the tables mentioned in join. Often, SELECT statement is used to retrieve the values from the database, and joins are mostly used along with it. However, we can even make use of JOIN in some other CRUD operations that include UPDATE and DELETE statement.
Setup for demonstration
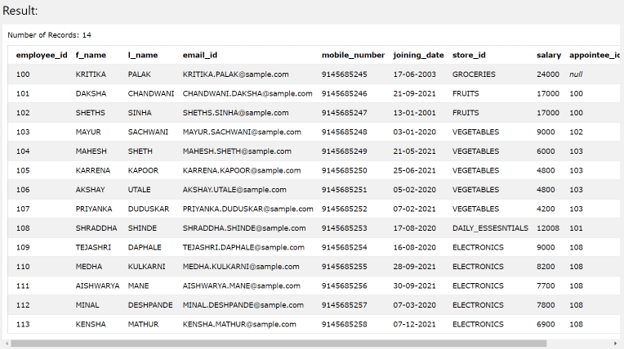
Let us study each of the join along with its syntax and examples one by one. But before that, we will do the setup for demonstrating the usage of joins. We have created two tables namely employee_details and contact_details. We also have inserted certain values in both the tables for sample purpose using the INSERT query statement. In order to retrieve the contents of both the tables. Let us execute the SELECT query on both the tables individually. The query to retrieve the rows from employee_details table is as shown below:
SELECT * FROM [employee_details];
The execution of above query statement gives out the following output –
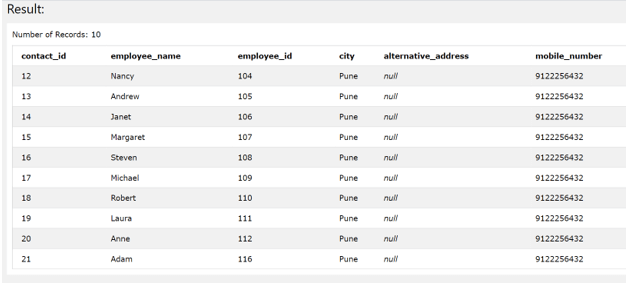
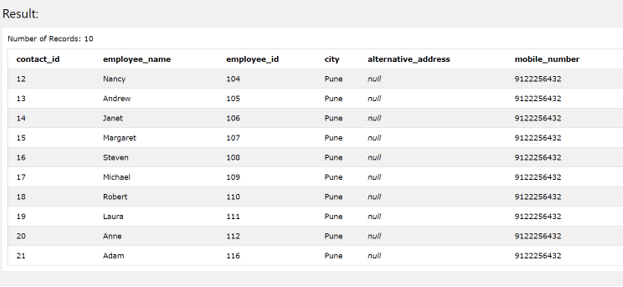
SELECT * FROM [contact_details];
The execution of above query statement gives out the following output –
Inner Join
When we use the inner join then only the rows that are present in both the tables that are right table of the join and the left table and for which the join condition evaluates to true are considered for the final resultant. Let us see the syntax of the inner join in DB2 which is as shown below:
SELECT * FROM
Table1
INNER JOIN / JOIN
Table2
ON join condition
[WHERE];
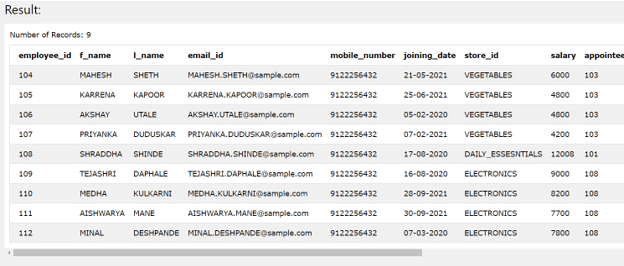
If we consider the same two tables for the sample demonstration of inner join usage then our qiery will have table1 as employee details and table2 as contact_details. Also, we will try to retrieve the details of only those employees who have the same employee_id in both tables. Hence our join condition will match the employee_id column of both tables. Therefore, our query statement will be as shown below –
SELECT * FROM
employee_details JOIN
contact_details ON
employee_details.employee_id = contact_details.employee_id;
The execution of above query statement gives out the following output containing the rows for whom the employee id has the matching entry in both of the tables –
Left Outer Join
When we use the Left Outer join then only the rows that are present in both the tables that are right table of the join and the left table and for which the join condition evaluates to true and all the rows of the left side table are considered for the final resultant. Let us see the syntax of the Left Outer join in DB2 which is as shown below-
SELECT * FROM
Left Table1
Left Outer JOIN
Right Table2
ON join condition
[WHERE];
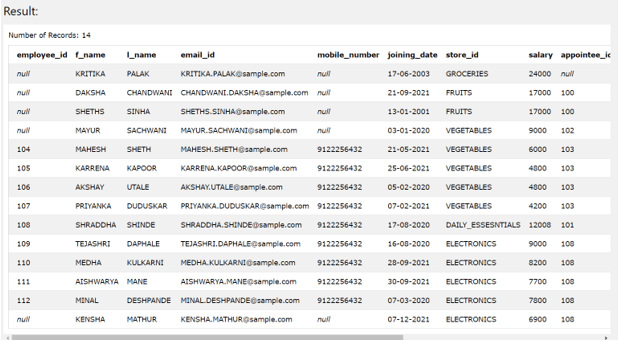
If we consider the same two tables for the sample demonstration of inner join usage then our query will have left table1 as employee details and right table2 as contact_details. Also, we will try to retrieve the details of only those employees who have the same employee_id in both the tables as well as all the records of employee details table. Hence our join condition will match the employee_id column of both tables. Therefore, our query statement will be as shown below –
SELECT * FROM
employee_details Left Outer JOIN
contact_details ON
employee_details.employee_id = contact_details.employee_id;
The execution of above query statement gives out the following output containing the rows for whom the employee id has the matching entry in both of the tables and all the records of the employee_details table –
Right Outer Join
When we use the Left-Right join then only the rows that are present in both the tables that are right table of the join and the left table and for which the join condition evaluates to true and all the rows of the right side table are considered for the final resultant. Let us see the syntax of the Right Outer join in DB2 which is as shown below:
SELECT * FROM
Left Table1
Right Outer JOIN
Right Table2
ON join condition
[WHERE];
If we consider the same two tables for the sample demonstration of inner join usage then our query will have left table1 as employee details and right table2 as contact_details. Also, we will try to retrieve the details of only those employees who have the same employee_id in both the tables as well as all the records of contact details table. Hence our join condition will match the employee_id column of both tables. Therefore, our query statement will be as shown below:
SELECT * FROM
employee_details Right Outer JOIN
contact_details ON
employee_details.employee_id = contact_details.employee_id;
The execution of above query statement gives out the following output containing the rows for whom the employee id has the matching entry in both of the tables and all the records of the contact_details table –
Conclusion
We can make use of joins to retrieve the rows from two or more tables depending on certain join condition. The rows to be retrieved also depend on the join condition evaluation of that row and the type of join being used. There are different types of joins supported by DB2 RDBMS out of which inner join, left outer join, and the right outer join are mostly used.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 Join. Here we discuss Introduction, syntax, and Different Types of Joins along with implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –