Updated March 4, 2023
Introduction to DB2 Data Types
Whenever a table is created in the DB2 database then while structuring the tables and the fields needed to be stored in that table, we assign the datatypes to each and every field when creating it. The DB2 datatype helps to specify what type of value, what type of functions and operators can be used with that particular field, the range of allowed values and the length of the field can that particular column contains in DB2 RDBMS. We can also modify the datatype assigned to a particular column after a table is created and values are inserted in it. In this case, the applied datatype is implemented for all the values of that column at the time of reorganization of the table.
There are two types of data types supported by DB2 which are one provided by IBM and the other ones are user-defined datatypes. The datatypes that are supplied by IBM are also called built-in datatypes. The user-defined data types are also called distinct datatypes when used for z/OS version of DB2. In this article, we will study different data types supported by DB2 RDBMS.
Built-in datatypes provided by IBM:
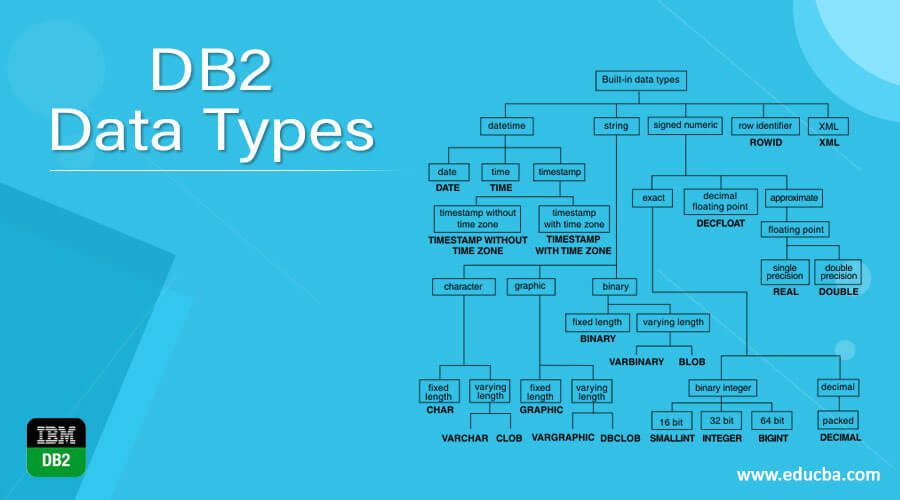
The following image of IBM displays all the built-in datatypes that are supported by DB2 RDBMS –
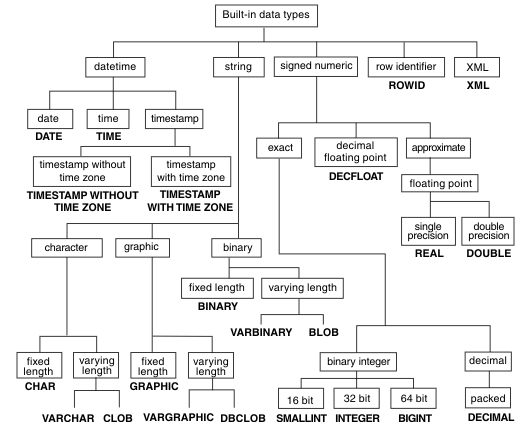
The datatypes of DB2 can be segregated into the following main categories –
- Numeric Datatypes – There are many in-built numeric datatypes supported by DB2, some of which are smallint, integer, bigint, decimal, float, real, decfloat, etc. Each one has its own range and characteristics.
- String Data types – The types of string datatypes supported by DB2 include character strings, binary strings, and graphic strings like varbinary, blob, char, varchar, graphic, vargraphic, dbclob, etc. For character strings, the length of the string depends upon the number of bytes as it is nothing but a sequence of bytes. When we do not store anything in that character string then it is treated as an empty string which is not as same as the NULL value. In the case of graphic strings, they are made up of double-byte characters and is the sequence of the same. Binary strings are also made up of a sequence of byte values.
- NULL values – It is a special type of value that is supported by all the datatypes when we want to store nothing that means an absence of NONNULL value in the column.
- Timestamp, date, and time datatypes – We can store the date and time-related data in RDBMS in a numeric format as well. But it is always recommended and suggested to use the date-time datatypes supported by DB2 like DATE, TIMESTAMP, and TIME because they can be used with string and arithmetic operations. DATE datatype helps us to store the information of day value, month value, and the year value in YYYY format. For storing the date value, we require 4 bytes of memory capacity. The TIME data type helps us to store the time hour, minutes, and seconds format for which we totally require 3 bytes of memory space. The TIMESTAMP datatype helps us to store the date and time completely containing year, month, day, seconds, minutes, and hour value. Along with this, we can optionally even store the information related to time zones in the TIMESTAMP datatype.
- Large object data types – If the size of the files is larger than 32 KB, then we can make use of large object datatypes to store media files like audio, images, video, and other types of files. Large object datatypes are referred to as LOBs which include CLOB, BLOB, and DBCLOB datatypes in DB2 RDBMS.
- XML data types – We can store the XML values in the columns by giving it XML datatype. It is possible to store the XML documents that are well structured in the database by using this datatype.
- Distinct Data types – We can create our own datatypes and define different constraints and characteristics for that type by using the built-in datatypes which are called user-defined data types or also distinct datatypes in DB2.
- ROWID data type – We can uniquely identify particular rows in DB2 RDBMS by using the ROWID datatype for the column. We can assign the host variable or a particular column as ROWID datatype.
- Boolean Datatype – Using this data type, we can store the values true or false which are internally stored as 1 and 0 in the field. Note that this data type does not fall in the string, DateTime, or numeric data type categories.
The following table gives the information about the data types that are provided by IBM (built-in datatypes) and the storage capacity for each of the datatypes if we assign that data type to our field.
| Data type in DB2 RDBMS | Size for storing the field value |
| DOUBLE | 8 |
| LONGVARCHAR(n) | n+1, 2- 32701 |
| TIME | 6 |
| SMALLINT | 2 |
| DECIMAL(p, s) | 8 |
| INTEGER | 4 |
| TIMESTAMP | 8 |
| DATE | 8 |
| FLOAT | 4 |
| BLOB | Default (12) |
| CHAR(n) | n+1, 2- 255 |
| VARCHAR(n) | n+1, 2- 4001 |
Comparison of different field values depending on datatype in DB2:
DB2 RDBMS helps us to compare the values of different columns having different lengths and types. Most of the time, the comparison is made when both the columns have character string values or both are numeric data typed columns or both fields contain graphic string values in them. However, we can also compare the graphic data with character or datetime data with character value provided if the DateTime data is in character representation format. One has to remember the fact while comparing different values that the performance is impacted due to comparisons of different numeric and string values.
Conclusion
DB2 RDBMS comes with a wide range of data types that can be assigned to the columns of the table while table creation and can also be modified later. These datatypes help in determining the behavior and characteristics of that column that include range, type of values stored in it, operators and function supported by that field, length, and many other things. The two main categories in which these data types are divided are the built-in datatypes and the user-defined datatypes. Built-in datatypes are the ones provided by IBM in DB2.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 Data Types. Here we discuss the Introduction, syntax, How DB2 Data Types works? and examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

