Updated April 27, 2023
Difference Between Data Science vs Data Mining
Data Mining is about finding the trends in a data set and using these trends to identify future patterns. It is an essential step in the Knowledge Discovery process. It often includes analyzing the vast amount of historical data which was previously ignored. Data Science is a field of study that includes everything from Big Data Analytics, Data Mining, Predictive Modeling, Data Visualization, Mathematics, and Statistics. Data Science has been referred to as the fourth paradigm of Science. (The other three are Theoretical, Empirical, and Computational). Academia often conducts exclusive research in Data Science.
Historical Perspective
Before we move to the technical descriptions, let’s look at the terms’ evolution. A historical investigation will clarify how the terms are used currently.
- The word’ Data Science’ has existed since the 1960s, but it was used as an alternative to ‘Computer Science’ back then. Presently, it carries an entirely different meaning.
- In 2008, D. J. Patil and Jeff Hammerbacher became the first to call themselves ‘Data Scientists’ to describe their roles at LinkedIn and Facebook, respectively.
- In 2012, a Harvard Business Review article cited Data Scientist as the ‘Sexiest Job of the 21st Century’.
- The term Data Mining has evolved parallelly. It became prevalent amongst the database communities in the 1990s.
- Data Mining owes its origin to KDD (Knowledge Discovery in Databases). KDD is a process of finding Knowledge from information present in databases. And Data Mining is a significant subprocess in KDD.
- Data Mining is often used interchangeably with KDD.
Although these names have come into the picture independently, they often come out as complementary to each other as they are closely related to data analysis.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Data Science vs Data Mining (Infographics)
Below are the Top 9 Comparison of Data Science vs Data Mining:
Example Use Case
Consider a scenario where you are a significant retailer in India. You have 50 stores in 10 major cities in India and have been operational for 10 years.
Let’s say you want to study the last 8 years’ data to find the number of sales of sweets during the festive seasons in 3 cities. If that’s your objective, I recommend employing a Data Mining expert. A Data Miner would probably review historical information stored in legacy systems and employ algorithms to extract trends.
Consider another case where you want to know which sweets have received more positive reviews. In this case, your data sources may not be limited to databases; they could extend to social websites or customer feedback messages. In this case, my suggestion to you would be to employ a Data Scientist. A person employed as a Data Scientist is more suited to apply algorithms and conduct this socio-computational analysis.
Key Differences Between Data Science vs Data Mining
Below is the key difference between data science vs data mining:
- Data Mining is an activity that is part of a broader Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) Process. At the same time, Data Science is a field of study like Applied Mathematics or Computer Science.
- Data Science is often looked upon broadly, while Data Mining is considered a niche.
- Some activities under Data Mining, such as statistical analysis, writing data flow, and pattern recognition, can intersect with Data Science. Hence, Data Mining becomes a subset of Data Science.
- Machine Learning in Data Mining is used more in pattern recognition, while it has a more general use in Data Science.
Note:
- Data Science and Data Mining should not be confused with Big Data Analytics, and one can have both Miners and Scientists working on big datasets.
Data Science vs Data Mining Comparison Table
Below is the comparison table between Data Science vs Data Mining:
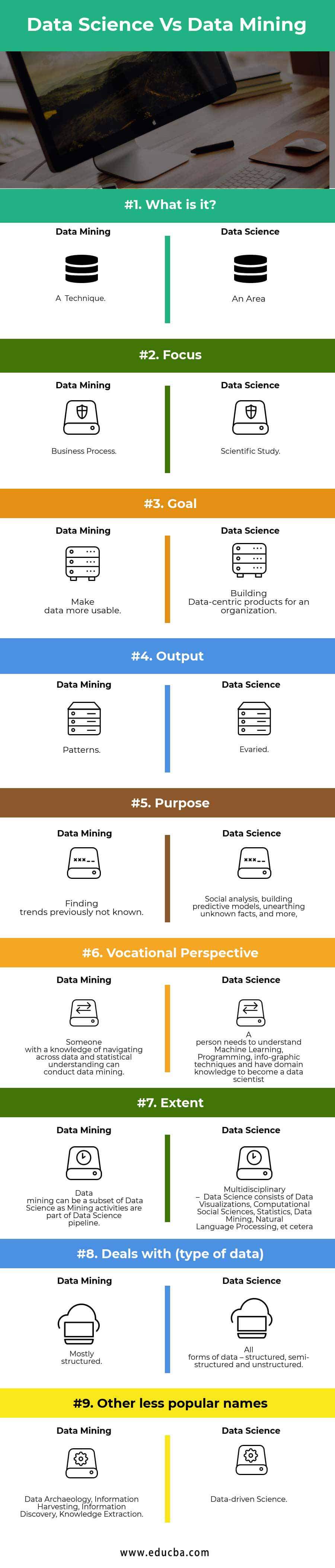
| Basis for Comparison | Data Mining | Data Science |
| What is it? | A technique | An area |
| Focus | Business process | Scientific study |
| Goal | Make data more usable | Building Data-centric products for an organization |
| Output | Patterns | Varied |
| Purpose | Finding trends previously not known. | Social analysis, building predictive models, unearthing unknown facts, and more. |
| Vocational Perspective | Someone knowledgeable in navigating across data and statistical understanding can conduct data mining. | A person needs to understand Machine Learning, Programming, and infographic techniques and have the domain knowledge to become a data scientist. |
| Extent | Data mining can be a subset of Data Science as Mining activities are part of the Data Science pipeline. | Multidisciplinary – Data Science consists of Data visualization, Computational Social Sciences, Statistics, Data Mining, Natural Language Processing, et cetera. |
| Deals with (the type of data) | Mostly structured | All forms of data – structured, semi-structured and unstructured |
| Other less popular names | Data Archaeology, Information Harvesting, Information Discovery, Knowledge Extraction | Data-driven Science |
Conclusion
So here you go! I am sure now you are more aware of the key differences between the two and in what context the two should be utilized. It would be best to remember that no formal and precise definitions of Data Science and Data Mining exist. There are still debates amongst academia and the industry about what constitutes an accurate definition. Everyone agrees on the high-level differences and descriptions of the two terms we explored in this article.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Data Science vs Data Mining. Here we have discussed Data Science vs Data Mining head-to-head comparison, key differences, and a comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –