What is Data Filtering?
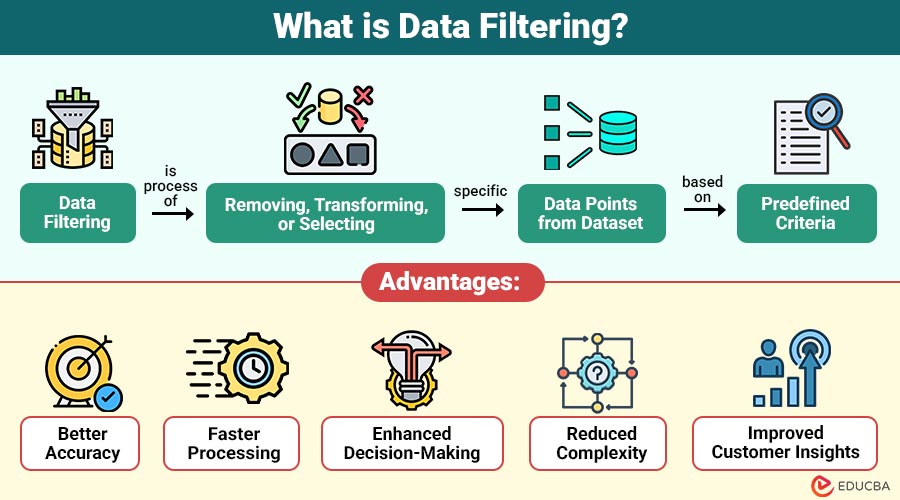
Data filtering is the process of removing, transforming, or selecting specific data points from a dataset based on predefined criteria. Its purpose is to improve the dataset’s quality and relevance so that analysis becomes accurate, meaningful, and efficient.
For example, a retail company removes all incomplete and duplicate customer records before analyzing shopping trends.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Data filtering is essential for cleaning datasets by removing unnecessary elements to enhance overall data quality.
- It removes irrelevant, incorrect, inconsistent, or noisy data to ensure reliability and meaningful analytical outcomes.
- Filtering improves accuracy, boosts system performance, and strengthens decision-making by refining data inputs effectively.
- Data filtering ensures regulatory compliance by efficiently removing sensitive, irrelevant, or non-compliant data from datasets.
Why is Data Filtering Important?
Here are the key reasons why data filtering plays an important role in data processing:
1. Eliminates Irrelevant Data
Filtering retains only information relevant to the analysis goal, improving accuracy, clarity, and reliability.
2. Enhances Data Quality
It removes duplicates, errors, outdated entries, and missing values, ensuring datasets remain clean, consistent, trustworthy, and highly usable.
3. Improves Performance
Smaller, cleaner datasets reduce computational load, accelerate processing tasks, improve system efficiency, and optimize overall data workflows.
4. Prevents Misleading Insights
Filtering removes noise and inaccuracies, preventing false patterns from skewing results and ensuring that decisions rely on valid, reliable data.
5. Strengthens Machine Learning Models
High-quality filtered training data improves model accuracy, generalization, reliability, and performance across a range of predictive tasks and applications.
How does Data Filtering Work?
It typically involves the following steps:
1. Define Criteria
Set clear rules like ranges, thresholds, categories, or conditions to guide accurate processes.
2. Identify Relevant Attributes
Determine which specific columns, variables, or fields are essential for meaningful analysis and accurate filtering decisions.
3. Remove or Transform Data
Apply appropriate filters to remove unwanted values or correct inconsistencies to improve dataset quality.
4. Validate Results
Check the filtered dataset to ensure no critical or useful information was accidentally removed.
5. Prepare the Final Dataset
Organize the cleaned, validated dataset properly so it becomes fully ready for accurate analysis or modeling.
Common Data Filtering Techniques
Below are the most widely used techniques to clean, refine, and prepare datasets for accurate analysis:
1. Value-Based Filtering
Filter dataset values using conditions such as greater than, less than, equal to, or not equal to.
2. Range Filtering
Retains only data points within a predefined lower and upper numeric range.
3. Category-Based Filtering
Selects or removes records based on predefined categories, keeping only relevant groups for analysis.
4. Duplicate Removal
Identifies and eliminates repeated entries to maintain dataset uniqueness, consistency, reliability, and improved accuracy.
5. Missing Value Filtering
Handles missing data by removing incomplete entries or filling gaps using mean, median, mode, or interpolation.
6. Outlier Filtering
Removes extreme data points using statistical techniques such as Z-scores, IQR, or percentile-based thresholds.
Advantages of Data Filtering
Here are the key advantages that organizations gain by applying effective techniques.
1. Better Accuracy
Clean, well-filtered data consistently produces highly reliable insights, minimizing prediction errors and improving overall analytical accuracy.
2. Faster Processing
Filtering removes unnecessary data, reducing computational load and significantly speeding up system, model, and dashboard performance.
3. Enhanced Decision-Making
High-quality filtered datasets enable clearer insights, supporting faster, smarter, and more confident data-driven business decisions.
4. Reduced Complexity
Filtering simplifies large datasets, making analysis easier, more structured, and more understandable, while improving analyst efficiency.
5. Improved Customer Insights
Removing noise reveals more unique behavioral patterns, which allows for a better knowledge of customer preferences, trends, and engagement.
Disadvantages of Data Filtering
While data filtering offers many benefits, it also has disadvantages.
1. Risk of Losing Important Information
Overly strict filtering rules can accidentally remove valuable data, reducing insight quality and harming overall analysis.
2. Requires Expertise
Inexperienced filtering decisions may distort results, making analysis inaccurate, unreliable, and potentially misleading for stakeholders.
3. Time-Consuming for Large Datasets
Filtering extremely large datasets demands substantial computing resources, powerful tools, and significantly longer processing times.
4. Potential Bias Introduction
Removing specific categories or groups may unintentionally introduce bias, negatively affecting the fairness and accuracy of the analysis.
Real-World Examples
Here are some practical examples of how data filtering is applied across different industries:
1. E-Commerce
- Filtering out canceled orders before analyzing sales
- Removing bots or fake accounts before customer segmentation
2. Finance
- Filtering fraud transactions by anomaly scores
- Removing duplicate entries in banking systems
3. Marketing
- Extracting only relevant leads based on demographic filters
- Cleaning email lists by removing invalid IDs
4. Telecom
- Filtering dropped calls before network performance modeling
- Removing stale records older than a specific period
Use Cases of Data Filtering
Below are some practical situations where it is extremely valuable:
1. Machine Learning Preprocessing
Before training any model, datasets must be thoroughly cleaned by removing noise, outliers, and irrelevant features to improve accuracy.
2. Business Intelligence and Reporting
Dashboards and reports require well-filtered, clean datasets to consistently generate accurate KPIs, insights, and performance metrics, and to support reliable, data-driven decisions.
3. Fraud Detection
Filtering techniques help isolate suspicious transactions by analyzing anomalous patterns in amounts, timing, frequency, or behavior, thereby improving fraud-detection accuracy.
4. Customer Segmentation
Filtering customer attributes such as age, gender, spending habits, and activity levels helps effectively create targeted, meaningful, high-performing market segments.
5. Social Media Analytics
Filtering removes spam comments, bot-generated activity, and irrelevant posts, enabling accurate sentiment analysis and improved understanding of audience behavior.
Final Thoughts
Data filtering is one of the most critical steps in data preparation. As datasets grow in size and complexity, filtering becomes increasingly important for maintaining accuracy, improving system performance, and deriving meaningful insights. Whether you are analyzing customer behavior, training machine learning models, or building dashboards, effective data filtering ensures your outputs are reliable and actionable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is data filtering the same as data cleaning?
Answer: Filtering is part of data cleaning, which also includes tasks such as validation, correction, and transformation.
Q2. Can filtering remove outliers?
Answer: Yes, outlier detection techniques such as IQR, Z-scores, and percentiles can filter out extreme data points.
Q3. What tools are used for data filtering?
Answer: Excel, SQL, Python (Pandas), Power BI, Tableau, R, and big data systems like Spark.
Q4. Does excessive filtering affect results?
Answer: Yes, over-filtering can remove important insights and lead to biased analysis.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Data Filtering” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.