What is Cyber Resilience?
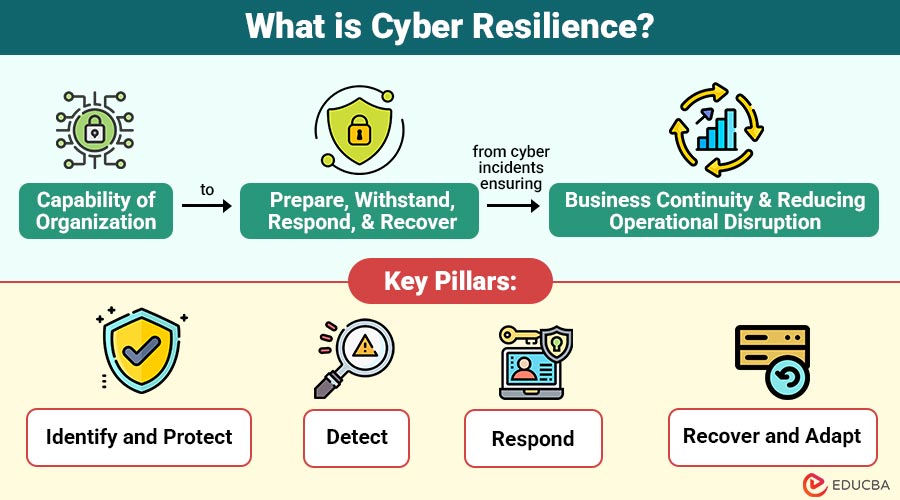
Cyber resilience is the capability of organization to prepare for, withstand, respond, and recover from cyber incidents, ensuring business continuity and reducing operational disruption.
Unlike traditional cybersecurity, which emphasizes protection, cyber resilience integrates both security and continuity. It assumes that breaches will occur, and the real test lies in how quickly and effectively an organization can bounce back.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Cyber resilience blends security and continuity, ensuring organizations recover swiftly while minimizing business disruptions.
- A structured framework with detection, response, and recovery pillars strengthens defenses against evolving cyber risks.
- Employee training, zero-trust models, and regular testing build organizational readiness for inevitable cyberattacks.
- Resilience boosts trust, compliance, and competitiveness but requires investment, updates, and continuous improvement efforts.
Why is Cyber Resilience Important?
Here are the key reasons why cyber resilience is important for every modern organization in today’s digital-first and threat-prone environment:
1. Cyber Threats are Evolving Constantly
Hackers use advanced tools like artificial intelligence, phishing campaigns, and zero-day exploits. Even the strongest cybersecurity defenses can be bypassed.
2. Data is a Critical Asset
With most businesses running on digital platforms, any disruption in data availability or integrity can cause massive financial and reputational damage.
3. Regulatory Requirements
Governments worldwide are enforcing stricter data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act. Non-compliance can lead to heavy fines.
4. Business Continuity is Non-Negotiable
Downtime can weaken organizations. A resilient system ensures that operations continue, even in the face of an attack.
5. Customer Trust
Cyber incidents erode customer confidence. Showing resilience reassures stakeholders that the organization is capable of safeguarding sensitive information.
Key Pillars of Cyber Resilience
Building cyber resilience requires a structured approach. Here are the four core pillars:
1. Identify and Protect
Organizations must understand their digital assets, networks, and data. This includes:
- Conducting risk assessments
- Identifying critical systems
- Deploying firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication
- Training employees on security best practices
2. Detect
The faster you detect an attack, the quicker you can respond. This involves:
- Real-time monitoring tools
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems
- Intrusion detection systems
- Threat intelligence sharing
3. Respond
A well-defined incident response plan ensures minimal disruption. Key elements:
- Clear roles and responsibilities
- Crisis communication plans
- Backup systems are ready for activation
- Regular drills and simulations
4. Recover and Adapt
Recovery goes beyond restoring systems. It is about learning and improving. Actions include:
- Restoring data from secure backups
- Updating security policies
- Conducting post-incident reviews
- Strengthening weak points discovered during the attack
Strategies to Build Cyber Resilience
Here are few strategies organizations can adopt to strengthen cyber resilience and ensure business continuity in the face of attacks:
1. Cyber Resilience Framework
Adopt frameworks like NIST or ISO 27001 to guide structured risk management, incident response, and recovery planning, ensuring organizational resilience against evolving threats.
2. Employee Training
Human error drives most breaches. Regular training on phishing, password hygiene, and suspicious activity reporting strengthens employee vigilance and organizational cyber defense.
3. Adopt a Zero-Trust Architecture
Zero Trust means never trust, always verify. Authenticate and authorize every access request continuously, reducing risks from insider threats and external breaches.
4. Regular Backups and Redundancy
Keep both offline and cloud backups. Regularly test recovery systems to make sure data stays safe, accessible, and reliable during cyberattacks, ransomware, or major system failures. Enterprise backup and recovery solutions automate these requirements while adding immutable storage and rapid restoration capabilities essential for cyber resilience.
5. Monitoring & Intelligence
Use AI-driven tools and real-time global threat intelligence to proactively monitor, detect anomalies, and anticipate potential cyber threats before they materialize.
6. Create an Incident Response Team
Assemble a multidisciplinary IRT including IT experts, legal advisors, executives, and PR professionals to coordinate rapid, structured responses during cyberattacks effectively.
7. Third-Party Risk Management
8. Regular Testing and Drills
Run red team and penetration testing exercises to find weaknesses, check readiness, and build resilience by simulating real cyberattacks and practicing recovery.
Advantages of Cyber Resilience
Here are the key advantages organizations gain by adopting strong cyber resilience strategies:
1. Business Continuity
Cyber resilience strategies guarantee essential operations remain functional during disruptions, minimizing downtime, financial damage, and customer dissatisfaction effectively.
2. Stakeholder Trust
Showing that the company can bounce back from problems gives confidence to customers, investors, and regulators. It helps build long-lasting trust, a good reputation, and strong relationships in the company’s online systems.
3. Financial Protection
Having quick recovery and continuity plans helps avoid long breaks in operations, protects revenue, and keeps the business running smoothly.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Resilience frameworks align with international standards, ensuring data security, legal compliance, and avoiding fines while supporting sustainable digital business practices consistently.
5. Competitive Advantage
Strong organizations stay ahead of competitors by quickly adjusting to problems, keeping operations running, and maintaining customer trust even during cyber threats.
Disadvantages of Cyber Resilience
Here are the main disadvantages organizations may face when implementing cyber resilience strategies:
1. High Costs
Implementing resilience strategies demands substantial budget allocation for advanced tools, cybersecurity experts, employee training, and continuous monitoring.
2. Implementation Complexity
Coordinating resilience strategies within large enterprises is challenging, requiring cross-department collaboration, governance, layered technologies, and consistent cultural change initiatives.
3. Operational Delays
Doing regular practice drills and penetration tests helps a company stay prepared, but they can also cause temporary work delays, lower productivity, and make employees feel frustrated while the tests are happening.
4. False Security
Outdated strategies reduce effectiveness, creating dangerous complacency. Regular updates are essential to address evolving cyber risks and maintain genuine resilience.
Real World Examples
Here are notable examples that demonstrate both the strengths and weaknesses of cyber resilience in action:
1. Maersk and the NotPetya Attack (2017)
Shipping giant Maersk was hit by a devastating ransomware attack that shut down its operations worldwide. Thanks to a single unaffected backup server in Africa, they restored their systems and resumed operations within days—an extraordinary act of resilience.
2. Equifax Data Breach (2017)
Equifax faced severe criticism after a breach exposed the data of 147 million people. Their slow recovery and poor communication highlight the consequences of lacking resilience.
3. Sony Pictures Hack (2014)
Despite a massive data breach, Sony Pictures managed to bounce back by restructuring its IT systems, improving its security culture, and restoring customer trust.
Future of Cyber Resilience
As technology evolves, cyber resilience will become even more critical. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. AI-Driven Cyber Defense
Artificial intelligence enhances real-time threat detection, prediction, and neutralization, enabling faster responses to attacks and strengthening resilience against advanced cyber threats globally.
2. Cloud Resilience
3. Quantum Computing
Future quantum computers could break classical encryption. Preparing with quantum-resistant algorithms ensures data confidentiality and resilience against emerging cyber risks.
4. Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance provides financial protection, covering recovery expenses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities after disruptive cyber incidents or devastating attacks.
5. Resilience by Design
Integrating resilience into every digital transformation stage ensures secure architectures, adaptive recovery, and sustained operations despite inevitable cyber challenges.
Final Thoughts
Cyber resilience is essential in today’s digital world, where cyberattacks are inevitable. By adopting proactive strategies, organizations minimize risks, recover quickly, and preserve stakeholder trust. True resilience combines people, processes, and technology to withstand disruptions. Companies embracing this mindset not only survive threats but also strengthen competitiveness, ensuring long-term growth and adaptability in an uncertain cyber landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is cyber resilience different from disaster recovery?
Answer: Disaster recovery focuses on restoring IT systems after an outage. Cyber resilience is broader, ensuring both IT and business operations continue during and after cyber incidents.
Q2. Is cyber resilience only for large corporations?
Answer: No. Cyber resilience is not limited to large corporations—small and medium businesses also face risks and must adopt scalable strategies.
Q3. How often should organizations test their resilience?
Answer: Regularly—at least quarterly for critical systems. Testing ensures plans remain effective against evolving threats.
Q4. Can outsourcing help in building cyber resilience?
Answer: Yes. Managed security service providers (MSSPs) can enhance resilience by offering expertise, monitoring, and rapid response capabilities.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cyber Resilience” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

