Updated June 12, 2023

Introduction to CSS display property
The CSS display property stipulates an element’s display behavior. In simple terms, this property describes in CSS how components like div, hyperlink, heading, etc., should be put on the web page. The display property, as implied by its name, describes the view of the different sections of a web page.
Explicitly, the display property determines the types of internal and external displays for an element. The outer type aims to set the participation of an element in the flow layout; the inner type wants to set the children’s layout. Additionally, we properly define several other display values with their specific characteristics.
Syntax and Parameters of CSS display property
You can write the syntax for the display property in CSS as shown below:
display: value;The display property uses the following parameters:
- inline: We use an element to display it as an inline element.
- block: Use to view an element as a block element.
- contents: It removes the container.
- flex: Use to view an element as a flex container at the block level.
- grid: Use to view an element as a grid container at the block level.
- inline-block: Use to view an element as a block container at the inline level.
- inline-flex: Use to view an element as a flex container at the inline level.
- inline-grid: Use to view an element as a grid container at the inline level.
- list-item: It shows all elements in < li > element.
- table: This defines the behavior for all elements as < table >.
- table-caption: The behavior is set as < caption > for all elements.
- table-column-group: The behavior is set as < column > for all elements.
- table-header-group: The behavior is set as < header > for all elements.
- table-footer-group: The behavior is set as < footer > for all elements.
- table-row-group: The behavior is set as < row > for all elements.
- table-cell: The behavior is set as < td > for all elements.
- table-column: The behavior is set as < col > for all elements.
- table-row: The behavior is set as < tr > for all elements.
- none: Use to eliminate the element.
- initial: Use to place the default value.
- inherit: It inherits the elements from the parent’s elements.
For instance,
p {
display: inline;
}How does display property work in CSS?
- HTML takes the default display property value from the HTML standards or the default style sheet of the browser/user.
- The CSS display values that create block-level elements behavior are block, list-item, and table.
- The block-level elements provide vertically different document lines, with a line break before and after the document.
- HTML elements such as < div >, < p >, < h1 >, < h2 >, among others, traditionally display block actions.
Examples of CSS display property
Given below are examples of CSS display properties:
Example #1
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title> CSS Display Property Example </title>
<style>
.main {
margin:30px;
text-align:center;
}
#para1{
height: 120px;
width: 180px;
background: darksalmon;
display: block;
}
#para2{
height: 120px;
width: 180px;
background: olive;
display: block;
}
#para3{
height: 120px;
width: 180px;
background: fuchsia;
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2> Display Block Example </h2>
<br>
<div class = "main">
<div id="para1"> Java is a highly object-oriented, platform-independent and secure programming language. </div>
<div id="para2"> Python is widely used, popular, high level, interpreted general-purpose programming language. </div>
<div id="para3"> HTML is abbreviated as Hyper Text Mark up Language the most expanded language used worldwide to display the result in the web pages.</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:

In the above example, we use the block property to display the element in the block structure. This property positions the div one after the other vertically. Using the block property, the div’s height and width can be altered if the width is not described; then, the div under the block property would then occupy the container width. Hence, we will define the three div blocks with specified colors, height, and width attributes.
Example #2
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title> CSS Display Property Example </title>
<style>
.main {
margin:30px;
}
#para1{
background: darksalmon;
display: inline;
}
#para2{
background: olive;
display: inline;
}
#para3{
background: fuchsia;
display: inline;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2> Display Inline Example </h2>
<br>
<div class = "main">
<div id="para1"> Java </div>
<div id="para2"> HTML </div>
<div id="para3"> CSS </div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:

In the above example, we use inline property values, which display the inline structure. In addition, it places the elements horizontally. This property ignores the height and the width set by the user.
Example #3
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title> CSS Display Property Example </title>
<style>
.main {
margin:30px;
}
#para1{
height: 120px;
width: 180px;
background: darksalmon;
display: inline-block;
}
#para2{
height: 120px;
width: 180px;
background: olive;
display: inline-block;
}
#para3{
height: 120px;
width: 180px;
background: fuchsia;
display: inline-block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2> Display Inline-block Example </h2>
<br>
<div class = "main">
<div id="para1"> Inline-block Element1 </div>
<div id="para2"> Inline-block Element2 </div>
<div id="para3"> Inline-block Element3 </div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
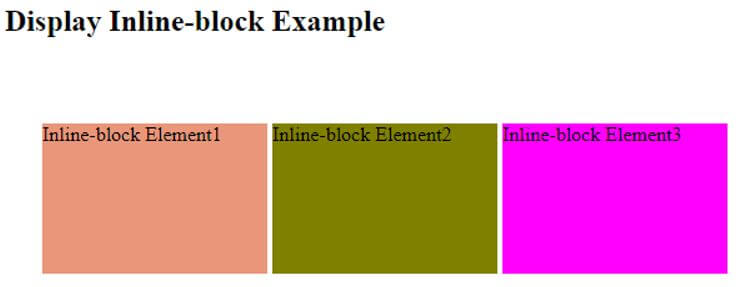
In the above example, we have used the inline-block property to create the block box in the same line and set the div element’s height and width. Hence, we will treat the created block element as an inline box.
Example #4
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title> CSS Display Property Example </title>
<style>
body {
display: inline;
}
p {
display: inherit;
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2> Display Inherit Example </h2>
<br>
<p> EDUCBA is a leading global provider of skill based education. </p>
<p> It is online learning model along with amazing 2500+ courses. </p>
</body>
</html>Output:

In the above example, we have used the inheritance property, which inherits the property from the parent element. To use this property, we have set the body to an inline property, which brings both paragraphs in one line.
Conclusion
So far, we have seen the display property, one of CSS’s most essential and effective properties. This can be very helpful to make web pages that look different and yet still meet the web standards. The web page recognizes each HTML item as a box, and we determine how to display certain boxes or whether to show or hide them using the display property.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “CSS Display Property” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


