Updated July 26, 2023
Difference Between CRR vs SLR
The Central Bank of every country is responsible for keeping a check and having certain control measures on inflation and money circulation in the industry. The central bank uses factors like CRR vs SLR to keep it under a tap.
CRR is the abbreviated version of the Cash Reserve Ratio. It is the mandatory ratio that must be retained with the central bank of the country. It is compulsory for each bank to maintain a specific percentage of their net demand and the time liabilities as cash balance with the RBI (Reserve Bank of India).
Banks prescribe and require a specified percentage of net demand and time liabilities to be maintained as an obligatory reserve known as a Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR).
These two ratios highly influence the factors of inflation and a country’s growth rate. Both Cash Reserve Ratio and Statutory Liquidity Ratio are financial tools that reduce the bank’s lending capacity and manage money flow in the market.
CRR – Cash Reserve Ratio
- The Central Bank of India requires commercial banks to keep a certain percentage of their total deposits in the form of cash reserves.
- The banks are not permitted to use this amount with the Central Bank for economic and commercial purposes.
- It is the mode of maintaining economic liquidity and the flow of money.
- If the Reserve Bank of India wishes to increase the money supply in the economy, it will reduce the CRR rate., thereby allowing banks to spend/ lend more.
- Conversely, if the RBI plans to limit the money supply in the economy, it will increase the CRR rate, and hence the banks will have limited funds to lend as their greater amount of funds (or cash) shall be blocked with the Reserve Bank.
SLR – Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- The percentage of Net Time and Demand Liabilities the bank keeps in the form of liquid assets.
- A unique way of sustainable stability is by putting a cap on the customer’s credit facility.
- The major reason to have a huge SLR is to fulfill the unexpected demands from the depositors.
- The banks usually maintain a higher SLR than what is required
- Time Liabilities is the amount payable to the depositors after a specific time
- Demand Liabilities is the amount payable to the depositors when the demand arises
For Example:
Consider a CRR rate of 4%. This means for every Rs. 100 deposited, Rs. 4 must be deposited with the Central Bank and shall not be used commercially. The remaining Rs. 96 can be used for commercial and lending purposes.
Consider an SLR rate of 15%. This means the banks shall keep Rs. 15 to meet the customers’ requirements, and the remaining Rs. 85 shall be available to the bank for other operations and commercial purposes.
Head To Head Comparison Between CRR vs SLR (Infographics)
Below is the top 6 difference between CRR vs SLR:
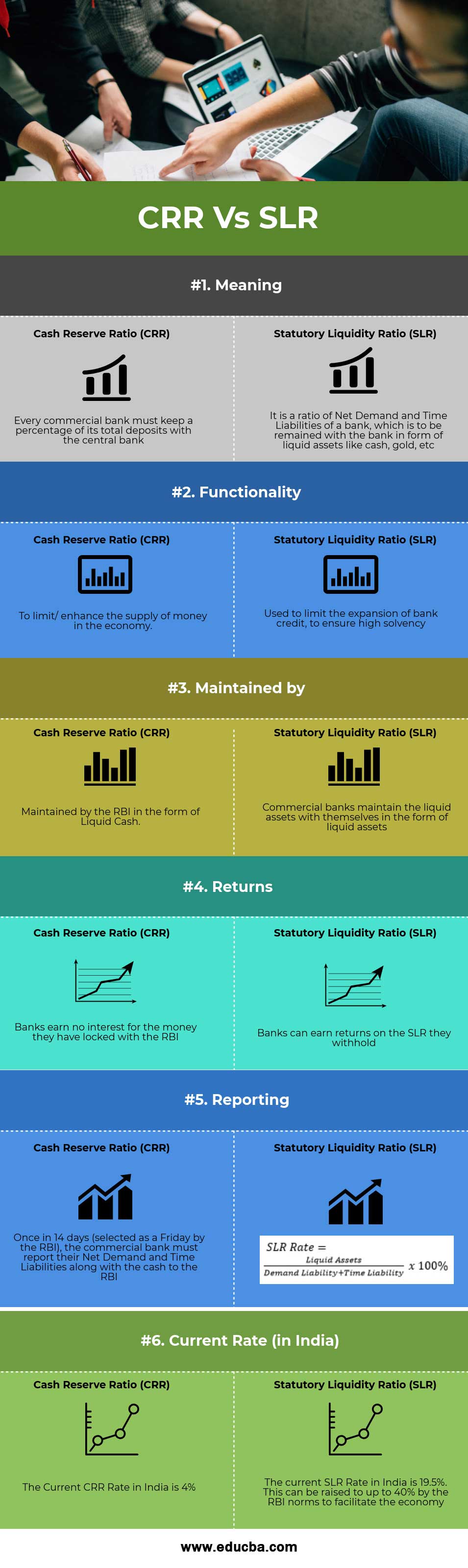
Key Differences CRR vs SLR
Both CRR vs SLR are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences :
- The percentage of the money parked by the commercial banks with the Reserve Bank of India in cash is CRR. In contrast, SLR is a portion of liquid assets to demand and time liabilities withheld with the bank.
- CRR is maintained in the form of cash, whereas the SLR is maintained in the form of liquid assets like gold, treasury bonds, etc.
- Commercial banks earn no interest on the money they have parked with the RBI, whereas they can earn good returns upon the SLR liquid assets they withhold.
- CRR is to regulate the flow of money in the economy, whereas SLR is to keep up with the solvency of the banks
- Moreover, CRR is to govern the country’s liquidity, and SLR is essential for the country’s credit growth.
- The Reserve Bank of India maintains CRR, but it does not maintain the SLR
CRR vs SLR – Comparison Table
Let’s have a look at the Comparison between CRR vs SLR:
| The basis of Comparison | Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) | Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) |
| Meaning | Every commercial bank must keep a percentage of its deposits with the central bank. | It is a ratio of a bank’s Net Demand and Time Liabilities, which is to be retained with the bank in the form of liquid assets like cash, gold, etc. |
| Functionality | To limit/ enhance the supply of money in the economy. | Used to limit the expansion of bank credit, to ensure high solvency |
| Maintained by | Maintained by the RBI in the form of Liquid Cash. | Commercial banks maintain liquid assets with themselves in the form of liquid assets |
| Returns | Banks earn no interest for the money they have locked with the RBI | Banks can earn returns on the SLR they withhold |
| Reporting | Once in 14 days (selected as a Friday by the RBI), the commercial bank must report their Net Demand and Time Liabilities and cash to the RBI. | 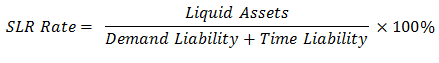 |
| Current Rate (in India) | The Current CRR Rate in India is 4% | The current SLR Rate in India is 19.5%. This can be raised to up to 40% by the RBI norms to facilitate the economy. |
Conclusion
The main responsibility of the Reserve Bank of India is to keep up the supply of money in the economy and to do this. The RBI uses instruments like Repo Rate, Reverse Repo Rate, Cash Reserve Ratio, Statutory Liquidity Ratio, and Bank Rate. Based on the economy and inflation situation, the RBI and the Finance Ministry of the country decide the fate of the inflation rates and the country’s growth rates. To contribute to this, CRR vs SLR are important financial instruments. Both CRR vs SLR are reserves that block the money flow in the economy and thereby reduce the lending and investments in the country.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between CRR vs SLR. Here we also discuss the CRR vs SLR key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more-


