What is Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)?
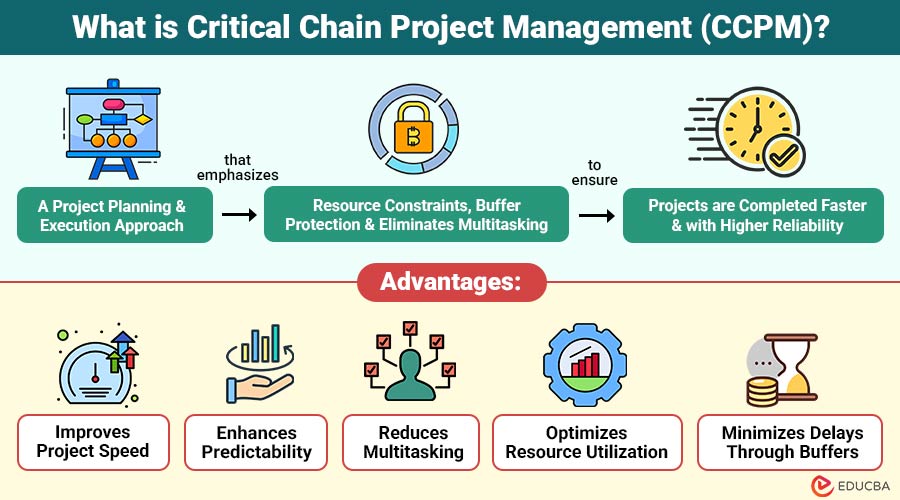
Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) is project planning and execution approach that emphasizes resource constraints, buffer protection, and eliminates multitasking to ensure projects are completed faster and with higher reliability.
Instead of padding every task with safety margins, CCPM bundles uncertainties into shared buffers, allowing teams to focus on flow, resource efficiency, and reducing delays.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- CCPM builds realistic schedules by prioritizing resource constraints to ensure smoother workflow and timely project completion.
- Centralized buffers protect project timelines from uncertainties, improving predictability and preventing cascading schedule delays.
- Single-tasking enhances productivity by reducing multitasking, minimizing context switching, and accelerating overall task execution.
- Buffer management offers proactive project control by highlighting risks early and supporting timely corrective actions.
Why is CCPM Important?
Below are the key reasons why CCPM is so important:
1. Improves Project Speed
CCPM shortens timelines by removing padding, reducing multitasking, ensuring resources, and using centralized protective buffers.
2. Enhances Predictability
CCPM increases schedule reliability through strong buffer management, clear priorities, and transparent project health visualization.
3. Reduces Multitasking
CCPM prevents multitasking, enabling focused work, faster task completion, fewer interruptions, and overall reduced performance inefficiencies.
4. Optimizes Resource Utilization
CCPM improves productivity by addressing resource constraints, preventing overload, prioritizing tasks, and eliminating wasteful idle time.
5. Minimizes Delays Through Buffers
CCPM uses project, feeding, and resource buffers to absorb uncertainties and prevent cascading project delays.
6. Addresses Human Behavior
CCPM reduces procrastination by countering Parkinson’s Law and Student Syndrome through shorter durations and centralized buffers.
Key Concepts of Critical Chain Project Management
Below are the key concepts of CCPM:
1. Critical Chain
Unlike the traditional critical path, the critical chain accounts for resource availability, making it a more realistic indicator of what truly governs project duration.
2. Buffers
CCPM uses three types of buffers to protect the project schedule:
- Project Buffer: Positioned at the project’s conclusion to cover essential chain delays.
- Feeding Buffers: Placed at merge points to protect the critical chain from delays in non-critical paths.
- Resource Buffers: Alerts assigned resources in advance to ensure they are ready when needed.
3. Resource Leveling
Ensures that no single resource is overloaded, reducing delays caused by overcommitment.
4. Single-Tasking
CCPM discourages multitasking. Resources focus on one task at a time to minimize context switching and increase productivity.
5. Buffer Management
Instead of tracking every task, CCPM tracks buffer consumption to monitor progress and proactively mitigate risks.
How does CCPM Work?
Here are the key steps that explain how CCPM is applied in real project environments.
Step 1: Build the Project Network
Start by identifying all tasks, their duration, and dependencies. This is like CPM’s process for mapping the workflow.
Step 2: Identify Resource Constraints
List all shared resources, including people, tools, equipment, and systems. Determine where resource overload is likely to occur and update the task sequence to avoid multitasking or conflicts.
Step 3: Determine the Critical Chain
The chain is formed by the longest path after adjusting for resource constraints. This becomes the key focus for scheduling and monitoring.
Step 4: Remove Safety Padding
Traditional project scheduling often inflates task durations for safety. CCPM cuts these estimates by 30–50% to create aggressive but realistic timelines.
Step 5: Add Buffers
Buffers are introduced to protect the project:
- The project buffer protects the final delivery.
- Feeding buffers protect the critical chain from non-critical paths.
- Resource buffers ensure resource readiness.
Step 6: Execute with Single-Tasking
Team members work without multitasking. They focus completely on the current task, significantly improving throughput.
Step 7: Monitor Using Buffer Management
Instead of micromanaging each task, managers track how fast the buffers are being consumed:
- Green Zone: Buffer consumption is healthy—the project is on track.
- Yellow Zone: Delays are present—prepare corrective actions.
- Red Zone: High buffer consumption—immediate intervention required.
Advantages of Critical Chain Project Management
Here are the key advantages that demonstrate why CCPM strengthens project delivery and overall performance.
1. Improves Project Speed
CCPM shortens timelines by removing padding, reducing multitasking, ensuring resources, and using centralized protective buffers.
2. Enhances Predictability
CCPM increases schedule reliability through strong buffer management, clear priorities, and transparent project health visualization.
3. Reduces Multitasking
CCPM stops people from multitasking, so they can focus better, finish tasks faster, have fewer interruptions, and work more efficiently.
4. Optimizes Resource Utilization
CCPM helps teams work better by not giving them too much work, focusing on the key tasks, and avoiding any wasted waiting time.
5. Minimizes Delays Through Buffers
CCPM uses project, feeding, and resource buffers to absorb uncertainties and prevent cascading project delays.
Disadvantages of Implementing CCPM
Here are the major disadvantages organizations commonly face when adopting Critical Chain Project Management.
1. Cultural Resistance
Teams used to padding tasks or multitasking may oppose CCPM’s aggressive schedules and disciplined single-tasking approach.
2. Requires Accurate Resource Data
Organizations must maintain precise visibility into resource availability to ensure realistic planning and avoid scheduling conflicts.
3. Changes in Mindset
Shifting from task-focused tracking to buffer-based control demands proper training, cultural alignment, and organizational behavioral changes.
4. Not Ideal for Every Project
Projects with high uncertainty, frequent changes, or exploratory R&D work may struggle to implement CCPM effectively.
Real-World Use Cases of CCPM
Here are real-world use cases of how different industries apply CCPM to improve project performance and outcomes.
1. Manufacturing & Production
Manufacturers use CCPM to remove delays, speed up production, use workers and machines better, and deliver products on time.
2. Software Development
Software teams use CCPM to cut down multitasking, handle changing priorities better, make their work process smoother, and deliver projects more consistently.
3. Construction
Construction projects apply CCPM to enhance scheduling accuracy, allocate resources efficiently, control risks with buffers, and improve on-time completion rates.
4. Aerospace & Defense
Aerospace and defense companies use CCPM to keep projects on track, manage resources smoothly, avoid schedule delays, and deliver complicated projects more reliably.
Final Thoughts
Critical Chain Project Management transforms project planning and execution by emphasizing resource limits, eliminating multitasking, and using protective buffers. It significantly improves delivery timelines and performance by addressing constraints that truly impact completion. Widely adopted across industries, CCPM enables predictable, faster, and efficient outcomes. Applied effectively, it allows teams to shift from reactive firefighting to proactive control and continuous improvement in modern project environments.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Critical Chain Project Management ” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
