What is Cost Optimization?
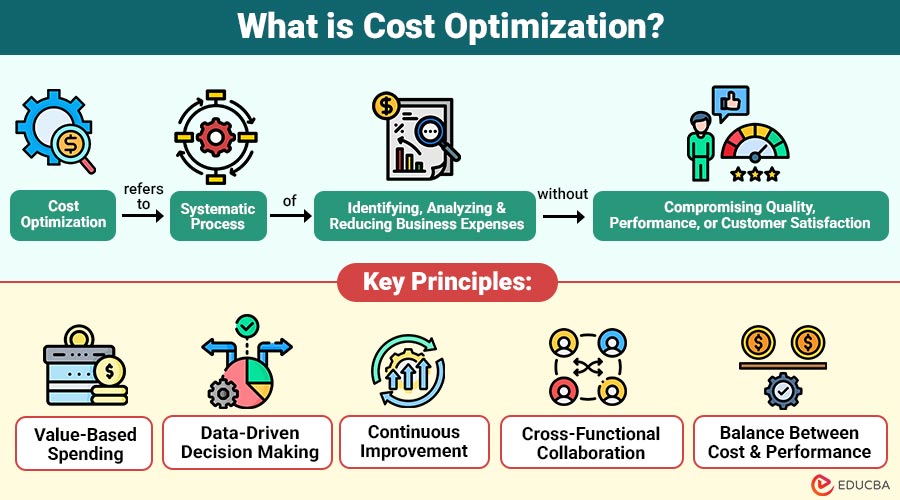
Cost optimization refers to the systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and reducing business expenses without compromising quality, performance, or customer satisfaction. To ensure every dollar spent delivers the business the greatest possible value, it requires making data-driven decisions.
Cost optimization is not a one-time initiative. It is an ongoing discipline that continuously evaluates spending patterns, resource utilization, and operational efficiency to align costs with strategic objectives.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Cost optimization is a continuous, value-driven approach that reduces waste while strengthening efficiency, performance, and long-term sustainability.
- Data-driven insights, analytics, and transparency help organizations clearly see where costs come from and focus on changes that deliver the biggest savings.
- Successful cost optimization balances savings with quality, employee morale, customer experience, and overall strategic business growth goals.
- Cross-functional collaboration, leadership commitment, and continuous review ensure that cost optimization consistently delivers a sustainable competitive advantage over time.
Key Principles of Cost Optimization
The following are the fundamental key principles that help businesses strategically and sustainably optimize costs.
1. Value-Based Spending
Every cost should directly or indirectly contribute to business value, revenue generation, customer experience, or strategic growth.
2. Data-Driven Decision Making
Involves accurate data, analytics, and performance indicators to find inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
3. Continuous Improvement
To keep up with changing company goals, new technologies, and market trends, businesses need to review their costs regularly.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Effective cost optimization requires collaboration across finance, operations, IT, HR, procurement, and leadership teams.
5. Balance Between Cost and Performance
Reducing costs should not negatively impact product quality, employee morale, or customer satisfaction.
Types of Cost Optimization
Cost optimization can be broadly classified into the following types based on business functions and areas of cost control:
1. Operational Cost Optimization
Examples:
- Process automation
- Lean management
- Reducing rework and waste
2. IT Cost Optimization
Cuts technology costs by improving infrastructure, managing software and cloud use, automating processes, and removing unused IT resources.
Examples:
- Cloud cost management
- License optimization
- Infrastructure consolidation
3. Workforce Cost Optimization
Controls employee costs by planning work, improving productivity, using automation, training staff, and offering fair pay, all without lowering engagement.
Examples:
- Workforce planning
- Skill-based staffing
- Reducing overtime and attrition
4. Procurement and Vendor Cost Optimization
Examples:
- Contract renegotiation
- Vendor consolidation
- Strategic sourcing
5. Financial Cost Optimization
Enhances financial efficiency by improving budgeting, forecasting accuracy, cash flow management, capital allocation, and cost control across business functions.
Examples:
- Zero-based budgeting
- Cost transparency models
- Expense control frameworks
Cost Optimization Techniques
Cost optimization techniques are systematic approaches organizations use to reduce expenses, improve efficiency, and maximize value across business operations.
1. Process Automation
Automating repetitive manual tasks reduces labor costs, minimizes errors, boosts productivity, and significantly improves overall operational efficiency.
2. Lean and Six Sigma Practices
Lean and Six Sigma effectively eliminate waste, streamline workflows, improve quality, reduce variability, and lower overall operational costs.
3. Cloud and Technology Optimization
Using the right amount of cloud and tech resources, tracking usage, and choosing scalable solutions helps avoid extra costs.
4. Strategic Outsourcing
Strategic outsourcing of non-core activities to specialized vendors lowers costs, increases efficiency, and enhances service quality and reliability levels.
5. Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-based budgeting requires justifying every expense from scratch, improving cost control, transparency, accountability, and financial discipline across organizations.
6. Spend Analytics
Spend analytics looks at a company’s expenses to find wasted money, extra vendors, inefficiencies, and ways to save.
Benefits of Cost Optimization
Cost optimization delivers measurable business benefits by improving financial performance, operational efficiency, and strategic flexibility.
1. Improved Profitability
Reducing operational expenses directly increases profit margins, enabling higher returns without requiring additional revenue growth from existing business sources.
2. Better Resource Utilization
Makes sure staff, technology, and money are used efficiently to boost productivity, reduce waste, and improve overall performance.
3. Increased Business Agility
Optimized cost structures enable organizations to adapt more quickly, reallocate resources more quickly, and respond effectively to changing market conditions and uncertainties.
4. Enhanced Decision Making
Using data helps businesses make better budgets, predict the future more accurately, choose the best investments, and make smarter decisions. It also ensures everyone in the company is clear, confident, and working together.
5. Competitive Advantage
Cost-optimized organizations gain a competitive advantage through greater pricing flexibility, increased innovation investment, operational efficiency, and sustained market leadership.
Challenges in Cost Optimization
Despite its benefits, it presents several challenges that can impact effectiveness, sustainability, and long-term business value.
1. Resistance to Change
Employees and managers might resist cost-saving efforts because they worry about job security, company culture, or extra work.
2. Short-Term Mindset
Prioritizing immediate savings over long-term value can significantly undermine sustainability, innovation, and overall organizational performance.
3. Lack of Data Visibility
When data is hard to see or reports are wrong, companies can’t find what really drives costs or make smart decisions.
4. Over-Optimization
Excessive cost reduction efforts can negatively affect product quality, customer satisfaction, employee morale, and long-term brand value.
5. Siloed Decision Making
Departmental silos and poor cross-functional collaboration reduce alignment, slow decision-making, and weaken overall cost optimization outcomes across organizations.
Cost Optimization Best Practices
Cost optimization best practices help organizations achieve sustainable savings by aligning cost initiatives with strategy, performance metrics, and long-term value creation.
1. Strategic Alignment
Make sure cost-cutting efforts match the company’s goals so savings help the business grow, stay competitive, and focus on long-term priorities.
2. Clear KPIs and Metrics
To analyze cost effectiveness, monitor progress, find gaps, and promote accountability across all functions, clearly define KPIs and performance indicators.
3. Real-Time Cost Monitoring
Use dashboards to monitor costs in real time, helping teams track spending, make fast decisions, and prevent budget overspending.
4. Leadership and Collaboration
5. Long-Term Value Focus
To maintain performance, innovation, customer happiness, and steady, long-term growth, prioritize long-term value creation over short-term cost reduction.
6. Continuous Review
Regularly check and improve costs to meet changing business needs, remove waste, and stay competitive in a fast-moving market.
Real-World Examples
Here are practical, real-world examples showing how organizations optimize costs while maintaining efficiency and business performance.
1. IT Cost Optimization
A large company moved its systems to the cloud and tracked how resources were used, which cut infrastructure costs by 30% and made scaling easier.
2. Workforce Cost Optimization
A company used employee data to plan staffing and keep employees longer, saving on hiring and training. A manufacturing firm also cut costs by using fewer suppliers and renegotiating contracts, without disrupting its supply chain.
Final Thoughts
Cost optimization is a strategic, continuous, and value-driven approach to managing expenses. It uses data, technology, and teamwork across departments to lower costs without hurting performance. It focuses on spending money where it creates the most value, rather than just cutting expenses. In competitive markets, this approach helps organizations stay efficient, flexible, and successful in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is cost optimization the same as cost reduction?
Answer: No, cost optimization focuses on maximizing value while reducing unnecessary costs, whereas cost reduction often prioritizes short-term savings.
Q2. How often should cost optimization be performed?
Answer: Cost optimization should be a continuous process with regular reviews.
Q3. Can cost optimization impact employee morale?
Answer: If poorly managed, yes. Transparent communication and value-based decisions help minimize negative impact.
Q4. What tools support cost optimization?
Answer: Analytics platforms, ERP systems, cloud cost management tools, and spend analysis software.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cost Optimization” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

