Updated March 18, 2023

Introduction to Control Statement in C++
A control statement is used in a programming language to control the flow of the program. They are nothing but a keyword or statements that are used in a program to transfer the flow of control to another statement based on the conditions. Based on the given condition, it evaluates the result and executes the corresponding statements. Control statements are the statement that controls the flow of the program in order to execute the piece of the code using various controls statement like if statement, if-else statement, break statement, continue statement, for loop, while loop, do while loop. In this article, we are going to discuss the various control statements available in the C++ language with the help of examples.
Different Control Statement in C++
Below is the different control statement in C++.
1. C++ Switch Statement
From the multiple conditions, a C++ Switch statement executes a single statement. It’s like a ladder statement if-else-if in C++.
Syntax of C++ Switch statement
Switch(expression)
{
case value1:
//code should be executed;
break;
case value2:
//code should be executed;
break;
…
Default:
//Code to execute if not all cases matched
break;
}Example of C++ Switch Statement
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int number;
cout << "To check the grade enter a number:";
cin >> number;
switch (number)
{
case 2: cout << "It is 2"; break;
case 3: cout << "It is 3"; break;
case 4: cout << "It is 4"; break;
default: cout << "Not 2, 3 or 4"; break;
}
}Output:
2. C++ if-else statement
To test the condition in C++ programming if the statement is been used. They are different types of if statement
- If statement in C++
- If-else statement in c++
- If-else-if ladder in c++
a. If statement in C++
C++ if the condition is evaluated by the argument. If the condition is valid, it is executed.
Syntax of if statement in c++
if(condition)
{
//code should be executed;
}Example of if Statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int number = 10;
if (number % 2 == 0)
{
cout << "The Number you have Enter it is Even";
}
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
b. If else statement in C++
The statement C++ if-else also checks the condition. The declaration executes if the condition is true otherwise the block is carried out.
Syntax of the if-else statement in c++
if(condition)
{
//code should be executed;
}else
{
//code should be executed;
}Example of if-else Statement
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int number = 15;
if (number % 2 == 0)
{
cout << "The Number you have Enter it is Even";
}
else
{
cout << "The Number you have Enter it is Odd";
}
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
c. If-else-if ladder statement in C++
The C++ if-else-if ladder declaration executes from multiple statements in one condition.
Syntax of if-else ladder statement in c++
If(condition1)
{
// code should be executed if condition1 is true
}
else if(condition2)
{
// code should be executed if condition2 is true
}
else if(condition3)
{
// code should be executed if condition3 is true
}
. . .
else{
// code should be executed if all condition is false
}Example of if-else ladder Statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
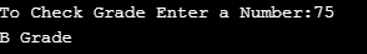
int number;
cout << "To Check Grade Enter a Number:";
cin >> number;
if (number < 0 || number > 100)
{
cout << "wrong No";
}
else if(number >= 0 && number < 40){
cout << "Fail";
}
else if (number >= 40 && number < 59)
{
cout << "D Grade";
}
else if (number >= 60 && number < 70)
{
cout <<" C Grade";
}
else if (number >= 71 && number < 79)
{
cout << "B Grade";
}
else if (number >= 80 && number < 89)
{
cout << "A Grade";
}
else if (number >= 90 && number <= 100)
{
cout << "A+ Grade";
}
}Output:
3. For Loop in C++
The C++ loop is used multiple times to iterate a part of the program. It is recommended that you use for loops when the iteration number is set. For loops, it is recommended.
Syntax of for loop statement in c++
For(initialization; condition; incr/decr){
//code should be executed;
}Example of for loop Statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for(int i = 2; i <= 20; i++){
cout << i << "\n";
}
}Output:

4. C++ Nested For Loop
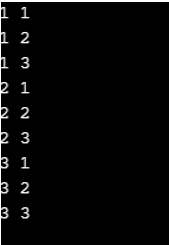
In C++, we can use the loop inside the loop, called loop nest. The inner loop is fully executed once the external loop is executed.
Example of Nested Loop in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= 3; j++){
cout << i << " "<< j << "\n";
}
}
}Output:
5. C++ While Loop
In C++, the loop is used several times for the iteration of a part of the program. If the iteration number is not set, it is advisable to use the loop rather than the loop.
Syntax of while loop statement in c++
While(condition0
{
//code should be executed;
}Example of while Loop in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int i = 5;
while(i <= 20)
{
cout << i << "\n";
i++;
}
}Output:

Nested Example of While loop in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int i = 2;
while(i <= 5)
{
int j = 3;
while (j <= 3)
{
cout << i << " " << j << "\n";
j++;
}
i++;
}
}Output:

6. Do while loop statement in C++
C++ is used many times to iterate a part of the software. It is advised that you use a do-while loop, if the number of iteration is not known and the loop must be performed at least once.
Syntax of a do-while loop statement in c++
do
{
//code should be executed;
}
While(condition);Example of do-while loop statement;
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int j = 2;
do{
cout << j << "\n";
j++;
} while (j <= 10) ;
}Output:

Nested Do-while loop statement in C++
In C++, when you use do-while in another do-while loop, the nested do-while loop is known. For each external loop the nestled do-whilst loop is completely executed.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int j = 1;
do{
int k = 1;
do{
cout << j << "\n";
k++;
} while (k <= 4) ;
j++;
} while (j <= 3) ;
}Output:

7. Break Statement in C++
The break C++ is used for loop breakage or statement switching. It breaks the program’s current flow in the given state. In the case of an inner loop, only an internal loop splits.
Syntax of break statement in C++
Jump-statement;
break;Example of Break statement in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int j = 1; j <= 10; j++)
{
if (j == 10)
{
break;
}
cout << j << "\n";
}
}Output:

Inner loop break statement in C++
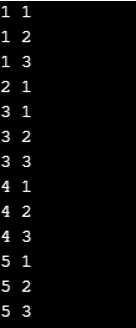
The C++ break declaration only breaks the inner loop if you use an inside break statement.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for(int j = 1; j <= 5; j++){
for(int k = 1; k <= 3; k++){
if(j == 2&&k == 2){
break;
}
cout << j << " " << k << "\n";
}
}
}Output:
8. Continue Statement in C++
The declaration C++ is used for the continuation of the loop. The current program flow continues and the remaining code is omitted at a specified state. If there is an inner loop, only an inner loop continues.
Syntax of continue statement in C++
Jump-statement;
Continue;Example of break statement in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for(int j = 1; j <= 10; j++){
if(j == 10){
continue;
}
cout << j << "\n";
}
}Output:

9. Goto statement in C++
The C+ + goto declaration is also called a jump declaration. The control to the other part of the program is transferred. It saves to the specified label unconditionally.
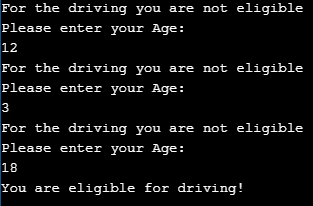
Example of Goto Statement in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ineligible:
cout << "For the driving you are not eligible \n";
cout << "Please enter your Age:\n";
int age;
cin >> age;
if (age < 18){
goto ineligible;
}
else
{
Cout << "You are eligible for driving!";
}
}Output:
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Control Statement in C++. Here we discuss the basic concept, Different Control Statement in C++ along with the various Syntax, Examples, and Outputs. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–


