Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Continue Statement in C
Here, we are going to learn about the continue statement in C. This statement is majorly used in the case of iterators or in the case of looping. As the name already suggests, this statement makes sure that the code continues running after a particular statement is executed. It is used in the same way as the break statement, but the break statement would stop the execution of the loop or series of statements, but the continue statement in return would continue the execution of the code.
Below is the syntax for the continue statement in C.
Syntax:
continue;As already mentioned, the continue statement is used in loops. So the only syntax for the statement would be like above.
Flow Chart
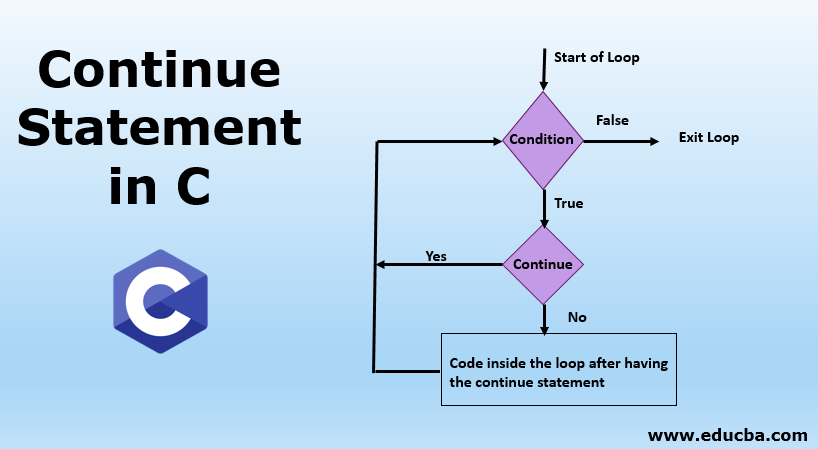
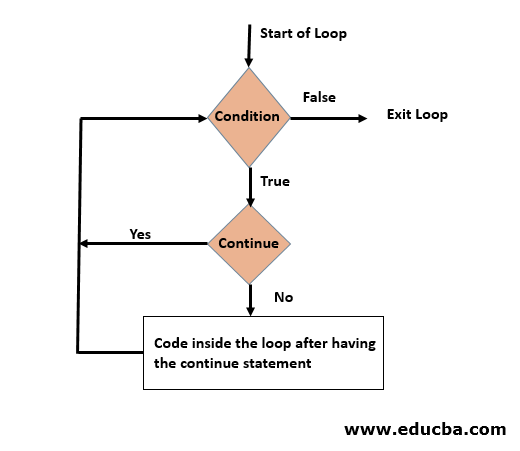
We can understand it better through a flow chart; let’s see it below.
Explanation
- As already known, any loop starts with a condition, and there would be two scenarios for it. One is the statement that has to be executed when a condition is true and others when it is false.
- When a condition is false, it is going to obviously exit the loop.
- And when a condition is true and have our continue statement, the iterator again goes back to the condition, and the above process continues.
- If the condition does not have that continue statement, then the code below is executed.
Now let’s move on to use this statement in our program and see how it works.
Examples
We will have a look at 3 examples of how to continue statement can be used in C language.
Example #1
Finding odd numbers from o to 20.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
{
if(i%2==0)
{
continue;
}
printf("%d ",i);
}
}Output:
![]()
As per the observation, we can see how the program works:
- We declared a variable i.
- We made for a loop by initializing the value of I to 0 and incrementing it by one till the number is less than 20.
- And then we have another condition that if, modulo division of I with 2 is zero; that is it would denote an even number, then we are using our continue statement, which is, in turn, iterating the program back to them for a loop by incrementing its value by 1.
- If the variable I will not be an even number, then the print statement is being executed, which in turn prints only odd numbers.
Now, what if we try to write some code or some statements after a continue statement? Will those are executed? Let’s check here.
We have just modified the above program; we have just added a print statement below the continue statement.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
{
if(i%2==0)
{
continue;
printf("This will not be executed");
}
printf("%d ",i);
}
}</code>Output:
![]()
The same output as the first example program is obtained. Through this change, we can tell that after the continue statement is encountered; the iteration directly goes above again. Any statement to the immediate below or continue statement present in the same loop or if/else condition will not be executed.
Example #2
Let a movie theater has 30 seats, and 5 seats from the 15th seat are booked, so how can we show the remaining seats to people.
We are trying to write this using a do-while loop, and we can write in a similar way as above just to display the numbers.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int a = 0;
/* do loop execution */
do {
if( a == 15) {
a = a + 5;
continue;
}
printf("%d ", a);
a++;
} while( a < 30 );
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
These are the steps on how we are writing this code.
- We initialized the value of a to zero, and the having do loop.
- Then we are having if a loop with the condition of variable a being equal to 15.
- Then incrementing the value of a by 5 and then using continue to start the loop again.
- Then we can get the numbers after 20, and then our while loop will check the value for ‘a’ value till 30 numbers.
Example #3
Print stars in increasing order and skips printing the row with star count 7.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 1;
int count = 0;
for (int a = 1; a <= 10; )
{
if (count < a)
{
printf("* ");
count++;
continue;
}
if(count==6)
{
count++;a++;
continue;
}
if (count == a)
{
printf("\n");
a++;
count = 0;
}
}
}Output:
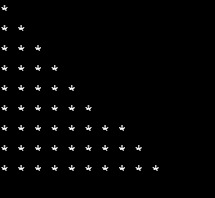
What exactly did we do here?
- Firstly, we declared and initialized two values. One for the line count denoted by ‘a’ and the other for the number of star count that is denoted by ‘count’.
- Then we are running for loop for the number of lines less than 10.
- And inside that, we have 3 if loops.
- The first if loop would print the stars and make sure that the line number is in sync with the stars’ number.
- The third if the loop would increment the line number once the line count and a number of stars count are equal.
- The second if the loop is our condition where if we encounter count as 6, we are just incrementing both count and line number such that line number 7 having 7 stars is prohibited from printing.
We have seen different examples here.
So as an exercise, can you try printing only even the number of stars in decreasing order starting from number 20?
And in the same way, can you try writing this continue statement in a case functionality?
Conclusion – Continue Statement in C
I hope you had a good time learning about the continue statement and understood where exactly we need this statement. We had discussed where we can use it and how it can help us in different programming scenarios. Keep trying and playing around, continue statements in different scenarios and have fun learning.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Continue Statement in C. Here we discuss the syntax, flowchart, and different examples of continue statements in c with code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


