What is Content Syndication?
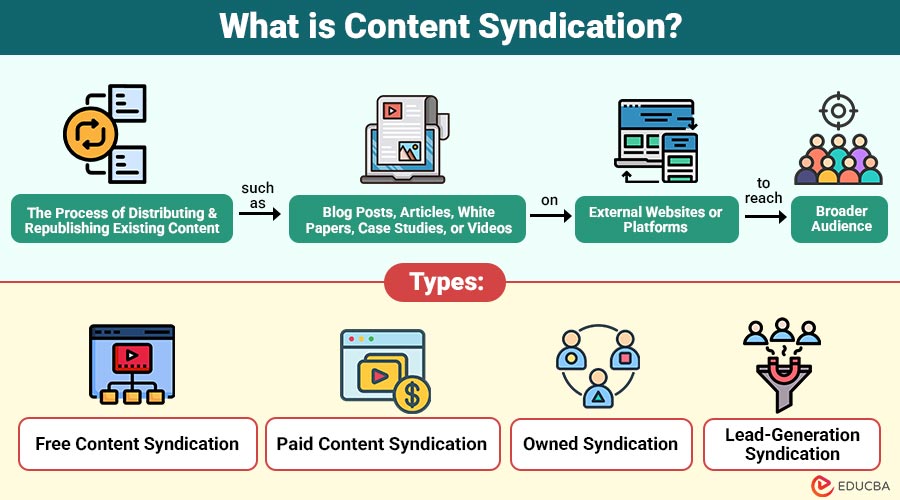
Content syndication is process of distributing and republishing existing content—such as blog posts, articles, white papers, case studies, or videos—on external websites or platforms to reach a broader audience.
Instead of publishing content only on your own website, you allow third-party platforms to share it, either in full or as an excerpt with a link back to the source. The goal is to attract new audiences, drive traffic, and generate leads while maintaining content ownership.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Content syndication amplifies reach by republishing existing assets on relevant third-party platforms to attract new audiences.
- When executed correctly, content syndication drives qualified traffic and leads while preserving brand ownership and authority.
- Successful syndication requires careful partner selection, SEO safeguards, performance tracking, and alignment with broader marketing goals.
- Reusing high-performing content through syndication improves marketing efficiency, accelerates market entry, and maximizes overall ROI potential.
How Content Syndication Works?
It typically follows these steps:
1. Content Selection
You identify high-performing, evergreen content to ensure relevance, value, and long-term audience engagement across platforms.
2. Syndication Partner Identification
Suitable publishers, industry websites, or syndication networks are selected based on audience relevance and credibility.
3. Content Distribution
You can republish selected content as full articles, summaries, or gated assets across third-party platforms.
4. Audience Engagement
New audiences discover, read, share, and interact with the syndicated content on partner platforms.
5. Traffic or Lead Capture
Interested readers are redirected to the original website or converted into qualified leads.
Types of Content Syndication
Below are the main types of content syndication commonly used by businesses to expand reach, visibility, and lead generation.
1. Free Content Syndication
Content is shared on third-party sites at no cost, gaining exposure, backlinks, and organic traffic.
2. Paid Content Syndication
Companies pay networks or publishers to distribute content to targeted audiences, thereby effectively boosting reach.
3. Owned Syndication
Content is republished on the brand’s own channels, like partner blogs, microsites, or newsletters.
4. Lead-Generation Syndication
Gated content collects user information, generating qualified leads while delivering valuable educational material.
Difference Between Content Syndication and Content Distribution
The table below highlights the key differences between content syndication and content distribution.
| Aspect | Content Syndication | Content Distribution |
| Purpose | Republish content on external sites | Promote content across channels |
| Ownership | Retained by original publisher | Fully owned by the brand |
| Reach | New third-party audiences | Existing and new audiences |
| Examples | Industry blogs, media sites | Email, social media, SEO |
Benefits of Content Syndication
Here are the benefits that help businesses expand reach, generate leads, and maximize content value.
1. Increased Brand Visibility
Republishing content on reputable platforms effectively exposes the brand to larger, more targeted, and more relevant audiences.
2. Lead Generation
Gated content syndication enables businesses to generate high-quality leads, especially in B2B marketing.
3. Improved Website Traffic
Syndicated content links drive referral traffic back to the original website, increasing engagement and visibility.
4. Cost-Effective Marketing
Reusing existing content reduces the need for constant content creation, saving significant time, effort, and marketing resources.
5. Faster Market Penetration
Syndication provides faster access to new markets, industries, and audiences through established external platforms.
Challenges of Content Syndication
While beneficial, it also presents challenges:
1. Lead Quality Variations
Some leads generated by syndicated content may not convert well, reducing overall marketing effectiveness.
2. Content Control Limitation
Brands have limited control over how syndicated content appears on third-party websites or platforms.
3. SEO Risks
Incorrect implementation of syndicated content can harm search rankings and significantly reduce organic traffic.
4. Cost Concerns
Paid syndication campaigns can become expensive without careful targeting, monitoring, and performance optimization strategies.
Content Syndication Use Cases
Here are common use cases that help businesses expand reach, generate leads, and strengthen market presence.
1. B2B Lead Generation Campaigns
Syndicating valuable content helps attract and convert high-quality leads for business-to-business marketing efforts.
2. Brand Awareness Initiatives
Republishing content on external platforms effectively exposes the brand to larger, more targeted, and more relevant audiences.
3. Market Expansion Strategies
Enables faster access to new markets, industries, and audience segments efficiently and cost-effectively.
4. Product Launches
Sharing content about new products on third-party platforms drives visibility, engagement, and early customer adoption.
5. Thought Leadership Building
Distributing insightful content positions the brand as an industry authority, fostering credibility and trust.
Real-World Example
Here is a real-world example that illustrates how content syndication delivers measurable business results.
E-Commerce Retailer
An online fashion retailer syndicated blog articles and lookbooks to fashion blogs and paid networks during a seasonal launch.
Results:
- Increased referral traffic and site engagement
- Gained new audiences and email subscribers
- Boosted brand visibility without creating new content
Best Practices for Effective Content Syndication
Here are proven best practices for content syndication that help maximize reach, engagement, and marketing ROI.
1. Choose the Right Content
Evergreen, educational, and high-performing content ensures maximum audience engagement and syndication success.
2. Partner with Relevant Platforms
Collaborate with publishers that match your target audience and industry for effective content reach.
3. Avoid Duplicate Content Issues
Implement canonical tags or partial content excerpts to protect SEO and prevent ranking penalties.
4. Track Performance Metrics
Regularly monitor traffic, engagement, lead quality, and conversion rates to optimize syndication strategy.
5. Maintain Brand Consistency
Keep messaging, tone, and branding consistent across all syndicated platforms to maintain credibility and recognition.
Final Thoughts
Content syndication is a strategic approach that helps organizations extend the reach of their content, generate qualified leads, and maximize marketing ROI. By selecting the right content, partnering with relevant platforms, and following best practices, businesses can leverage content syndication as a scalable and cost-effective growth channel. When aligned with overall marketing goals, content syndication transforms existing content into a powerful engine for brand visibility and long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is content syndication good for SEO?
Answer: Yes, when implemented correctly using canonical links or excerpts, it supports traffic growth without harming SEO.
Q2. Is content syndication only for B2B marketing?
Answer: No, both B2B and B2C businesses can benefit, though it is more commonly used in B2B lead generation.
Q3. What type of content works best for syndication?
Answer: Whitepapers, blogs, case studies, and research reports perform best.
Q4. How do you measure content syndication success?
Answer: Key metrics include traffic, engagement, leads generated, cost per lead, and conversion rates.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Content Syndication” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
