Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to Constructor in PHP
The constructor is the PHP5 OOP (Object Oriented Programming) concept. The constructor is associated with the classes we declare in the program. The constructor is called automatically when the object of the class is instantiated, thus the definition of constructor goes like this, “A constructor is a special method which is called automatically when the object of the class is instantiated”. In this topic, we are going to learn about constructors in PHP.
Syntax
<?php
Class Classname {
//constructor
function __construct() {
//statements
}
}
?>In the above piece of code, the constructor begins with an __ double underscore followed by the keyword construct. A constructor without __construct() or in case the name of the class is changed then the method defined is just a method and not a constructor. Thus it is important to define the constructor in a class as per the syntax defined.
Types of Constructor
Here are some of the types of Constructor with their output given below
1) Pre-defined Constructor
To clarify about Pre-defined Constructor, Let us look at an example given below
Example of Pre-defined Constructor
Code:
<?php
class Person {
function CanSpeak() {
echo " Not a constructor method " . '<br>';
}
function __construct() {
echo " In the constructor method " . '<br>';
}
}
//Object of class calling the constructor internally
$p = new Person();
// Object of class calling the normal method
$p->CanSpeak();
?>Output:

In the above example
We have a class Person, which has two methods, where a person CanSpeak() Method and the constructor method __construct(). Next, we have instantiated the class as an object $p. Using the $p we have called the normal method. As soon as the object is created the constructor method is called and the statement inside the method is executed, similarly further the CanSpeak() method which is a normal method and not a constructor method is called using the same object $p and the statement inside that method is executed. Also, since the constructor defined above does not have any arguments we will call it a zero-argument constructor or predefined constructor.
2) Parameterized Constructor
A constructor can be with or without arguments. The constructor with arguments is called the parameterized constructor and the constructor without arguments is called the zero-argument constructor. Let us look at an example.
Example of Parameterized Constructor
Code:
class Person {
private $first;
private $email;
private $mobile;
public function __construct($name, $email, $mobile) {
echo "Initialising the object...<br/>";
$this->name = $name;
$this->email = $email;
$this->mobile = $mobile;
}
public function showProfile() {
echo "My name is: " . $this->name. " " . $this->email. " " . $this->mobile;
}
}
$john = new Person("John","[email protected]", "9187986786");
$john->showProfile();Output:

How does Constructor Work?
Let us take a look at the base class constructor and derived class which extends the base class using the extends keyword which has its own constructor to execute and the parent constructor to execute as well. Till now we learned only about the constructor declared in a class. Let us add some more knowledge to the constructor here. With the following example, the base class Person has a constructor, now this constructor is called by the derived class or the Sub Class by using parent keyword and thus can access the Base Class Person’s constructor.
The Output flow
First, the Person constructor is called, then the Customer constructor is called which internally calls again the Person constructor and then its own customer constructor and last the Employee class which extends the Person class thus the Person constructor is called again.
Code:
class Person {
function __construct() {
echo "In Person constructor"."<br>";
}
}
class Customer extends Person {
function __construct() {
parent::__construct();
echo "In Customer constructor"."<br>";
}
}
class Employee extends Person {
// inherits Person’s constructor
}
// In Person constructor
$p = new Person();
// In Person constructor
// In Customer constructor
$c = new Customer();
// In Employee constructor
$e = new Employee();Output:

In the below example we have shown how the set method and the get method works. Using the encapsulation concept in OOP. Initially, the program is declared with a constructor, a set_name method and a get_name method. Note that the constructor is a parameterized constructor which is definitely called when the class is instantiated and therefore the first output is John Doe next created an object of the class and called the set_name and get_name methods which print the output as Alice.
Code:
<?php
class Person {
public $name;
function __construct($name) {
echo $this->name = $name;
}
function set_name($name) {
$this->name = $name;
}
function get_name() {
echo $this->name;
}
}
// In Person constructor
$p = new Person('John Doe');
echo "\n";
$p->set_name('Alice');
$p->get_name();
?>Output:

The Access Specifier
There are three access specifier in PHP
- Public
- Protected
- Private
Public: Members of the class declared as public are accessible everywhere.
Protected: Members of the class declared as protected are accessible only within the base class and the derived class which extends the base class.
Private: Members of the class declared as private are accessible with the class that defines it.
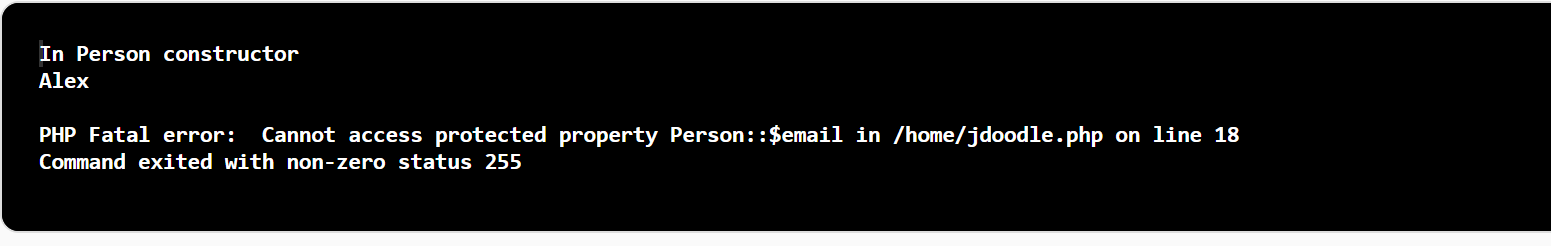
Also, the variables declared are called data members or properties and the functions declared are called as data methods. In the below example we have Base Class declared as Person which has the following properties along with the access specifiers public name, protected email and private mobile. Now the class is instantiated with an object $p and these three properties which are accessed from the object. which outputs are an error, why because, the protected property says that protected are accessible only within the base class and the derived class which extends the base class?
Code:
<?php
class Person {
public $name=;
protected $email;
private $mobile;
function __construct() {
print "In Person constructor";
}
}
// In Person constructor
$p = new Person();
echo $p->name;
echo $p->email;
echo $p->mobile;
?>Output:
Conclusion
Hope this article finds you what you have been searching for. The article has different examples for you to learn. The more you put the examples in practice the easier it will become to grasp.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Constructor in PHP. Here we have discussed the basic concept with types of constructor and how does the Constructor in PHP works. You may also look at the following article to learn more –


