Updated March 28, 2023

Introduction to Constants in C
In C programming language, a name given to a variable whose values cannot be changed such variables is known as constants. These are also called as literals in C programming language as they are similar to variables but with one condition of which values of these variables cannot be altered or the values are fixed for such variables. There are different basic types of constants provided by C, in turn, they are categorized into two major categories that are primary constants and secondary constants. In primary constants, we have integer constants, real constants, and character constants, etc. In secondary constants, we have Array, structure, union, pointer, etc.
Functions of Constants in C
As discussed above constants are variables with fixed values. In C programming language, constants can be declared or defined in two ways one is using a keyword “const” and the other is using #define preprocessor. Let us see the syntax and its example:
1. Use of Const keyword for Defining Constants
Syntax:
const contant_type constant_name = value;Or
constant_type const const_name = value;Example #1
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
const float PI=3.14;
int radius = 2;
float area = PI * radius * radius;
printf("The area of circle is: %f",area);
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
In the above program, we have declared a “const” keyword for defining pi value and this variable is used to calculate the area of the circle. So using constant “PI” we can use it directly in the formula for calculating the area of the circle with the value declared once using the “const” keyword with value as 3.142 which is not altered during the execution of the code. If we try to change the “PI” value then it will give an error. Let us try changing the value of “PI”.
Example #2
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
const float PI=3.14;
PI = 5.76;
int radius = 2;
float area = PI * radius * radius;
printf("The area of circle is: %f",area);
return 0;
}Output:

Normally constants can be of any data types. Let us see an example for this:
Example #3
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
const int var1 = 70;
printf("Integer constant:%d \n", var1 );
const float var2 = 35.89;
printf("Floating point constant: %.2f\n", var2 );
const char var3 = 'S';
printf("Character constant: %c\n", var3 );
const char var4[10] = "string";
printf("String constant: %s\n", var4);
return 0;
}Output:
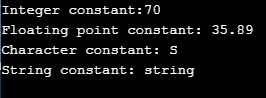
In the above code, we have used integer constant “int”, real constant as “float”, a character constant as “char” and string constant as “char”.
2. Constant Can be Defined Using #define
In this method, constants can be declared or defined using the #define preprocessor directive. In C programming, this method is explained using macros in C. Let us see how this preprocessor directive will be used to define constants which are used to declare constant values for the entire code.
Syntax:
#define constant_name valueExample #1
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#define LENGTH 20
#define WIDTH 30
int main() {
int area_r, area_s;
area_r = LENGTH * WIDTH;
printf("Area of rectange is l * b = %d\n", area_r);
area_s = LENGTH * LENGTH;
printf("Area of square is l * b = %d", area_s);
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
In the above code, we can see that we are declaring “LENGTH” and “WIDTH” as two constants using the #define preprocessor directive. These constants can be used in the entire program. In the above code, we are calculating the area of rectangle and square, where these constants are declared or defined only once at the starting and we can use these constants in the entire program any number of times.
Points to Remember for Constants in C
Generally, in C programming language, constants are assigned with some value and this value is known as literal. Hence in C programming language constants are also known as literals.
Example:
const int max =100;Here “100” is constant integer literal in the above constant expression.
- We should be careful while defining the constants, as just using the “const” keyword and declaring is as simple as declaring the variables in C. But declaration should be done as
int a = 5;The below two declarations are not valid for defining the constants:
const int a;
const int a;
= 5;- For the declaration of constants, it is always the best practice for writing constant names in capital letters or uppercase letters. This helps in understanding and readable program to others as well as for us.
- We cannot change the value of the constant once assigned using “const” keyword or #define directive, because it will give an error if try to assign some other value to the constant that is declared.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the constants in the C programming language. The constants are divided into two categories primary and secondary constants in which primary constants consist of numerical constants like integer, decimal, real, etc and character constants like character, string, backslash, etc. In secondary constants, we have an array, pointer, structure, union, etc. Constants in C are those whose values cannot be altered once declared and these constants are also known as literals.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Constants in C. Here we discuss the Introduction and working of constants in c along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


