Introduction to Communication Strategies
Communication strategies are intentional methods and approaches used to convey information, ideas, emotions, and intentions in an effective manner. They include verbal and non-verbal techniques, as well as written or spoken forms, tailored to suit different contexts and purposes. These strategies help ensure clear understanding, foster positive relationships, and resolve conflicts by adapting communication styles to meet the needs of the audience or situation.
Why are Communication Strategies Important?
Effective communication strategies help you:
- Avoid misunderstandings
- Build trust and relationships
- Influence and persuade
- Solve problems and resolve conflicts
- Increase productivity and cooperation
Top 10 Effective Types of Communication Strategies
Let us explore the most impactful communication strategies that you can use in various aspects of life:
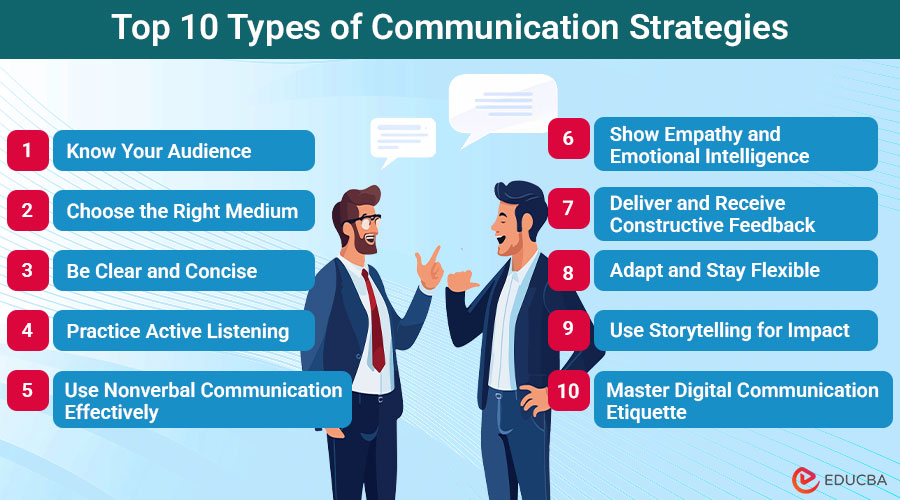
#1. Know Your Audience
Understanding your audience permits you to tailor your message to their specific needs, background, and expectations, ensuring clarity, engagement, and relevance in communication across professional, academic, or personal contexts.
Examples:
- Adjusting technical language when presenting to non-experts
- Using an informal tone and emojis when chatting with friends
- Presenting concise metrics when speaking to executives
Tips:
- Research your audience beforehand
- Consider their background, expectations, and knowledge level
- Match your tone and language to their preferences
#2. Choose the Right Medium
Selecting the most appropriate communication channel—email, phone, video, or face-to-face—enhances the effectiveness, urgency, and emotional tone of the message, depending on the situation, audience, and nature of the content being shared.
Examples:
- Using email for documentation and follow-ups
- Hosting video calls for remote brainstorming
- Choosing in-person meetings for sensitive discussions
Tips:
- Match the medium to the urgency and complexity of the message
- Use richer media (video, voice) for emotionally charged or detailed content
- Be mindful of time zones and availability
#3. Be Clear and Concise
Expressing ideas with clarity and brevity ensures your message is understood quickly, avoids confusion, and maintains attention, especially in fast-paced environments or when addressing large, diverse, or time-constrained audiences.
Examples:
- Using bullet points in reports
- Avoiding jargon in customer communication
- Getting straight to the point in team updates
Tips:
- Use short, direct sentences
- Focus on one key message per paragraph or slide
- Remove unnecessary words or filler phrases
#4. Practice Active Listening
Active listening involves focusing entirely on the speaker, understanding their message, and responding thoughtfully, fostering trust, minimizing misunderstandings, and improving collaboration in both professional and personal communications.
Examples:
- Nodding and making eye contact during conversations
- Paraphrasing: “So you’re saying that…”
- Asking follow-up questions to show interest
Tips:
- Eliminate distractions when listening
- Do not interrupt—wait for the speaker to finish
- Reflect to confirm understanding
#5. Use Nonverbal Communication Effectively
Nonverbal cues—such as facial expressions, gestures, eye contact, and tone—convey emotions and intentions, often more powerfully than words, making them essential to delivering a clear and congruent message.
Examples:
- Smiling during greetings to show friendliness
- Using hand gestures to emphasize key points
- Maintaining an open posture during discussions
Tips:
- Be aware of your body language in different settings
- Align nonverbal cues with your words
- Observe others’ nonverbal reactions to gauge understanding
#6. Show Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
Demonstrating empathy and managing emotions during communication enhances understanding, reduces conflict, and builds stronger relationships by showing respect, compassion, and self-awareness in emotionally charged or sensitive conversations.
Examples:
- Acknowledging a colleague’s stress: “I can tell this week’s been overwhelming.”
- Remaining calm during heated conversations
- Using compassionate language in conflict resolution
Tips:
- Listen actively without interrupting
- Watch for emotional cues and respond accordingly
- Avoid judgmental or dismissive language
#7. Deliver and Receive Constructive Feedback
Constructive feedback focuses on behavior and solutions rather than personal traits, enabling growth, performance improvement, and mutual respect when delivered and received with clarity, care, and an open mindset.
Examples:
- Using the “sandwich method”: Praise → Suggestion → Praise
- Saying, “I noticed a missed deadline—how can I help you stay on track next time?”
- Receiving feedback with openness: “Thanks for pointing that out.”
Tips:
- Focus on actions, not personality
- Be specific and solution-oriented
- Ask for feedback regularly and act on it
#8. Adapt and Stay Flexible
Flexibility in communication means adjusting your tone, method, or language to fit changing contexts, audiences, or technologies, ensuring continued effectiveness and relevance in dynamic or unpredictable environments.
Examples:
- Shifting tone between formal presentations and casual team chats
- Adjusting speed or vocabulary when talking to non-native speakers
- Modifying communication methods during a crisis (e.g., daily updates)
Tips:
- Stay open to changing communication plans
- Observe what works best in different situations
- Seek feedback regularly to refine your approach.
#9. Use Storytelling for Impact
Storytelling enhances communication by connecting emotionally with audiences, simplifying complex ideas, and making messages more engaging, relatable, and memorable through the use of narrative structure, characters, and real-life examples.
Examples:
- Sharing customer success stories in marketing
- Using personal experiences to motivate your team
- Framing data through a real-world scenario
Tips:
- Start with a relatable setup, include a challenge, and end with a resolution
- Keep stories relevant and concise
- Use visuals or anecdotes for a more substantial impact
#10. Master Digital Communication Etiquette
Digital communication etiquette involves using appropriate tone, language, and formatting in emails, texts, and online messages to maintain professionalism, prevent misunderstandings, and foster respectful virtual interactions.
Examples:
- Using subject lines and greetings in emails
- Avoiding all caps in chat (which can appear aggressive)
- Keeping a respectful tone in comments and replies
Tips:
- Reread messages before sending
- Use proper grammar and punctuation
- Respond promptly and set expectations for replies
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How can I rapidly get better at communicating?
Answer: Practice active listening, seek feedback, observe skilled communicators, and apply clear, concise language daily. Regular practice and self-reflection build confidence and effectiveness fast.
Q2: What role does cultural awareness play in communication?
Answer: Cultural awareness prevents misunderstandings by respecting diverse values and communication styles. It fosters trust and inclusivity by adapting messages to fit cultural expectations.
Q3: How do I handle communication breakdowns in a team?
Answer: Address breakdowns by promoting open dialogue, identifying causes, clarifying misunderstandings, and resetting clear expectations. This rebuilds trust and improves teamwork effectiveness.
Q4: Why is nonverbal communication important?
Answer: Nonverbal cues reveal emotions beyond words. They reinforce or contradict messages, influencing perception, building rapport, and ensuring the true meaning is understood.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Communication Strategies ” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.