What is Churn Prediction?
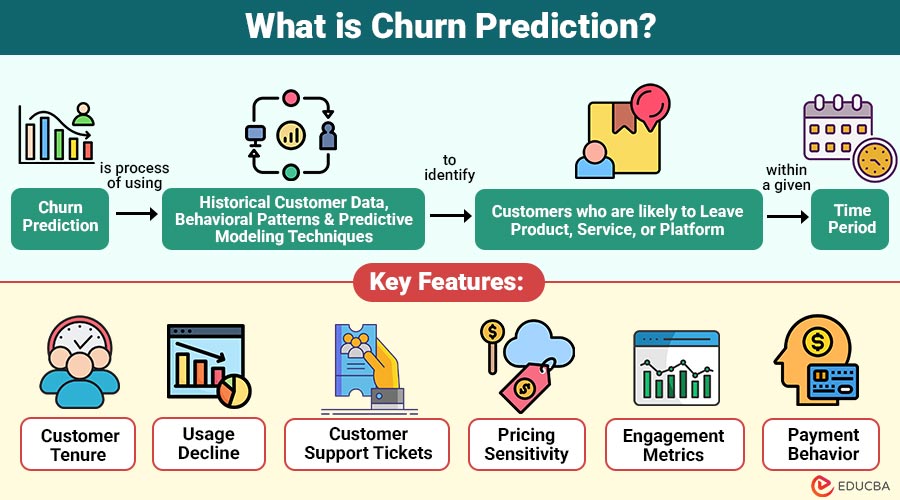
Churn prediction is process of using historical customer data, behavioral patterns, and predictive modeling techniques to identify customers who are likely to leave a product, service, or platform within a given time period.
The objective is not only to predict churn but also to understand why customers leave, enabling organizations to design targeted retention strategies such as personalized offers, improved support, or product enhancements.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Churn prediction transforms raw customer data into actionable insights that guide timely retention and engagement decisions.
- Combining predictive models with business context helps organizations understand the causes of churn, not just its probabilities.
- Effective churn strategies balance model accuracy, interpretability, and continuous adaptation to evolving customer behavior.
- Long-term success depends on aligning churn prediction outputs with marketing, product, and customer support actions.
Why is Churn Prediction Important?
Churn prediction delivers strategic value across multiple business functions:
1. Revenue Protection
Retaining existing customers costs significantly less than acquiring new ones, directly protecting recurring revenue streams
2. Customer Experience Improvement
Churn prediction reveals dissatisfied drivers, enabling businesses to improve products, services, and customer experiences
3. Targeted Retention Campaigns
Businesses can design personalized offers, incentives, and interventions for customers at risk of churn.
4. Operational Efficiency
Resources are focused on high-risk customers, improving efficiency, and reducing unnecessary retention efforts.
5. Data-Driven Strategy
Churn insights support accurate forecasting, strategic planning, and informed long-term business decision-making.
How Does Churn Prediction Work?
The churn prediction process typically follows these steps:
1. Data Collection
Customer data is collected from demographic, transactional, usage behavior, support interactions, and billing systems.
2. Feature Engineering
Relevant features such as usage frequency, complaints, tenure, last activity, and payment delays are derived.
3. Model Selection
Statistical and machine learning models are selected to accurately estimate customer churn likelihood.
4. Model Training and Evaluation
Accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and ROC AUC are used to evaluate models trained on historical data.
5. Deployment and Monitoring
Churn predictions are deployed into workflows and continuously monitored for performance, accuracy, and data drift.
Types of Customer Churn
Understanding the nature of churn helps build accurate predictive models.
1. Voluntary Churn
Customers intentionally leave due to dissatisfaction, high pricing, better competitors, poor service, or changing needs.
2. Involuntary Churn
Customers are lost because of payment failures, expired cards, technical issues, or account suspensions.
3. Contractual Churn
Customers discontinue services upon contract completion, a common pattern in telecom, SaaS, insurance, and subscription services.
4. Non-Contractual Churn
Customers stop purchasing without formal contracts, typically seen in retail, e-commerce, and consumer businesses.
Common Algorithms Used in Churn Prediction
Here are some commonly used algorithms in churn prediction, along with brief descriptions and their typical use cases.
| Algorithm | Description | Use Case |
| Logistic Regression | Interpretable statistical model | Baseline churn models |
| Decision Trees | Rule-based classification | Business explainability |
| Random Forest | Ensemble learning technique | High-accuracy predictions |
| Gradient Boosting (XGBoost, LightGBM) | Boosted decision trees | Large-scale datasets |
| Support Vector Machines | Margin-based classifier | High-dimensional data |
| Neural Networks | Deep learning approach | Complex customer behavior |
Key Features Influencing Churn
Churn prediction models rely heavily on feature quality. Common predictive features include:
1. Customer Tenure
Customers with shorter tenure often show higher churn risk due to weaker brand loyalty.
2. Usage Decline
Reduced product usage indicates declining engagement and an increased likelihood of customer churn.
3. Customer Support Tickets
Frequent support tickets and complaints signal dissatisfaction and potential intent to leave.
4. Pricing Sensitivity
Customers who react negatively to price increases are more likely to churn.
5. Engagement Metrics
Low login frequency and limited feature adoption indicate reduced engagement and churn risk.
6. Payment Behavior
Missed, delayed, or irregular payments strongly correlate with increased customer churn probability.
Use Cases of Churn Prediction
Here are key industry-specific scenarios where churn prediction helps identify at-risk customers and improve retention strategies.
1. SaaS Companies
Identify declining user engagement early and trigger in-app guidance, personalized support, or retention discounts.
2. Telecommunications
Predict subscribers likely to switch providers and offer tailored loyalty plans, incentives, or service upgrades.
3. Banking and Financial Services
Detect customer account moves and proactively strengthen relationships with personalized offers and engagement.
4. E-Commerce
Target customers with reduced purchase frequency using personalized recommendations, promotions, and timely re-engagement campaigns.
5. Media and Streaming Platforms
Analyze viewing behavior patterns to prevent subscription cancellations through content recommendations and retention strategies.
Advantages of Churn Prediction
Below are the key advantages of using churn prediction models to improve customer retention and business performance.
1. Reduces Customer Acquisition Costs
Early detection of at-risk clients reduces marketing spend by retaining existing clients rather than acquiring new ones.
2. Improves Customer Lifetime Value
Increases long-term revenue by retaining customers longer through timely interventions and targeted engagement strategies.
3. Enables Proactive Decision-making
Allows businesses to act early on churn signals, preventing losses before customers disengage completely.
4. Supports Personalized Customer Experiences
Delivers tailored offers, content, and support based on predicted churn risk and individual behavior patterns.
5. Scales Across Large Customer Bases
Efficiently analyzes millions of customer records using automated models without manual effort or performance degradation.
Disadvantages of Churn Prediction
Below are the disadvantages businesses may face when implementing churn prediction models.
1. Data Quality Dependency
Inaccurate, incomplete, or siloed data can significantly reduce the effectiveness and reliability of churn prediction models.
2. Model Bias Risk
Biased training data can lead to unfair predictions, customer misclassification, and reduced trust in decision-making.
3. Ongoing Maintenance
Models require regular retraining and performance checks to remain accurate as customer behavior evolves.
4. Limited Interpretability
Complex algorithms like deep learning reduce transparency, making churn predictions harder for stakeholders to understand.
5. Privacy & Compliance Risks
Handling customer data must follow regulations, increasing governance, security, and compliance management efforts.
Final Thoughts
Churn prediction is a powerful analytical capability that enables organizations to retain customers, protect revenue, and enhance customer experience. By leveraging data science and machine learning, businesses can anticipate churn and act decisively. When combined with strong retention strategies and continuous model improvement, churn prediction becomes a cornerstone of sustainable, customer-centric growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is churn prediction only for subscription businesses?
Answer: No. While common in subscriptions, it is also valuable in retail, banking, and service industries.
Q2. How accurate are churn prediction models?
Answer: Accuracy depends on data quality, feature selection, and model choice. Well-designed models can achieve high reliability.
Q3. Can churn prediction be automated?
Answer: Yes. Modern ML platforms support automated model training, deployment, and monitoring.
Q4. What is churn rate?
Answer: Churn rate is the percentage of customers who leave a business within a given period.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Churn Prediction” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

