What is Cause Marketing?
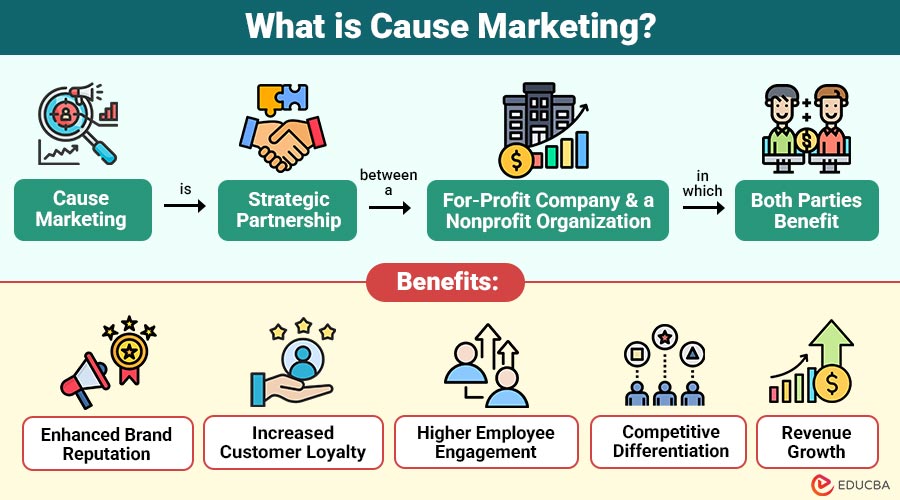
Cause marketing is strategic partnership between a for-profit company and a nonprofit organization in which both parties benefit. The business supports social cause while enhancing brand visibility, customer trust, and revenue growth.
The concept gained widespread recognition in 1983 when American Express launched campaign to restore the Statue of Liberty. The company donated a portion of every transaction to the restoration fund, increasing card usage while supporting a national cause. Many marketers and historians often cite this campaign as the first large-scale example of modern cause marketing.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Key Characteristics
- Working
- Types
- Benefits
- Real-World Examples
- Limitations
- How to Create a Effective Cause Marketing Strategy?
Key Takeaways:
- Cause marketing combines social impact initiatives with strategic business growth and brand development.
- Successful campaigns require authentic cause alignment, transparency, and measurable long-term commitment.
- Revenue-linked donations significantly strengthen customer engagement, loyalty, and overall brand trust.
- Strong nonprofit partnerships enhance credibility, reputation, and sustainable competitive advantage.
Key Characteristics of Cause Marketing
Here are the key characteristics that define and strengthen cause marketing initiatives:
1. Mutual Benefit
Both the company and nonprofit organization gain measurable value, including increased revenue, visibility, credibility, funding support, and long-term relationship growth.
2. Brand Alignment
The selected cause closely aligns with the company’s mission, core values, products, and target audience’s interests, ensuring authenticity and stronger emotional connections.
3. Revenue-Linked Contribution
Donations are directly tied to product sales or customer actions, so each purchase clearly and transparently supports the cause.
4. Public Engagement
Campaigns actively involve customers through purchases, social sharing, events, or volunteering, encouraging participation and strengthening community relationships around the cause.
5. Transparency
Clear communication about donation amounts, fund allocation, and campaign outcomes builds consumer trust, credibility, and long-term brand loyalty.
How Does Cause Marketing Work?
A typical cause marketing campaign follows these steps:
1. Identify a Relevant Cause
The cause should resonate with the brand’s identity and target audience. For example, a sportswear brand may support youth fitness programs.
2. Partner with a Nonprofit Organization
Businesses collaborate with credible nonprofit organizations that align with their values.
3. Define the Campaign Structure
Common structures include:
- Donation per purchase
- Percentage of profits
- Buy-one-give-one model
- Limited-edition cause-based products
- Social media engagement campaigns
4. Promote the Campaign
Marketing channels include digital advertising, social media, email campaigns, and influencer partnerships.
5. Measure and Report Impact
Companies track metrics such as:
- Sales growth
- Brand awareness
- Customer engagement
- Social impact generated
Types of Cause Marketing Campaigns
Here are the major types of cause marketing campaigns businesses use to create social impact while driving brand growth:
1. Transaction-Based Campaigns
A fixed amount or percentage from every product sold is donated to support a partnered social cause initiative.
2. Sponsorship-Based Campaigns
Companies financially support charitable events, awareness programs, or community initiatives aligned with their corporate values and mission.
3. Point-of-Sale Campaigns
Customers are invited to make small donations at checkout, with the collected funds directed to specific nonprofit causes.
4. Digital Engagement Campaigns
Brands pledge donations when consumers participate online through shares, hashtags, clicks, or other social media engagement activities.
5. Co-Branded Partnerships
Businesses and nonprofits work together to create goods, services, or campaigns that further common social goals.
Benefits of Cause Marketing
Here are the benefits businesses gain by implementing cause marketing strategies:
1. Enhanced Brand Reputation
Supporting meaningful social causes strengthens public trust, improves brand image, and positions the company as socially responsible and ethical.
2. Increased Customer Loyalty
Consumers remain loyal to brands reflecting their personal values, increasing repeat purchases, advocacy, and long-term customer relationships.
3. Higher Employee Engagement
Morale, productivity, retention rates, and workplace happiness all increase when workers feel inspired and honored to work for ethical organizations.
4. Competitive Differentiation
Purpose-driven branding distinguishes businesses from competitors, helping attract socially conscious consumers in highly competitive marketplaces globally.
5. Revenue Growth
Consumers often choose brands that support meaningful causes, thereby increasing sales, market share, and overall long-term business profitability.
Real-World Examples
Here are some well-known real-world examples that demonstrate the impact and effectiveness of cause marketing:
1. Nike Community Empowerment Initiatives
Nike partners with nonprofits to support youth sports and equality, strengthening brand purpose and social impact.
2. TOMS Shoes One-for-One Model
The brand gained global recognition for linking product sales directly to charitable giving.
3. Starbucks Ethical Sourcing Initiatives
Starbucks promotes ethically sourced coffee and community support programs as part of its broader social responsibility efforts.
Limitations of Cause Marketing
Here are the key limitations businesses should consider before implementing cause marketing initiatives:
1. Risk of Perceived Insincerity
If campaigns appear profit-driven rather than purpose-driven, audiences may question authenticity, significantly damaging trust and long-term brand credibility.
2. Short-Term Impact if Not Sustained
One-time campaigns without long-term commitment may generate temporary attention but fail to create lasting social or business impact.
3. Potential Backlash if Cause Alignment is Weak
Misaligned causes may trigger criticism, customer dissatisfaction, and reputational damage if audiences perceive inconsistency with brand values.
4. Complexity in Measuring Social Impact
Evaluating actual social outcomes requires data, transparency, and reporting mechanisms, making impact measurement challenging and resource-intensive.
5. Dependency on Nonprofit Partner Credibility
If the nonprofit partner faces controversy or credibility issues, associated brands may suffer reputational harm and public distrust.
How to Create a Effective Cause Marketing Strategy?
Here are some essential steps to build a successful and impactful cause marketing strategy:
1. Ensure Authentic Alignment
Select social causes that genuinely connect with your brand mission, values, audience expectations, and long-term strategic objectives.
2. Be Transparent
To establish credibility and confidence, be sure to convey donation amounts, campaign duration, beneficiary information, and impact reports in an understandable manner.
3. Involve Customers
Encourage active participation through social media campaigns, branded hashtags, community events, and meaningful volunteer engagement opportunities.
4. Measure Performance
Track financial results, customer engagement, brand perception, and measurable social impact metrics to evaluate campaign effectiveness.
5. Maintain Long-Term Commitment
Demonstrate sustained support for chosen causes to strengthen credibility, deepen stakeholder relationships, and create lasting positive impact.
Final Thoughts
Cause marketing blends profit with purpose, enabling businesses to drive growth while supporting meaningful social causes. When brands authentically align with societal needs, they enhance trust, loyalty, and long-term brand equity. From early corporate initiatives to modern purpose-driven strategies, cause marketing has become essential. Transparent, measurable, and sustained efforts position brands as responsible leaders in competitive markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is cause marketing the same as charity?
Answer: No. Charity focuses solely on donations, while cause marketing combines social impact with business objectives.
Q2. Can small businesses use cause marketing?
Answer: Yes. Even local businesses can partner with community nonprofits for impactful campaigns.
Q3. How do companies choose the right cause?
Answer: They select causes aligned with their brand mission, audience values, and long-term strategy.
Q4. Does cause marketing guarantee higher sales?
Answer: Not always. Success depends on authenticity, communication, and strategic alignment.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cause Marketing” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
