What is Capital Structure?
Capital structure refers to the mix of debt and equity a company uses to finance its business operations and growth. Debt can be raised through bank loans, bond issues, or commercial papers, while equity can come from common stock, preferred stock, or retained earnings.
Usually, a company’s capital structure is expressed as a debt-to-equity ratio or debt-to-capital ratio.

Features
Some key features of a suitable capital structure for a company are as follows:
- Flexibility: It provides flexibility in terms of financing options so that the finance manager can alter the debt-equity mix based on the needs of the hour. For instance, a growing company might employ higher debt, while a mature company would rely more on equity.
- Profitability: A sound capital structure can be leveraged to improve profitability, translating into higher earnings per share. An optimum capital structure can result in maximum leverage at a minimum cost.
- Solvency: Excessive debt or very high leverage can threaten a company’s solvency and credit rating. The portion of debt in a capital structure should be limited to the extent the company can comfortably service.
- Conservatism: The company should be conservative and ensure it does not exceed its debt capacity. Any debt entails principal repayment and periodic interest payment that depends on future cash flows. If the future cash flows are inadequate for debt servicing, it can result in legal insolvency. Companies dealing with short-term funding often review interest rates on bridging loans to assess how these costs affect overall leverage. KIS Finance offers a clear overview of current rates and repayment expectations.
- Control: An increase in leverage means a higher amount of debt that might lead to business owners relinquishing control of the company in the case of inability to repay. Hence, the capital structure should be such that it does not lead to a loss of control in the company.
Examples of Capital Structure (With Excel Template)
Below are various examples:
Example #1
Let us assume that a company plans to invest in an expansion project. The project will be financed 35% through equity infusion, and the remaining funding will occur through bank loans. Determine the debt-to-equity ratio of the project based on the given information:
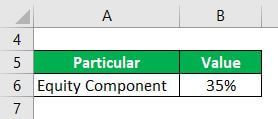
Solution:
One calculates the Debt Component using the formula given below:
Debt Component = 1 – Equity Component
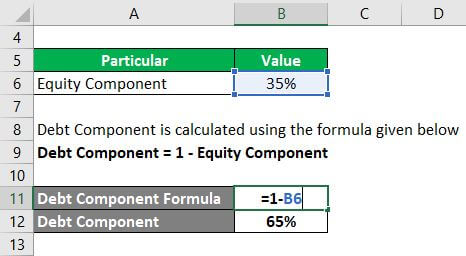
Thus,
- Debt Component = 1 – 35%
- Debt Component = 65%
One calculates the debt-to-equity ratio of the project using the formula given below.
Debt-to-equity Ratio = Debt Component / Equity Component

Thus,
- Debt-to-equity Ratio = 65% / 35%
- Debt-to-equity Ratio = 1.86x
Hence, the debt-to-equity ratio of the project is 1.86x.
Example #2
Let us take the example of a company engaged in a trading business. The company has an outstanding cash credit of $4.5 million, a term loan of $0.25 million, and a tangible net worth of $1.5 million. Determine the company’s debt-to-equity ratio based on the given information.
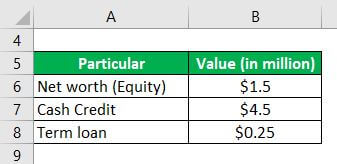
Solution:
One calculates the Debt using the formula given below:
Debt = Cash Credit + Term Loan
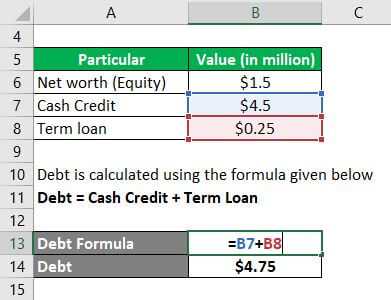
Thus,
- Debt = $4.5 million + $0.25 million
- Debt = $4.75 million
One calculates the debt-to-equity ratio using the formula given below:
Debt-to-equity Ratio = Debt / Equity
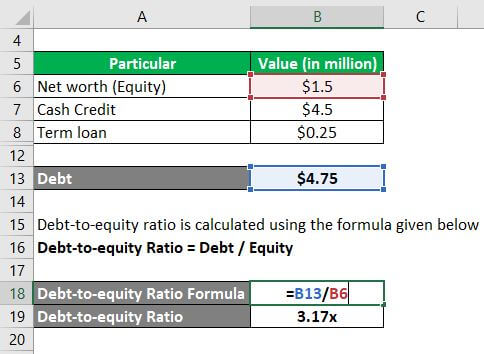
Thus,
- Debt-to-equity ratio = $4.75 million / $1.5 million
- Debt-to-equity ratio = 3.17x
Hence, the company’s debt-to-equity ratio is 3.17x.
Types of Capital Structure
Companies fund their business operations by either issuing debt or equity. Based on the mix of debt and equity, the capital structure can be broadly classified into three major categories – highly leveraged, lowly leveraged, and optimal.
- Highly leveraged: Companies increase their leverage through increased debt funding to improve profit margins. However, this creates the obligation to pay back lenders, which can worsen the woes of a struggling business.
- Lowly leveraged: Companies issue more equity and give up some ownership. In this way, they can fund business requirements and avoid the liability of paying back lenders.
- Optimal: One achieves optimal capital structure when companies can achieve the perfect mix of debt and equity financing that results in maximum company value at the minimum cost of capital.
Factors
The factors that play a key role in determining a company’s capital structure are as follows:
- Cost of capital: This is the cost of capital raised from different fund sources. The interest rate is the cost of capital for debt, while the rate of return is the cost of equity.
- Degree of control: The different types of shareholders and their voting rights influence a company’s capital structure. Typically, equity shareholders enjoy more rights than preference shareholders or debenture shareholders.
- Government policies: The rules and policies introduced by the government impact corporate decisions pertaining to the structure.
Importance
It is a crucial factor in determining a company’s overall stability. Some of its important aspects are:
- A company with a sound capital structure typically enjoys a higher valuation in the investor community.
- An optimal structure ensures the efficient use of available funds, avoiding over or undercapitalization issues.
- Companies can use appropriate capital structures to boost profits, resulting in higher shareholder returns.
Key Takeaways
Some of the key takeaways of the article are:
- A company’s capital structure shows how it finances its business growth.
- A sound structure provides flexibility in financing options and boosts shareholders’ returns by improving profitability.
- The debt-to-equity ratio is a commonly used indicator of capital structure and is useful for determining a company’s borrowing capacity.
Conclusion
Capital structure is a crucial financial aspect for any company, as it determines the proportion of debt or equity in its fund sources. Achieving the optimal capital structure is vital for a company, as it helps maximize shareholders’ capital while minimizing the overall cost of capital. Thus, it is evident that capital structure plays a significant role in a company’s financial stability and growth.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles for expanding understanding:

