Updated April 13, 2023

Introduction to C++ Vector Functions
Vectors are containers that can store elements. It holds objects of the same data type. The elements are stored in the containers in sequential order. The main advantage of a container is that it changes their size dynamically, in other words, it can be considered as a dynamic array. The elements in a container are stored in contiguous storage locations allowing the elements to be accessed using pointers. Vectors can resize automatically whenever an element is added or removed. This article will cover in detail about vectors, related functions, and vector implementation.
Syntax of C++ Vector Functions
vector<object_type>variable_name;Object type is the data type of the vector
Since vector is a dynamic array, the size doesn’t need to be declared.
Inserting and Deleting an element from a vector
In vectors, a new element is always added at the end. The time for insertion operation varies as in some cases there may be a need to extend the array. Removing the last element always takes constant time. Adding or removing elements in the beginning or from the middle takes time-based on the position of the element, in other words it can be said as a linear operation.
Top Functions of C++ Vector Functions
The functions related to vector can be categorized into three types. They are iterators, modifiers, and capacity.
- Iterators: The functions under iterators are used to iterate through the vector. These functions act as a pointer. Five types of iterators are available. They are input, forward, output, random, and bidirectional. Some of the iterator’s functions are begin(), end(), rbegin(), rend().
- Modifiers: The modifier functions are used to modify the vector such as modifying the data type of the vector. Some example of functions under this category are assign(), push_back(), pop_back() etc.
- Capacity: The capacity category functions are used to modify the capacity or size of the vector. Some example of this category of functions are size(), max_size() capacity() etc.
1. Iterator Functions and Their Definition
| Function Name | Use |
| begin() | This points to the first element in the vector. |
| end() | This points to the last element in the vector. |
| rbegin() | This is the opposite of begin. This starts in the reverse direction. |
| rend() | This is the reverse of the end(). This starts with the first element in the vector. |
| Ccbegin() | This returns the value pointing to the vector’s first element. |
| cend() | This returns the value pointing to the vectors the last element. |
| crbegin() | The reverse of begin(). |
| crend() | The reverse of cend(). |
Below are the examples of C++ Vector Functions:
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
intmain()
{
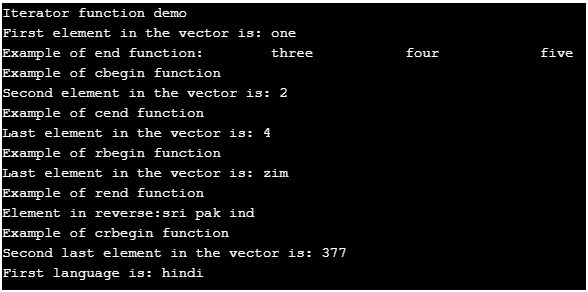
cout<< "Iterator function demo";
vector<string>vobj{"one","two","three", "four", "five"};
//begin function
auto ptr=vobj.begin();
cout<< "\nFirst element in the vector is: " ;
cout<<*ptr;
//end function
cout<< "\nExample of end function: " ;
for(ptr=vobj.begin()+2;ptr!=vobj.end();ptr++)
cout<<"\t"<<*ptr<<"\t";
vector<int>vint{1,2,3,4};
//cbegin function
auto intiter=vint.cbegin()+1;
cout<< "\nExample of cbegin function" ;
cout<< "\nSecond element in the vector is: " ;
cout<<*intiter;
//cend function
cout<< "\nExample of cend function" ;
cout<< "\nLast element in the vector is: " ;
for(intiter=vint.cbegin()+3;intiter!=vint.cend();intiter++)
cout<<*intiter;
//rbegin function
vector<string>vrbeg{"ind","pak","sri", "sa", "zim"};
//rbegin function
auto rbgniter=vrbeg.rbegin();
cout<< "\nExample of rbegin function" ;
cout<< "\nLast element in the vector is: " ;
cout<<*rbgniter;
//rend function
cout<< "\nExample of rend function" ;
cout<< "\nElement in reverse:" ;
for (auto irbgnitert = vrbeg.rbegin()+2; irbgnitert != vrbeg.rend();irbgnitert++)
cout<< *irbgnitert<< " ";
vector<int> vint1{100,200,377,400};
//crbegin function
auto intiter1=vint1.crbegin()+1;
cout<< "\nExample of crbegin function" ;
cout<< "\nSecond last element in the vector is: " ;
cout<<*intiter1;
//crend function
vector<string>lang{"hindi","tamil","malayalam","telugu"};
auto lngptr=lang.crend()-1;
cout<< "\nFirst language is: " ;
cout<< *lngptr;
return 0;
}Output:
2. Capacity functions and Their Definitions
| Function Name | Use |
| size() | This function is used to find out the number of elements in the vector. |
| max_size() | This function gives the maximum number of elements a vector can store. |
| capacity() | It gives the current storage space of the vector. |
| resize(n) | This function shrinks the vector to the mentioned size. |
| empty() | This function is used to find out if the vector is empty. |
| shrink_to_fit() | This reduces the vector to its capacity and clears the elements that are beyond it. |
| reserve() | This makes the vector capacity to hold a specified number of elements. |
Below are the examples of C++ Vector Functions:
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
intmain()
{
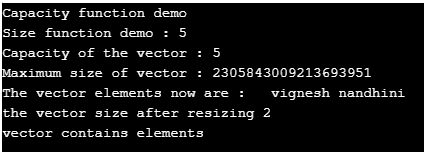
cout<< "Capacity function demo";
vector<string>names{"vignesh","nandhini","vyapini", "vijay", "sethu"};
cout<< "\nSize function demo : " <<names.size();
cout<< "\nCapacity of the vector : " <<names.capacity();
cout<< "\nMaximum size of vector : " <<names.max_size();
names.resize(2);
cout<<"\nThe vector elements now are :";
for (auto itr1 = names.begin(); itr1 != names.end(); itr1++)
cout<<"\t" << *itr1 ;
cout<< "\nthe vector size after resizing " <<names.size();
if (names.empty() == false)
cout<< "\nvector contains elements";
else
cout<< "\nempty vector";
return 0;
}Output:
3. Modifiers Functions and Their Definition
| Function | Use |
| assign() | This function is used to clear the existing values in the vector and replace it with new ones. |
| push_back() | This function is used to add an element to the vector from the back. |
| pop_back() | This function is used to remove an element to the vector from the back. |
| insert() | This function is used to insert an element into the vector. |
| erase() | This function is used to remove an element from the vector. |
| swap() | This function is used to swap two vectors of the same data type. |
| clear() | This function is used to erase the elements in the vector. |
Below are the examples of C++ Vector Functions:
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
intmain()
{
cout<< "Modifiers function demo";
vector<string>names{"vignesh","nandhini","vyapini", "vijay", "sethu"};
names.push_back("siva");
cout<<"\nThe vector elements now are: ";
for (inti = 0; i<names.size(); i++)
cout<< names[i] << " ";
cout<<"\nRemoving the last element using pop method";
names.pop_back();
cout<<"\nThe vector elements now are: ";
for (inti = 0; i<names.size(); i++)
cout<< names[i] << " ";
cout<< "\nInserting new element at the first position";
names.insert(names.begin(), "newname");
cout<<"\nThe first element is: ";
cout<<names[0];
vector<string> names1{"nayan","sam","nithya"};
cout<<"swap example";
names.swap(names1);
cout<<"\nFirst vector values after swap :";
for (inti = 0; i<names.size(); i++)
cout<< names[i] << " ";
cout<<"\nSecond vector values after swap :";
for (inti = 0; i< names1.size(); i++)
cout<< names1[i] << " ";
cout<<"\nGoing to clear the vectors";
names.clear();
names1.clear();
cout<<"\nFirst vector size now:\t" <<names.size();
cout<<"\nSecond vector size now:\t" <<names1.size();
return 0;
}Output:

Conclusion
Thus, the article explained in detail about the vector in c++. It also explained the various types of vector functions and their types with appropriate examples and their use. To learn more in detail it is advisable to write sample programs and practice them.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to C++ Vector Functions. Here we discuss the Introduction to C++ Vector Functions and its Examples along with Code Implementation and Output. you can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –


