Updated March 31, 2023

Introduction to C++ Reference
In programming, we might come across so many variables with the same names but can refer to each other if we assign a reference to them. References in C ++ also behaves in a similar way. In reference, there is an alternate name for the declared variable or previously existing variable in your source code. Therefore, any variables can be declared using one operator known as ampersand and it is denoted by “ & ”. References are used in programming because it saves huge lines of code and unnecessary declaration of variables in the code. Hence, saves memory also while making an efficient code.
Let’s have a look at the syntax for declaring a reference to a variable:
Syntax:
int i = 10 ;
int& r = i ;As you can see we have declared an integer variable “i” and we have also assigned the value 10 to it. After that, we have declared a reference variable “r” as an alternate reference to the variable “i”.
Now let’s discuss the working of references in C ++ programming through some examples.
Working of References in C ++ Programming with Examples
A Reference is always declared as an alternate for a variable hence it works as a parameter.
Example #1
Here is the C ++ code to determine the working of references in programming:
Code:
#include <iostream>
int main ()
{
int value { 50 } ; // Declaring an integer with assigned value 50
int &reference { value } ; // creating a reference to the variable value we declared above
value = 60 ; // the changed value is now 60
reference = 70 ; // the reference value is now 70
std :: cout << value << '\n'; // prints 7
++reference ;
std :: cout << value << '\n'; // prints 8
return 0 ;
}Output:

Code Explanation: As in the above code, you can see we have declared an integer variable with the assigned value and then we have created a reference variable and gave it a reference to a declared integer variable. Initially, we have declared the value to 60 and then we assigned value 70 to the references variable. Therefore, on the successful execution of the code, you will see that the reference variable value is selected and then incremented.
Example #2
Here is another C ++ code to determine the working of references in programming:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std ;
int main () {
// declaring two simple variables of integer and double data type
int x ;
double y ;
// declaring two reference variables of integer and double data type
int& p = x ;
double& q = y ;
x = 14 ; // Assigning value 14 to the variable x
cout << " The Value of x is : " << x << endl;
cout << " The Value of x reference is : " << p << endl;
y = 54.7 ; // Assigning value 54.7 to the variable y
cout << " The Value of y is : " << y << endl ;
cout << " The Value of y reference is : " << q << endl ;
return 0 ;
}Output:
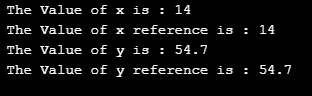
Code Explanation: As in the above code, you can see we have declared two integer variables x and y then we have created two reference variables and gave it a reference to the two declared integer variables. Initially, we have declared the value of x to 14 and then we assigned value 54.7 to the variable y. Therefore, on the successful execution of the code, you will see that the value and reference variable value of x and y.
If a function is receiving any kind of reference to a variable then it can also modify the value of the variable it is known as modifying the passing parameters in a function. Let’s see how this is possible through a code.
Example #3
Here is another C ++ code to demonstrate the modifying of passed parameter value in a function:
Code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std ;
void swapping (int& initial, int& last)
{
int temporary = initial ;
initial = last ;
last = temporary ;
}
int main()
{
int x = 98 , y = 89 ;
swapping ( x , y ) ;
cout << x << " " << y ;
return 0 ;
}Output:
![]()
Code Explanation: In the above code, you can see we have modified the value of passed parameter in the function swapping. For swapping we have declared one initial, one temporary, and one last variable. We declared the working of swapping function first then in int main() class we declared x and y variables and then passed these values to the swapping function so that it can be swapped.
We can also use pass-by-reference with reference arguments in your source code. Let’s see how can we do that in C ++ programming.
Example #4
Here is another C ++ code to demonstrate pass-by-reference with reference arguments:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std ;
void square (int &) ;
int main() {
int num = 12 ;
cout << " In main () : " << &num << endl ;
cout << num << endl ; // 12
square(num); // Implicitly referencing
cout << num << endl ; // 144
}
void square (int & rNum) { // Function takes an integer reference
cout << " In square () : " << &rNum << endl ;
rNum *= rNum ; // Implicit de-referencing
}Output:
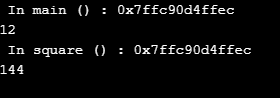
Code Explanation: In the above code, you can see we have passed the value of a parameter in the function through creating a reference with the help of reference parameters. We have declared num for normal variable and rNum for reference variable to do explicit and implicit referencing.
Conclusion – C++ Reference
References in C + + programming can be created easily. Therefore, to access the value of the actual variable in your source code we don’t have to dereference the variable explicitly. It will be done automatically. References variables can be used for passing in the function as an argument.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C++ Reference. Here we discuss the introduction and working of references in C ++ programming along with different examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


