Updated June 23, 2023

Introduction to C++ find_if()
The find_if() function in C++ is part of the standard library and is used to search for the first element in a defined range that satisfies a specified condition provided by a predicate function. When find_if() encounters the first element in the range for which the predicate function returns true, that element is considered the result. It uses a unary predicate to specify the location of elements from the range to consider for manipulating values or elements in the range.
Syntax:
InputIterator find_if (InputIterator fir_st, InputIterator l_st, UnaryPredicate predefined);The syntax flow is in a way where the parameters represent the following:
- fir_st: This represents and specifies the range for the first element of the entire range.
- l_st: This represents and specified the range for the last element of the entire range specified.
- predefined: This predefined parameter is part of the Unary Predicate class in the template, which is used for checking the return type, which is considered as a boolean value with true or false as the value.
How find_if() Algorithm Function work in C++?
- find_if() algorithm in C++ plays a vital role in terms of making elements search with a specified range. It first searches for elements required from the defined range. Once it encounters the first element, it will check for its boolean condition with true or false values. Then it will use a unary predicate to locate an element from the range to make changes on consideration. The function returns the iterator value if the element range satisfies the first value with the boolean value as true.
- There is not much complexity in the find_if() algorithm function because it makes the element search in a linear fashion starting from the first element of the range towards the last element of the range and then for each element present in the range, which checks for each element and then lists all values of the range using unary Predicate for verification and returning the value to the algorithmic function. All objects which are part of the find_if algorithm() specified range will be accessible depending on the condition which needs to be satisfied.
- Some race condition prevails in the find_if algorithmic function of C++. Some other functions also function in a way to search the elements from the first element of the range to the last element of the range that includes find(), find_end(), find_first_of(), and many more. All these functions mentioned are also part of find_if() algorithm, which is part of the standard library in C++.
- It uses almost the same functionality as the find_if() function except for minor changes, which may include the time complexity and other data race conditions. The find_if() function makes use of many other data structures like vectors and lists which further makes all manipulations possible in a linear fashion with minor changes in the complexity factor or any other factor like manipulation element. Sometimes this function gets confused with the find_if_not() function where the functionality and traversal techniques are the same as the find_if function with some mere changes in conventions like the predefined value of the unary operator must be false i.e. boolean value for the unary operator comes out to be false. This function works completely opposite to the find_if function of C++.
Examples of C++ find_if()
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Here’s an example program that demonstrates the usage of the find_if() function in C++ to search for the first odd digit within a specified range of elements:
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<array>
int main()
{
std::array<int,4> ar_1={2,3,5,8};
std::array<int,4>::iterator r_t=std::find_if (ar_1.begin(), ar_1.end(), [](int o)
{
return o%2;
} );
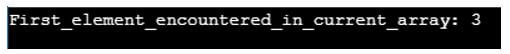
std::cout<<"First_element_encountered_in_current_array: "<<*r_t<<"\n";
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2
The following program demonstrates the usage of the find_if() function in C++. It searches for the first even number in the range and, if not found, checks for the odd number of elements in the range:
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool un_ary_pred(int r_p)
{
return ((r_p % 2) == 0);
}
int main(void)
{
vector<int> vctr = {8, 10, 9, 2, 14};
auto y_o = find_if(vctr.begin(), vctr.end(), un_ary_pred);
if (y_o != end(vctr))
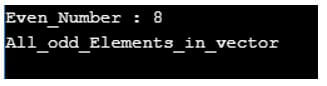
cout << "Even_Number : " << *y_o << endl;
vctr = {7};
y_o = find_if(vctr.begin(), vctr.end(), un_ary_pred);
if (y_o == end(vctr))
cout << "All_odd_Elements_in_vector" << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
Advantages of C++ find_if()
- The complexity of the algorithmic function comes out to be linear after searching elements specified in the range of first to last.
- This function gives programmers flexibility and eases them to manipulate and work for the requirement.
Conclusion
This function makes the overall implementation of the algorithm and search of elements satisfying the conditions with the first and last elements of the range. It provides flexibility and versatility to the programmers to work for desired elements and manipulation elements in a specific search pattern. Overall like other standard library functions find_if also plays a pivotal role in terms of element searching and requirement implementation.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C++ find_if(). Here we discuss how find_if() algorithm function works in C++ with advantages and programming examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


