Updated April 4, 2023

Introduction to C++ Bitset Function
C++ Bitset is a very good optimization technique for the set of boolean values represented with the help of array bools. These special set of boolean values consist of values in the format of true or false. If the value is true, then it is representing that the array bool set consists of value as 1 which shows that it occupies the unit bit space of one bit. If the array bool values consist a value as false which means representation is with value 0 which means bit is unsaved for transition and changes.
How to Use Bitset Functions in C++?
Below are the Functions of C++ Bitset:
- bitset::all()
- bitset::any()
- bitset::count()
- bitset::flip ()
- bitset::none()
- bitet::operator()
- bitset::reset()
- bitset::set()
- bitset::size()
- bitset::test()
- bitset::to_string()
- bitset::to_ullong()
- bitset::to_ulong()
- bitset::hash()
1. bitset::all()
This function is part of C++ Bitset which is used for testing and verifying whether all the bits are set properly or not.
Example: This program demonstrates bitsetall() function for setting of every bit in the set.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<6> f;
bitset<6> override("111111");
if (!f.all())
cout << "Let us set all the bits repectively" << endl;
f |= override;
if (f.all())
cout << "Every single bit set is ready for execution and can be overriden as well." << endl;
return 0;
}Output:

2. bitset::any()
This function is used by the C++ bitset library function to set at least one bit of the stream. If not set it will not return the actual value which is needed.
Example: This program demonstrates that the bitset::any() function is used for at least set one value for the function.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<8> p;
bitset<8> ovridr("0");
if (!p.any())
cout << "Minimum of one single bit needs to get set in the array" << endl;
p |= ovridr;
if (p.any())
cout << "Any one single or minimum one bit should get set." << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
3. bitset::count()
As the name suggests this bitset::count function is also part of the bitset standard library which is used to count the number of bits present in the bitset.
Example: This program is to illustrate the bitset::count function for keeping a track and check on the count of the number of bits occupying the bit and space compared with the bits apart from the set of bits which don’t have values.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<8> k("01010000");
cout << "Given Bitset " << k << ", " << k.count() << " possess number of set bits" << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
4. bitset::flip()
bitset::flip function is used to represent the set of bit characters which toggles between the entire bit stream.
Example: This program is used to represent the bitset::flip() function which is used to represent the bits in an order like the bits before calling a flip() function and bit representation after calling a flip() function.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<6> m("001101");
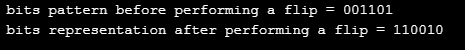
cout << " bits pattern before performing a flip = " << m << endl;
m.flip();
cout << " bits representation after performing a flip = " << m << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
5. bitset::none()
This function is also part of the C++ bitset stream library which is further used to test whether all the bits are properly set or kept as unset and it can be confirmed seamlessly by making use of this function.
Example: This program illustrates the function bitset::none () to represent whether all the bits are set or all the bits are unset.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<8> e;
bitset<8> overide("00");
if (e.none())
cout << "Ths function tests result whether all the bits are set or unset" << endl;
e |= overide;
if (!e.none())
cout << "Minimum one bit shoud get set among all the unset bits" << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
6. bitset::operator()
bitset::operator as part of the standard library of C++ is used to make bitset operator as bool version and reference version. Bool version with this bitset operator is used to return the values of this operator at that position. Reference bool is used to refer to that position of return value.
Example: This program is used to demonstrate the function bitset::operator both for single bool version and reference version.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<7> g("111010");
for (int j = 0; j < 7; ++j)
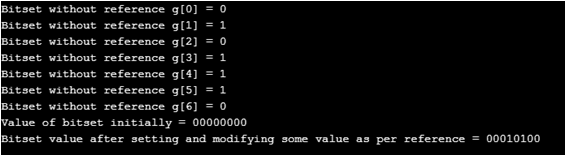
cout << "Bitset without reference g[" << j << "] = " << g[j] << endl;
bitset<8> l;
cout << "Value of bitset initially = " << l << endl;
l[2] = 1;
l[4] = 1;
cout << "Bitset value after setting and modifying some value as per reference = " << l << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
7. bitset::reset()
bitset::reset as part of C++ bitset is used to reset a single bit or multiple bit of the bitset to perform the operation.
Example: This program demonstrates both to set a single bit or all the bits to zero using reset function.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<5> h("01011");
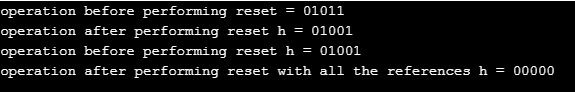
cout << "operation before performing reset = " << h << endl;
h.reset(1);
cout << "operation after performing reset h = " << h << endl;
cout << "operation before performing reset h = " << h << endl;
h.reset();
cout << "operation after performing reset with all the references h = " << h << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
8. bitset::set()
bitset::set function is used to set either a single bit or all the bits into some value of one or zero.
Example: This program demonstrated the bitset::set function either to zero or one.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<8> s;
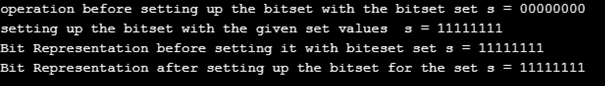
cout << "operation before setting up the bitset with the bitset set s = " << s << endl;
s.set();
cout << "setting up the bitset with the given set values s = " << s << endl;
cout << "Bit Representation before setting it with biteset set s = " << s << endl;
s.set(0, 1);
cout << "Bit Representation after setting up the bitset for the set s = " << s << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
9. bitset::size()
This function is used to calculate the size of the bitset being defined.
Example: This program illustrates the calculation of the size of the defined bitset.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<6> j;
cout << "size of the bitset becomes " << j.size() << " bits." << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
10. bitset::test()
This function as part of the C++ bitset is used for testing whether every bit in the bitset is set or unset.
Example: This program illustrates the bitset::test for verifying the bits in the bitset whether set or unset.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<6> o(10110);
if (o.test(5))
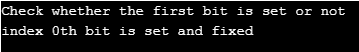
cout << "Check whether the first bit is set or not" << endl;
if (!o.test(0))
cout << "index 0th bit is set and fixed" << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
11. bitset::to_string()
This function is used to convert the object defined in the bitset to string object.
Example: This program illustrates the bitset::to_string function for converting the bitset object into string object.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<6> w(111010);
bitset<6>ovrride;
string s = ovrride.to_string();
cout << w << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
12. bitset::to_ullong()
This function is used to convert the biteset to unsigned long means double type of unsigned long long as part of C++ bitset.
Example: This program illustrates unsigned long long conversion using the bitset::to_ullong.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<6> h("101010");;
auto result = h.to_ullong();
cout << "Representation of the decimal value using the ullong function " << h << " = " << result << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
13. bitset::to_ulong()
This function is used for converting the bitset to unsigned long.
Example: This program is used to demonstrate the bitset to unsigned long using the bitset::to_ulong.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<5> v("11010");;
auto result = v.to_ulong();
cout << "Representation of decimal value using the ulong function " << v << " = " << result << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
14. bitset::hash()
bitset::hash function is considered as a non-member function which is used to return the hash value of the bitset returning the hash value based on the provided bitset.
Example: This program is used to demonstrate the bitset::hash function returning the hash of the value.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
bitset<5> a1(2);
bitset<5> a2(3);
std::hash<std::bitset<5>>hash_fun;
cout << "return a1 as Hash function = " <<hash_fun(a1) << endl;
cout << "return a2 as Hash function = " <<hash_fun(a2) << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
Conclusion
C++ bitset is used as an optimization method with a fixed set of representation of the entire array or vector based bitset represented in the form of true or false and 0 and 1 which represents the unset and set state of the bitset representation within a stream.Thus, it can be concluded that bitset C++ standard library has improvised and ease the processes.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C++ Bitset. Here we discuss the Introduction and how to use C++ Bitset function and its Examples along with its Code Implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


